Page 1996 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1996
1770 Part XI Transfusion Medicine
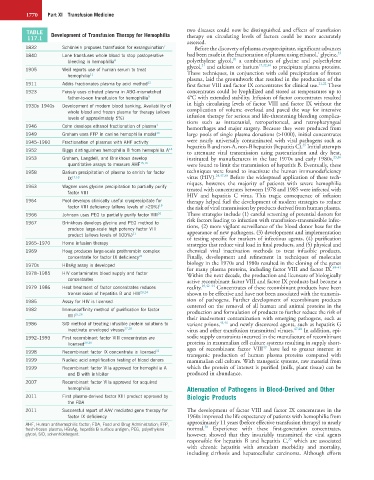
TABLE Development of Transfusion Therapy for Hemophilia two diseases could now be distinguished and effects of transfusion
117.1 therapy on circulating levels of factors could be more accurately
assessed.
1832 Schönlein proposes transfusion for exsanguination 7 Before the discovery of plasma cryoprecipitate, significant advances
1
33
1840 Lane transfuses whole blood to stop postoperative had been made in the fractionation of plasma using ethanol, glycine,
20
bleeding in hemophilia 8 polyethylene glycol, a combination of glycine and polyethylene
21
glycol, and calcium or barium 17,22,34 to precipitate plasma proteins.
1905 Weil reports use of human serum to treat These techniques, in conjunction with cold precipitation of frozen
hemophilia 11
plasma, laid the groundwork that resulted in the production of the
1911 Addis fractionates plasma by acid method 12 first factor VIII and factor IX concentrates for clinical use. 21,22 These
1923 Feissly uses citrated plasma in ABO-mismatched concentrates could be lyophilized and stored at temperatures up to
father-to-son transfusion for hemophilia 9 4°C with extended stability. Infusion of factor concentrates resulted
1930s–1940s Development of modern blood banking. Availability of in high circulating levels of factor VIII and factor IX without the
whole blood and frozen plasma for therapy (allows complication of volume overload and paved the way for intensive
levels of approximately 5%) infusion therapy for serious and life-threatening bleeding complica-
tions such as intracranial, retroperitoneal, and retropharyngeal
1946 Cohn develops ethanol fractionation of plasma 1 hemorrhages and major surgery. Because they were produced from
1949 Graham uses FFP in canine hemophilia model 13 large pools of single plasma donations (>1000), initial concentrates
1945–1960 Fractionation of plasmas with AHF activity were nearly universally contaminated with viral pathogens such as
35
1952 Biggs distinguishes hemophilia B from hemophilia A 14 hepatitis B and non-A, non-B hepatitis (hepatitis C). Initial attempts
to attenuate viral transmission using pasteurization and dry heat,
1953 Graham, Langdell, and Brinkhous develop instituted by manufacturers in the late 1970s and early 1980s, 23,36
quantitative assays to measure AHF 15,16 were found to limit the transmission of hepatitis B. Eventually, these
1958 Barium precipitation of plasma to enrich for factor techniques were found to inactivate the human immunodeficiency
24,37,38
IX 17,18 virus (HIV). Before the widespread application of these tech-
niques, however, the majority of patients with severe hemophilia
1963 Wagner uses glycine precipitation to partially purify treated with concentrates between 1978 and 1985 were infected with
factor VIII
HIV and hepatitis C virus. This tragic consequence of infusion
1964 Pool develops clinically useful cryoprecipitate for therapy helped fuel the development of modern strategies to reduce
factor VIII deficiency (allows levels of >20%) 19 the risk of viral transmission by products derived from human plasma.
1966 Johnson uses PEG to partially purify factor VIII 20 These strategies include (1) careful screening of potential donors for
risk factors leading to infection with transfusion-transmissible infec-
1967 Brinkhous develops glycine and PEG method to tions, (2) more vigilant surveillance of the blood donor base for the
produce large-scale high potency factor VIII appearance of new pathogens, (3) development and implementation
product (allows levels of 100%) 21
of testing specific for markers of infectious agents, (4) purification
1965–1970 Home infusion therapy strategies that reduce viral load in final products, and (5) physical and
1969 Hoag produces large-scale prothrombin complex chemical viral inactivation methods to treat infusible products.
concentrate for factor IX deficiency 22 Finally, development and refinement in techniques of molecular
1970s HBsAg assay is developed biology in the 1970s and 1980s resulted in the cloning of the genes
39–41
for many plasma proteins, including factor VIII and factor IX.
1978–1985 HIV contaminates blood supply and factor Within the next decade, the production and licensure of biologically
concentrates active recombinant factor VIII and factor IX products had become a
1979–1986 Heat treatment of factor concentrates reduces reality. 29,42–44 Concentrates of these recombinant products have been
transmission of hepatitis B and HIV 23,24 shown to be effective and have not been associated with the transmis-
1985 Assay for HIV is licensed sion of pathogens. Further development of recombinant products
centered on the removal of all human and animal proteins in the
1982 Immunoaffinity method of purification for factor production and formulation of products to further reduce the risk of
VIII 25,26
their inadvertent contamination with emerging pathogens, such as
1986 S/D method of treating infusible protein solutions to variant prions, 45,46 and newly discovered agents, such as hepatitis G
inactivate enveloped viruses 27,28 virus and other transfusion transmitted viruses. 47,48 In addition, epi-
1992–1993 First recombinant factor VIII concentrates are sodic supply constraints incurred in the manufacture of recombinant
licensed 29,30 proteins in mammalian cell culture systems resulting in supply short-
49
1998 Recombinant factor IX concentrate is licensed 31 ages of recombinant factor VIII have led to greater interest in
transgenic production of human plasma proteins compared with
1999 Nucleic acid amplification testing of blood donors mammalian cell culture. With transgenic systems, raw material from
1999 Recombinant factor VIIa approved for hemophilia A which the protein of interest is purified (milk, plant tissue) can be
and B with inhibitor produced in abundance.
2007 Recombinant factor VIIa approved for acquired
hemophilia Attenuation of Pathogens in Blood-Derived and Other
2011 First plasma-derived factor XIII product approved by Biologic Products
the FDA
2011 Successful report of AAV mediated gene therapy for The development of factor VIII and factor IX concentrates in the
factor IX deficiency 1960s improved the life expectancy of patients with hemophilia from
AHF, Human antihemophilic factor; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; FFP, approximately 11 years (before effective transfusion therapy) to nearly
50
fresh-frozen plasma; HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen; PEG, polyethylene normal. Experience with these first-generation concentrates,
glycol; S/D, solvent/detergent. however, showed that they invariably transmitted the viral agents
35
responsible for hepatitis B and hepatitis C, which are associated
with chronic hepatitis with attendant morbidity and mortality,
including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Although efforts