Page 1991 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1991
Chapter 116 Preparation of Plasma-Derived and Recombinant Human Plasma Proteins 1765
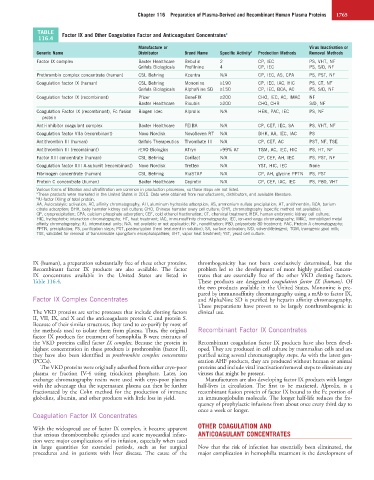
TABLE Factor IX and Other Coagulation Factor and Anticoagulant Concentrates a
116.4
Manufacture or Virus Inactivation or
Generic Name Distributor Brand Name Specific Activity b Production Methods Removal Methods
Factor IX complex Baxter Healthcare Bebulin 2 CP, IEC PS, VHT, NF
Grifols Biologicals Profilnine 4 CP, IEC PS, S/D, NF
Prothrombin complex concentrate (human) CSL Behring Kcentra N/A CP, IEC, AS, CPA PS, PST, NF
Coagulation factor IX (human) CSL Behring Mononine ≥190 CP, IEC, IAC, HIC PS, CT, NF
Grifols Biologicals AlphaNine SD ≥150 CP, IEC, BCA, AC PS, S/D, NF
Coagulation factor IX (recombinant) Pfizer BeneFIX ≥200 CHO, IEC, AC, IMAC NF
Baxter Healthcare Rixubis ≥200 CHO, CHR S/D, NF
Coagulation Factor IX (recombinant), Fc fusion Biogen Idec Alprolix N/A HEK, PAC, IEC PS, NF
protein
Anti-inhibitor coagulant complex Baxter Healthcare FEIBA N/A CP, CEF, IEC, SA PS, VHT, NF
Coagulation factor VIIa (recombinant) Novo Nordisk NovoSeven RT N/A BHK, AA, IEC, IAC PS
Antithrombin III (human) Grifols Therapeutics Thrombate III N/A CP, CEF, AC PST, NF, TSE
Antithrombin III (recombinant) rEVO Biologics ATryn >99% AT TGM, AC, IEC, HIC PS, HT, NF
Factor XIII concentrate (human) CSL Behring Corifact N/A CP, CEF, AH, IEC PS, PST, NF
Coagulation factor XIII A-subunit (recombinant) Novo Nordisk Tretten N/A YST, HIC, IEC None
Fibrinogen concentrate (human) CSL Behring RiaSTAP N/A CP, AH, glycine PPTN PS, PST
Protein C concentrate (human) Baxter Healthcare Ceprotin N/A CP, CEF, IAC, IEC PS, P80, VHT
Various forms of filtration and ultrafiltration are common in production processes, so those steps are not listed.
a These products were marketed in the United States in 2015. Data were obtained from manufacturers, distributors, and available literature.
b IU-factor IX/mg of total protein.
AA, Autocatalytic activation; AC, affinity chromatography; AH, aluminum hydroxide adsorption; AS, ammonium sulfate precipitation; AT, antithrombin; BCA, barium
citrate adsorption; BHK, baby hamster kidney cell culture; CHO, Chinese hamster ovary cell culture; CHR, chromatography (specific method not available);
CP, cryoprecipitation; CPA, calcium phosphate adsorption; CEF, cold ethanol fractionation; CT, chemical treatment; HEK, human embryonic kidney cell culture;
HIC, hydrophobic interaction chromatography; HT, heat treatment; IAC, immunoaffinity chromatography; IEC, ion-exchange chromatography; IMAC, immobilized metal
affinity chromatography; IU, international units; N/A, not available or not applicable; NF, nanofiltration; P80, polysorbate 80 treatment; PAC, Protein A chromatography;
PPTN, precipitation; PS, purification steps; PST, pasteurization (heat treatment in solution); SA, surface activation; S/D, solvent/detergent; TGM, transgenic goat milk;
TSE, validated for removal of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies; VHT, vapor heat treatment; YST, yeast cell culture.
IX (human), a preparation substantially free of these other proteins. thrombogenicity has not been conclusively determined, but the
Recombinant factor IX products are also available. The factor problem led to the development of more highly purified concen-
IX concentrates available in the United States are listed in trates that are essentially free of the other VKD clotting factors.
Table 116.4. These products are designated coagulation factor IX (human). Of
the two products available in the United States, Mononine is pre-
pared by immunoaffinity chromatography using a mAb to factor IX,
Factor IX Complex Concentrates and AlphaNine SD is purified by heparin affinity chromatography.
These preparations have proven to be largely nonthrombogenic in
The VKD proteins are serine proteases that include clotting factors clinical use.
II, VII, IX, and X and the anticoagulants protein C and protein S.
Because of their similar structures, they tend to co-purify by most of
the methods used to isolate them from plasma. Thus, the original Recombinant Factor IX Concentrates
factor IX products for treatment of hemophilia B were mixtures of
the VKD proteins called factor IX complex. Because the protein in Recombinant coagulation factor IX products have also been devel-
highest concentration in these products is prothrombin (factor II), oped. They are produced in cell culture by mammalian cells and are
they have also been identified as prothrombin complex concentrates purified using several chromatography steps. As with the latest gen-
(PCCs). eration AHF products, they are produced without human or animal
The VKD proteins were originally adsorbed from either cryo-poor proteins and include viral inactivation/removal steps to eliminate any
plasma or fraction IV-4 using tricalcium phosphate. Later, ion viruses that might be present.
exchange chromatography resins were used with cryo-poor plasma Manufacturers are also developing factor IX products with longer
with the advantage that the supernatant plasma can then be further half-lives in circulation. The first to be marketed, Alprolix, is a
fractionated by the Cohn method for the production of immune recombinant fusion protein of factor IX bound to the Fc portion of
globulins, albumin, and other products with little loss in yield. an immunoglobulin molecule. The longer half-life reduces the fre-
quency of prophylactic infusions from about once every third day to
once a week or longer.
Coagulation Factor IX Concentrates
OTHER COAGULATION AND
With the widespread use of factor IX complex, it became apparent
that serious thromboembolic episodes and acute myocardial infarc- ANTICOAGULANT CONCENTRATES
tion were major complications of its infusion, especially when used
in large quantities for extended periods, such as for surgical Now that the risk of infection has essentially been eliminated, the
procedures and in patients with liver disease. The cause of the major complication in hemophilia treatment is the development of