Page 1994 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1994
1768 Part XI Transfusion Medicine
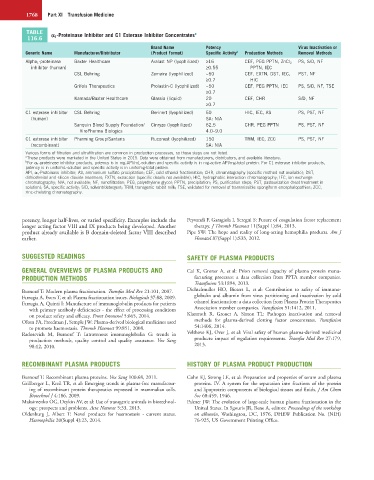
TABLE α 1-Proteinase Inhibitor and C1 Esterase Inhibitor Concentrates a
116.6
Brand Name Potency Virus Inactivation or
Generic Name Manufacturer/Distributor (Product Format) Specific Activity b Production Methods Removal Methods
Alpha 1 -proteinase Baxter Healthcare Aralast NP (lyophilized) ≥16 CEF, PEG PPTN, ZnCl 2 PS, S/D, NF
inhibitor (human) ≥0.55 PPTN, IEC
CSL Behring Zemaira (lyophilized) ~50 CEF, EXTN, DST, IEC, PST, NF
≥0.7 HIC
Grifols Therapeutics Prolastin-C (lyophilized) ~50 CEF, PEG PPTN, IEC PS, S/D, NF, TSE
≥0.7
Kamada/Baxter Healthcare Glassia (liquid) 20 CEF, CHR S/D, NF
≥0.7
C1 esterase inhibitor CSL Behring Berinert (lyophilized) 50 HIC, IEC, AS PS, PST, NF
(human) SA: N/A
Sanquin Blood Supply Foundation/ Cinryze (lyophilized) 62.5 CHR, PEG PPTN PS, PST, NF
ViroPharma Biologics 4.0–9.0
C1 esterase inhibitor Pharming Group/Santaris Ruconest (lyophilized) 150 TRM, IEC, ZCC PS, PST, NF
(recombinant) SA: N/A
Various forms of filtration and ultrafiltration are common in production processes, so those steps are not listed.
a These products were marketed in the United States in 2015. Data were obtained from manufacturers, distributors, and available literature.
b For α 1 -proteinase inhibitor products, potency is in mg-API/mL-solution and specific activity is in mg-active API/mg-total protein. For C1 esterase inhibitor products,
potency is in units/mL-solution and specific activity is in units/mg-total protein.
API, α 1 -Proteinase inhibitor; AS, ammonium sulfate precipitation; CEF, cold ethanol fractionation; CHR, chromatography (specific method not available); DST,
dithiothreitol and silicon dioxide treatment; EXTN, extraction (specific details not available); HIC, hydrophobic interaction chromatography; IEC, ion-exchange
chromatography; N/A, not available; NF, nanofiltration; PEG, polyethylene glycol; PPTN, precipitation; PS, purification steps; PST, pasteurization (heat treatment in
solution); SA, specific activity; S/D, solvent/detergent; TRM, transgenic rabbit milk; TSE, validated for removal of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies; ZCC,
zinc-chelating chromatography.
potency, longer half-lives, or varied specificity. Examples include the Peyvandi F, Garagiola I, Seregni S: Future of coagulation factor replacement
longer acting factor VIII and IX products being developed. Another therapy. J Thromb Haemost 11(Suppl 1):84, 2013.
product already available is B domain-deleted factor VIII described Pipe SW: The hope and reality of long-acting hemophilia products. Am J
earlier. Hematol 87(Suppl 1):S33, 2012.
SUGGESTED READINGS SAFETY OF PLASMA PRODUCTS
GENERAL OVERVIEWS OF PLASMA PRODUCTS AND Cai K, Groner A, et al: Prion removal capacity of plasma protein manu-
PRODUCTION METHODS facturing processes: a data collection from PPTA member companies.
Transfusion 53:1894, 2013.
Burnouf T: Modern plasma fractionation. Transfus Med Rev 21:101, 2007. Dichtelmuller HO, Biesert L, et al: Contribution to safety of immuno-
Farrugia A, Evers T, et al: Plasma fractionation issues. Biologicals 37:88, 2009. globulin and albumin from virus partitioning and inactivation by cold
Farrugia A, Quinti I: Manufacture of immunoglobulin products for patients ethanol fractionation: a data collection from Plasma Protein Therapeutics
with primary antibody deficiencies - the effect of processing conditions Association member companies. Transfusion 51:1412, 2011.
on product safety and efficacy. Front Immunol 5:665, 2014. Klamroth R, Groner A, Simon TL: Pathogen inactivation and removal
Ofosu FA, Freedman J, Semple JW: Plasma-derived biological medicines used methods for plasma-derived clotting factor concentrates. Transfusion
to promote haemostasis. Thromb Haemost 99:851, 2008. 54:1406, 2014.
Radosevich M, Burnouf T: Intravenous immunoglobulin G: trends in Velthove KJ, Over J, et al: Viral safety of human plasma-derived medicinal
production methods, quality control and quality assurance. Vox Sang products: impact of regulation requirements. Transfus Med Rev 27:179,
98:12, 2010. 2013.
RECOMBINANT PLASMA PRODUCTS HISTORY OF PLASMA PRODUCT PRODUCTION
Burnouf T: Recombinant plasma proteins. Vox Sang 100:68, 2011. Cohn EJ, Strong LE, et al: Preparation and properties of serum and plasma
Grillberger L, Kreil TR, et al: Emerging trends in plasma-free manufactur- proteins. IV. A system for the separation into fractions of the protein
ing of recombinant protein therapeutics expressed in mammalian cells. and lipoprotein components of biological tissues and fluids. J Am Chem
Biotechnol J 4:186, 2009. Soc 68:459, 1946.
Maksimenko OG, Deykin AV, et al: Use of transgenic animals in biotechnol- Palmer JW: The evolution of large-scale human plasma fractionation in the
ogy: prospects and problems. Acta Naturae 5:33, 2013. United States. In Sgouris JR, Rene A, editors: Proceedings of the workshop
Oldenburg J, Albert T: Novel products for haemostasis - current status. on albumin, Washington, DC, 1976, DHEW Publication No. (NIH)
Haemophilia 20(Suppl 4):23, 2014. 76-925, US Government Printing Office.