Page 1990 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1990
1764 Part XI Transfusion Medicine
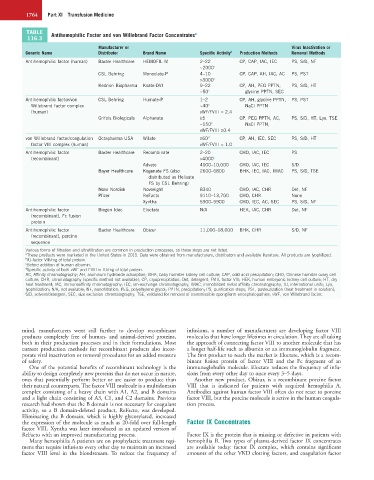
TABLE Antihemophilic Factor and von Willebrand Factor Concentrates a
116.3
Manufacturer or Virus Inactivation or
Generic Name Distributor Brand Name Specific Activity b Production Methods Removal Methods
Antihemophilic factor (human) Baxter Healthcare HEMOFIL M 2–22 CP, CAP, IAC, IEC PS, S/D, NF
~2000 c
CSL Behring Monoclate-P 4–10 CP, CAP, AH, IAC, AC PS, PST
>3000 c
Kedrion Biopharma Koāte-DVI 9–22 CP, AH, PEG PPTN, PS, S/D, HT
~50 c glycine PPTN, SEC
Antihemophilic factor/von CSL Behring Humate-P 1–2 CP, AH, glycine PPTN, PS, PST
Willebrand factor complex ~40 c NaCl PPTN
(human) vWF/FVIII = 2.4
Grifols Biologicals Alphanate ≥5 CP, PEG PPTN, AC, PS, S/D, HT, Lyo, TSE
~150 c NaCl PPTN,
vWF/FVIII ≥0.4
von Willebrand factor/coagulation Octapharma USA Wilate ≥60 d CP, AH, IEC, SEC PS, S/D, HT
factor VIII complex (human) vWF/FVIII = 1.0
Antihemophilic factor Baxter Healthcare Recombinate 2–20 CHO, IAC, IEC PS
(recombinant) >4000 c
Advate 4000–10,000 CHO, IAC, IEC S/D
Bayer Healthcare Kogenate FS (also 2600–6800 BHK, IEC, IAC, IMAC PS, S/D, TSE
distributed as Helixate
FS by CSL Behring)
Novo Nordisk Novoeight 8340 CHO, IAC, CHR Det, NF
Pfizer ReFacto 9110–13,700 CHO, CHR None
Xyntha 5900–9900 CHO, IEC, AC, SEC PS, S/D, NF
Antihemophilic factor Biogen Idec Eloctate N/A HEK, IAC, CHR Det, NF
(recombinant), Fc fusion
protein
Antihemophilic factor Baxter Healthcare Obizur 11,000–18,000 BHK, CHR S/D, NF
(recombinant), porcine
sequence
Various forms of filtration and ultrafiltration are common in production processes, so those steps are not listed.
a These products were marketed in the United States in 2015. Data were obtained from manufacturers, distributors and available literature. All products are lyophilized.
b IU-factor VIII/mg of total protein.
c Before addition of human albumin.
d Specific activity of both vWF and FVIII in IU/mg of total protein.
AC, Affinity chromatography; AH, aluminum hydroxide adsorption; BHK, baby hamster kidney cell culture; CAP, cold acid precipitation; CHO, Chinese hamster ovary cell
culture; CHR, chromatography (specific method not available); CP, cryoprecipitation; Det, detergent; FVIII, factor VIII; HEK, human embryonic kidney cell culture; HT, dry
heat treatment; IAC, immunoaffinity chromatography; IEC, ion-exchange chromatography; IMAC, immobilized metal affinity chromatography; IU, international units; Lyo,
lyophilization; N/A, not available; NF, nanofiltration; PEG, polyethylene glycol; PPTN, precipitation; PS, purification steps; PST, pasteurization (heat treatment in solution);
S/D, solvent/detergent; SEC, size exclusion chromatography; TSE, validated for removal of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
mind, manufacturers went still further to develop recombinant infusions, a number of manufacturers are developing factor VIII
products completely free of human- and animal-derived proteins, molecules that have longer lifetimes in circulation. They are all taking
both in their production processes and in their formulations. Most the approach of connecting factor VIII to another molecule that has
current production methods for recombinant products also incor- a longer half-life such as albumin or an immunoglobulin fragment.
porate viral inactivation or removal procedures for an added measure The first product to reach the market is Eloctate, which is a recom-
of safety. binant fusion protein of factor VIII and the Fc fragment of an
One of the potential benefits of recombinant technology is the immunoglobulin molecule. Eloctate reduces the frequency of infu-
ability to design completely new proteins that do not occur in nature, sions from every other day to once every 3–5 days.
ones that potentially perform better or are easier to produce than Another new product, Obizur, is a recombinant porcine factor
their natural counterparts. The factor VIII molecule is a multidomain VIII that is indicated for patients with acquired hemophilia A.
complex consisting of a heavy chain with A1, A2, and B domains Antibodies against human factor VIII often do not react to porcine
and a light chain consisting of A3, C1, and C2 domains. Previous factor VIII, but the porcine molecule is active in the human coagula-
research had shown that the B domain is not necessary for coagulant tion process.
activity, so a B domain-deleted product, ReFacto, was developed.
Eliminating the B domain, which is highly glycosylated, increased
the expression of the molecule as much as 20-fold over full-length Factor IX Concentrates
factor VIII. Xyntha was later introduced as an updated version of
ReFacto with an improved manufacturing process. Factor IX is the protein that is missing or defective in patients with
Many hemophilia A patients are on prophylactic treatment regi- hemophilia B. Two types of plasma-derived factor IX concentrates
mens that require infusions every other day to maintain an increased are available today: factor IX complex, which contains significant
factor VIII level in the bloodstream. To reduce the frequency of amounts of the other VKD clotting factors, and coagulation factor