Page 1998 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1998
1772 Part XI Transfusion Medicine
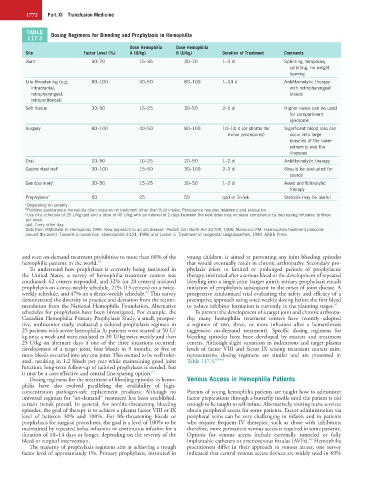
TABLE Dosing Regimens for Bleeding and Prophylaxis in Hemophilia
117.3
Dose Hemophilia Dose Hemophilia
Site Factor Level (%) A (U/kg) B (U/kg) Duration of Treatment Comments
Joint 30–70 15–35 30–70 1–3 d Splinting, temporary
splinting, no weight
bearing
Life threatening (e.g., 80–100 40–50 80–100 1–14 d Antifibrinolytic therapy
intracranial, with retropharyngeal
retropharyngeal, bleeds
retroperitoneal)
Soft tissue 30–50 15–25 30–50 2–5 d Higher levels can be used
for compartment
syndrome
Surgery 80–100 40–50 80–100 10–14 d (or shorter for Significant blood loss can
minor procedures) occur into large
muscles of the lower
extremity and the
iliopsoas
Oral 20–50 10–25 20–50 1–2 d Antifibrinolytic therapy
Gastrointestinal a 30–100 15–50 30–100 2–3 d Should be evaluated for
source
Genitourinary b 30–50 15–25 30–50 1–2 d Avoid antifibrinolytic
therapy
Prophylaxis c 50 25 50 qod or 3×/wk Steroids may be useful
a Depending on severity.
b Painless spontaneous hematuria often requires no treatment other than fluid intake. Persistence requires treatment and evaluation.
c Use of a schedule of 25 U/kg qod and a dose of 40 U/kg with an interval of 2 days between the next dose may increase compliance by decreasing infusions to three
per week.
qod, Every other day.
Data from DiMichele D: Hemophilia 1996. New approach to an old disease. Pediatr Clin North Am 43:709, 1996; Mannucci PM: Haemophilia treatment protocols
around the world: Towards a consensus. Haemophilia 4:421, 1998; and Lusher J: Treatment of congenital coagulopathies, 1999, AABB Press.
and even on-demand treatment prohibitive to more than 60% of the young children, is aimed at preventing any joint bleeding episodes
hemophilia patients in the world. 59 that would eventually result in chronic arthropathy. Secondary pro-
To understand how prophylaxis is currently being instituted in phylaxis refers to limited or prolonged periods of prophylactic
the United States, a survey of hemophilia treatment centers was therapy, instituted after a serious bleed or the development of repeated
conducted: 62 centers responded, and 32% (or 20 centers) initiated bleeding into a single joint (target joint); tertiary prophylaxis entails
prophylaxis on a once-weekly schedule, 21% (13 centers) on a twice- initiation of prophylaxis subsequent to the onset of joint disease. A
60
weekly schedule, and 47% on a thrice-weekly schedule. This survey prospective randomized trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of a
demonstrated the diversity in practice and deviation from the recom- preemptive approach using once-weekly dosing before the first bleed
mendation from the National Hemophilia Foundation. Alternative to reduce inhibitor formation is currently in the planning stages. 62
schedules for prophylaxis have been investigated. For example, the To prevent the development of a target joint and chronic arthropa-
Canadian Hemophilia Primary Prophylaxis Study, a small, prospec- thy, many hemophilia treatment centers have recently adopted
tive, multicenter study, evaluated a tailored prophylaxis regimen in a regimen of two, three, or more infusions after a hemarthrosis
25 patients with severe hemophilia A; patients were started at 50 U/ (aggressive on-demand treatment). Specific dosing regimens for
kg once a week and were escalated to 30 U/kg twice weekly and then bleeding episodes have been developed by treaters and treatment
25 U/kg on alternate days if one of the three situations occurred: centers. Although slight variations in indications and target plasma
development of a target joint, four bleeds in 3 months, or five or levels of factor VIII and factor IX among treatment centers exist,
more bleeds occurred into any one joint. This seemed to be well toler- representative dosing regimens are similar and are presented in
ated, resulting in 1.2 bleeds per year while maintaining good joint Table 117.3. 63–65
function; long-term follow-up of tailored prophylaxis is needed, but
it may be a cost-effective and central line-sparing option. 61
Dosing regimens for the treatment of bleeding episodes in hemo- Venous Access in Hemophilia Patients
philia have also evolved paralleling the availability of high-
concentration pathogen-safe replacement products. Although no Parents of young hemophilia patients are taught how to administer
universal regimen for “on-demand” treatment has been established, factor preparations through a butterfly needle until the patient is old
certain trends prevail. In general, for nonlife-threatening bleeding enough to be taught to self-infuse. Alternatively, visiting nurse services
episodes, the goal of therapy is to achieve a plasma factor VIII or IX obtain peripheral access for some patients. Factor administration via
level of between 30% and 100%. For life-threatening bleeds or peripheral veins can be very challenging in infants and in patients
prophylaxis for surgical procedures, the goal is a level of 100% to be who require frequent IV therapies, such as those with inhibitors;
maintained by repeated bolus infusions or continuous infusion for a therefore, more permanent venous access is required in some patients.
duration of 10–14 days or longer, depending on the severity of the Options for venous access include externally tunneled or fully
66
bleed or surgical intervention. implantable catheters or arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs). Hemophilia
The majority of prophylaxis regimens aim at achieving a trough practitioners differ in their approach to venous access; one survey
factor level of approximately 1%. Primary prophylaxis, instituted in indicated that central venous access devices are widely used in 89%