Page 2241 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2241
1988 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
more sensitive assays, such as those for prothrombin fragment 1+2,
thrombin-antithrombin complexes and plasmin-antiplasmin com-
plexes, often reveal low-grade activation of coagulation and fibrino-
lytic pathways. Evidence of renal involvement may include hematuria,
proteinuria, granular or red cell casts, and mild azotemia, but anuria
and renal failure are uncommon presenting features. Severe deficiency
(<5%–10%) of ADAMTS13 in the appropriate clinical setting is
considered diagnostic of TTP, though TTP cannot be entirely
excluded by a normal or only moderately decreased level (see box on
ADAMTS13 in the Management of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic
Purpura). Levels should be measured before initiation of plasma
exchange to accurately assess baseline activity.
The prototypic vascular lesions of TTP are characterized by
platelet-rich thrombi within or beneath damaged endothelium.
Involved microvascular endothelial cells are swollen and in some cases
detached. The subendothelium contains hyaline material that is rela-
tively poor in fibrin and consists largely of vWF and platelet remnants.
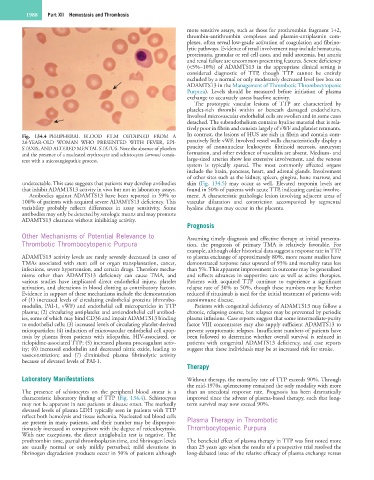
Fig. 134.4 PERIPHERAL BLOOD FILM OBTAINED FROM A In contrast, the lesions of HUS are rich in fibrin and contain com-
28-YEAR-OLD WOMAN WHO PRESENTED WITH FEVER, EPI- paratively little vWF. Involved vessel walls characteristically display a
STAXIS, AND ALTERED MENTAL STATUS. Note the absence of platelets paucity of mononuclear leukocytes; fibrinoid necrosis, aneurysm
and the presence of a nucleated erythrocyte and schistocytes (arrows) consis- formation, and other evidence of vasculitis are absent. Medium- and
tent with a microangiopathic process. large-sized arteries show less extensive involvement, and the venous
system is typically spared. The most commonly affected organs
include the brain, pancreas, heart, and adrenal glands. Involvement
of other sites such as the kidney, spleen, gingiva, bone marrow, and
undetectable. This case suggests that patients may develop antibodies skin (Fig. 134.5) may occur as well. Elevated troponin levels are
that inhibit ADAMTS13 activity in vivo but not in laboratory assays. found in 50% of patients with acute TTP, indicating cardiac involve-
Antibodies against ADAMTS13 have been reported in 59% to ment. A characteristic pathologic lesion involving adjacent areas of
100% of patients with acquired severe ADAMTS13 deficiency. This vascular dilatation and constriction accompanied by segmental
variability probably reflects differences in assay sensitivity. Some hyaline changes may occur in the placenta.
antibodies may only be detected by serologic means and may promote
ADAMTS13 clearance without inhibiting activity.
Prognosis
Other Mechanisms of Potential Relevance to Assuming timely diagnosis and effective therapy at initial presenta-
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura tion, the prognosis of primary TMA is relatively favorable. For
example, although older historical data suggest a response rate in TTP
ADAMTS13 activity levels are rarely severely decreased in cases of to plasma exchange of approximately 80%, more recent studies have
TMAs associated with stem cell or organ transplantation, cancer, demonstrated response rates upward of 95% and mortality rates less
infections, severe hypertension, and certain drugs. Therefore mecha- than 5%. This apparent improvement in outcome may be generalized
nisms other than ADAMTS13 deficiency can cause TMA, and and reflects advances in supportive care as well as active therapies.
various studies have implicated direct endothelial injury, platelet Patients with acquired TTP continue to experience a significant
activation, and alterations in blood clotting as contributory factors. relapse rate of 30% to 50%, though these numbers may be further
Evidence in support of these mechanisms include the demonstration reduced if rituximab is used for the initial treatment of patients with
of (1) increased levels of circulating endothelial proteins (thrombo- autoimmune disease.
modulin, PAI-1, vWF) and endothelial cell microparticles in TTP Patients with congenital deficiency of ADAMTS13 may follow a
plasma; (2) circulating antiplatelet and antiendothelial cell antibod- chronic, relapsing course, but relapses may be prevented by periodic
ies, some of which may bind CD36 and impair ADAMTS13 binding plasma infusions. Case reports suggest that some intermediate-purity
to endothelial cells; (3) increased levels of circulating platelet-derived factor VIII concentrates may also supply sufficient ADAMTS13 to
microparticles; (4) induction of microvascular endothelial cell apop- prevent symptomatic relapses. Insufficient numbers of patients have
tosis by plasma from patients with idiopathic, HIV-associated, or been followed to determine whether overall survival is reduced in
ticlopidine-associated TTP; (5) increased plasma procoagulant activ- patients with congenital ADAMTS13 deficiency, and case reports
ity; (6) increased endothelin and decreased nitric oxide, leading to suggest that these individuals may be at increased risk for stroke.
vasoconstriction; and (7) diminished plasma fibrinolytic activity
because of elevated levels of PAI-1.
Therapy
Laboratory Manifestations Without therapy, the mortality rate of TTP exceeds 90%. Through
the mid-1970s, splenectomy remained the only modality with more
The presence of schistocytes on the peripheral blood smear is a than an anecdotal response rate. Prognosis has been dramatically
characteristic laboratory finding of TTP (Fig. 134.4). Schistocytes improved since the advent of plasma-based therapy, such that long-
may not be apparent in rare patients at disease onset. The markedly term survival may now exceed 90%.
elevated levels of plasma LDH typically seen in patients with TTP
reflect both hemolysis and tissue ischemia. Nucleated red blood cells
are present in many patients, and their number may be dispropor- Plasma Therapy in Thrombotic
tionately increased in comparison with the degree of reticulocytosis. Thrombocytopenic Purpura
With rare exceptions, the direct antiglobulin test is negative. The
prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and fibrinogen levels The beneficial effect of plasma therapy in TTP was first noted more
are usually normal or only mildly perturbed; mild elevations in than 25 years ago when the results of a prospective trial resolved the
fibrinogen degradation products occur in 50% of patients although long-debated issue of the relative efficacy of plasma exchange versus