Page 2171 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2171
1924 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
XII VII
HK
PK
Tissue factor
XIIa XI VIIa
Amplification
Tissue factor/VIIa
XIa IX
PL, Ca ++ Initiation
Ca ++
IXa X
Ca ++
PL, Ca ++ Tenase
VIII VIIIa Xa
Prothrombin
PL, Ca ++
Prothrombinase
Va V
Thrombin
Fibrinogen XIII
Ca ++
Soluble fibrin monomers
Polymerized fibrin clot XIIIa
Covalently cross-linked fibrin clot
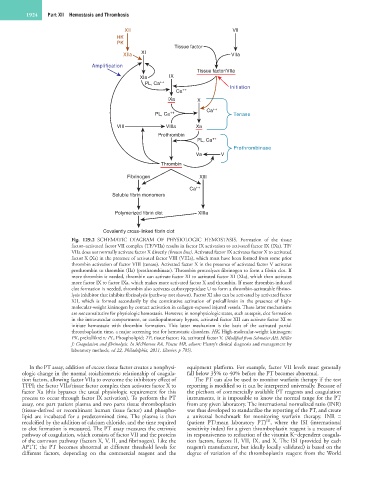
Fig. 129.2 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM OF PHYSIOLOGIC HEMOSTASIS. Formation of the tissue
factor–activated factor VII complex (TF/VIIa) results in factor IX activation to activated factor IX (IXa). TF/
VIIa does not normally activate factor X directly (brown line). Activated factor IX activates factor X to activated
factor X (Xa) in the presence of activated factor VIII (VIIIa), which must have been formed from some prior
thrombin activation of factor VIII (tenase). Activated factor X in the presence of activated factor V activates
prothrombin to thrombin (IIa) (prothrombinase). Thrombin proteolyzes fibrinogen to form a fibrin clot. If
more thrombin is needed, thrombin can activate factor XI to activated factor XI (XIa), which then activates
more factor IX to factor IXa, which makes more activated factor X and thrombin. If more thrombin-induced
clot formation is needed, thrombin also activates carboxypeptidase U to form a thrombin-activatable fibrino-
lysis inhibitor that inhibits fibrinolysis (pathway not shown). Factor XI also can be activated by activated factor
XII, which is formed secondarily by the constitutive activation of prekallikrein in the presence of high-
molecular-weight kininogen by contact activation in collagen-exposed injured vessels. These latter mechanisms
are not constitutive for physiologic hemostasis. However, in nonphysiologic states, such as sepsis, clot formation
in the intravascular compartment, or cardiopulmonary bypass, activated factor XII can activate factor XI to
initiate hemostasis with thrombin formation. This latter mechanism is the basis of the activated partial
thromboplastin time, a major screening test for hemostatic disorders. HK, High-molecular-weight kininogen;
PK, prekallikrein; PL, Phospholipid; TF, tissue factor; Va, activated factor V. (Modified from Schmaier AH, Miller
J: Coagulation and fibrinolysis. In McPherson RA, Pincus MR, editors: Henry’s clinical diagnosis and management by
laboratory methods, ed 22, Philadelphia, 2011, Elsevier, p 785).
In the PT assay, addition of excess tissue factor creates a nonphysi- equipment platform. For example, factor VII levels must generally
ologic change in the normal stoichiometric relationship of coagula- fall below 35% to 40% before the PT becomes abnormal.
tion factors, allowing factor VIIa to overcome the inhibitory effect of The PT can also be used to monitor warfarin therapy if the test
TFPI; the factor VIIa/tissue factor complex then activates factor X to reporting is modified so it can be interpreted universally. Because of
factor Xa (this bypasses the usual physiologic requirement for this the plethora of commercially available PT reagents and coagulation
process to occur through factor IX activation). To perform the PT instruments, it is impossible to know the normal range for the PT
assay, one part patient plasma and two parts tissue thromboplastin from any given laboratory. The international normalized ratio (INR)
(tissue-derived or recombinant human tissue factor) and phospho- was thus developed to standardize the reporting of the PT, and create
lipid are incubated for a predetermined time. The plasma is then a universal benchmark for monitoring warfarin therapy. INR =
ISI
recalcified by the addition of calcium chloride, and the time required (patient PT/mean laboratory PT) , where the ISI (international
to clot formation is measured. The PT assay measures the extrinsic sensitivity index) for a given thromboplastin reagent is a measure of
pathway of coagulation, which consists of factor VII and the proteins its responsiveness to reduction of the vitamin K−dependent coagula-
of the common pathway (factors X, V, II, and fibrinogen). Like the tion factors, factors II, VII, IX, and X. The ISI (provided by each
APTT, the PT becomes abnormal at different threshold levels for reagent’s manufacturer, but ideally locally validated) is based on the
different factors, depending on the commercial reagent and the degree of variation of the thromboplastin reagent from the World