Page 205 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 205
Chapter 15 Vascular Growth in Health and Disease 157
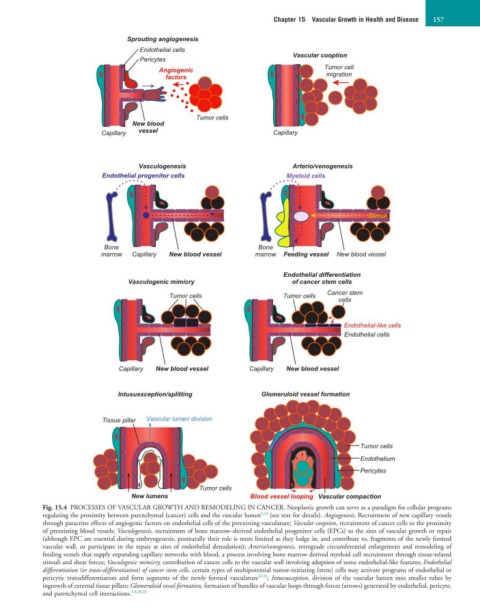
Sprouting angiogenesis
Endothelial cells
Pericytes Vascular cooption
Angiogenic Tumor cell
factors migration
Tumor cells
New blood
Capillary vessel Capillary
Vasculogenesis Arterio/venogenesis
Endothelial progenitor cells Myeloid cells
Stimuli
Bone Bone
marrow Capillary New blood vessel marrow Feeding vessel New blood vessel
Endothelial differentiation
Vasculogenic mimicry of cancer stem cells
Tumor cells Tumor cells Cancer stem
cells
Endothelial-like cells
Endothelial cells
Capillary New blood vessel Capillary New blood vessel
Intusussception/splitting Glomeruloid vessel formation
Tissue pillar Vascular lumen division
Tumor cells
Endothelium
Pericytes
Tumor cells
New lumens Blood vessel looping Vascular compaction
Fig. 15.4 PROCESSES OF VASCULAR GROWTH AND REMODELING IN CANCER. Neoplastic growth can serve as a paradigm for cellular programs
regulating the proximity between parenchymal (cancer) cells and the vascular lumen 2,24 (see text for details). Angiogenesis, Recruitment of new capillary vessels
through paracrine effects of angiogenic factors on endothelial cells of the preexisting vasculature; Vascular cooption, recruitment of cancer cells to the proximity
of preexisting blood vessels; Vasculogenesis, recruitment of bone marrow–derived endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) to the sites of vascular growth or repair
(although EPC are essential during embryogenesis, postnatally their role is more limited as they lodge in, and contribute to, fragments of the newly formed
vascular wall, or participate in the repair at sites of endothelial denudation); Arterio/venogenesis, retrograde circumferential enlargement and remodeling of
feeding vessels that supply expanding capillary networks with blood, a process involving bone marrow derived myeloid cell recruitment through tissue-related
stimuli and shear forces; Vasculogenic mimicry, contribution of cancer cells to the vascular wall involving adoption of some endothelial-like features; Endothelial
differentiation (or trans-differentiation) of cancer stem cells, certain types of multipotential tumor-initiating (stem) cells may activate programs of endothelial or
pericytic transdifferentiation and form segments of the newly formed vasculature 22,23 ; Intussusception, division of the vascular lumen into smaller tubes by
ingrowth of external tissue pillars; Glomeruloid vessel formation, formation of bundles of vascular loops through forces (arrows) generated by endothelial, pericyte,
and parenchymal cell interactions. 2,4,20,24