Page 2170 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2170
Chapter 129 Laboratory Evaluation of Hemostatic and Thrombotic Disorders 1923
Vessel
injury
vWF and platelet ↑TF+VIIa
adhesion
IXa IX
Platelet X Xa
Platelet activation Blood coagulation
contribution ADP PAR1 PAR4 protein contribution
to hemostasis THROMBIN II to hemostasis
Epi
Collagen PAR1* PAR4*
PAF Fibrin Fb
Platelet
aggregation
Hemostatic
plug
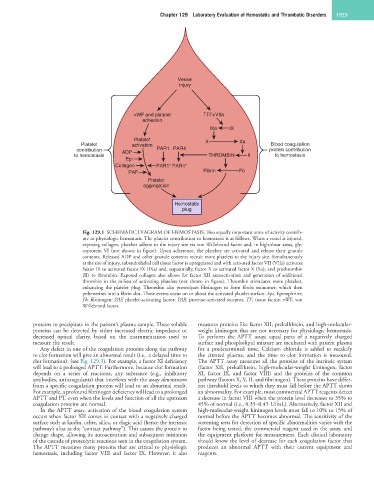
Fig. 129.1 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM OF HEMOSTASIS. Two equally important arms of activity contrib-
ute to physiologic hemostasis. The platelet contribution to hemostasis is as follows. When a vessel is injured,
exposing collagen, platelets adhere to the injury site via von Willebrand factor and, in high-shear areas, gly-
coprotein VI (not shown in figure). Upon adherence, the platelets are activated and release their granule
contents. Released ADP and other granule contents recruit more platelets to the injury site. Simultaneously
at the site of injury, subendothelial cell tissue factor is upregulated and with activated factor VII (VIIa) activates
factor IX to activated factor IX (IXa) and, sequentially, factor X to activated factor X (Xa), and prothrombin
(II) to thrombin. Exposed collagen also allows for factor XII autoactivation and generation of additional
thrombin in the milieu of activating platelets (not shown in figure). Thrombin stimulates more platelets,
enhancing the platelet plug. Thrombin also proteolyzes fibrinogen to form fibrin monomer, which then
polymerizes into a fibrin clot. These events occur on or about the activated platelet surface. Epi, Epinephrine;
Fb, fibrinogen; PAF, platelet-activating factor; PAR, protease-activated receptor, TF, tissue factor; vWF, von
Willebrand factor.
proteins to precipitate in the patient’s plasma sample. These soluble measures proteins like factor XII, prekallikrein, and high-molecular-
proteins can be detected by either increased electric impedance or weight kininogen that are not necessary for physiologic hemostasis.
decreased optical clarity, based on the instrumentation used to To perform the APTT assay, equal parts of a negatively charged
measure the result. surface and phospholipid mixture are incubated with patient plasma
Any defect in one of the coagulation proteins along the pathway for a predetermined time. Calcium chloride is added to recalcify
to clot formation will give an abnormal result (i.e., a delayed time to the citrated plasma, and the time to clot formation is measured.
clot formation), (see Fig. 129.3). For example, a factor XI deficiency The APTT assay measures all the proteins of the intrinsic system
will lead to a prolonged APTT. Furthermore, because clot formation (factor XII, prekallikrein, high-molecular-weight kininogen, factor
depends on a series of reactions, any substance (e.g., inhibitory XI, factor IX, and factor VIII) and the proteins of the common
antibodies, anticoagulants) that interferes with the assay downstream pathway (factors X, V, II, and fibrinogen). These proteins have differ-
from a specific coagulation protein will lead to an abnormal result. ent threshold levels to which they must fall before the APTT shows
For example, a profound fibrinogen deficiency will lead to a prolonged an abnormality. For example, most commercial APTT reagents detect
APTT and PT, even when the levels and function of all the upstream a decrease in factor VIII when the protein level decreases to 35% to
coagulation proteins are normal. 45% of normal (i.e., 0.35–0.45 U/mL). Alternatively, factor XII and
In the APTT assay, activation of the blood coagulation system high-molecular-weight kininogen levels must fall to 10% to 15% of
occurs when factor XII comes in contact with a negatively charged normal before the APTT becomes abnormal. The sensitivity of the
surface such as kaolin, celite, silica, or elagic acid (hence the intrinsic screening tests for detection of specific abnormalities varies with the
pathway’s alias as the “contact pathway”). This causes the protein to factor being tested, the commercial reagent used in the assay, and
change shape, allowing its autoactivation and subsequent initiation the equipment platform for measurement. Each clinical laboratory
of the cascade of proteolytic reactions seen in the coagulation system. should know the level of decrease for each coagulation factor that
The APTT measures many proteins that are critical to physiologic produces an abnormal APTT with their current equipment and
hemostasis, including factor VIII and factor IX. However, it also reagents.