Page 2239 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2239
1986 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
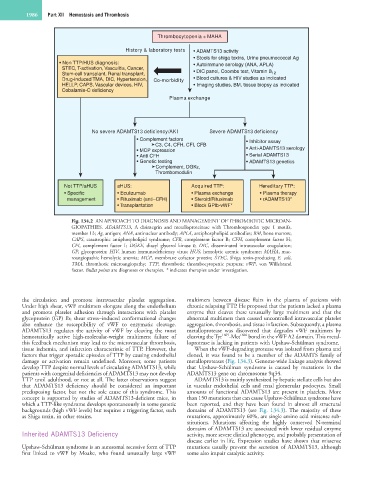
Thrombocytopenia + MAHA
History & laboratory tests • ADAMTS13 activity
• Stools for shiga toxins, Urine pneumococcal Ag
• Non TTP/HUS diagnosis: • Autoimmune serology (ANA, APLA)
STEC, T-activation, Vasculitis, Cancer,
Stem-cell transplant, Renal transplant, • DIC panel, Coombs test, Vitamin B 12
Drug-induced TMA, DIC, Hypertension, Co-morbidity • Blood cultures & HIV studies as indicated
HELLP, CAPS, Vascular devices, HIV, • Imaging studies, BM, tissue biopsy as indicated
Cobalamin-C deficiency
Plasma exchange
No severe ADAMTS13 deficiency/AKI Severe ADAMTS13 deficiency
• Complement factors • Inhibitor assay
C3, C4, CFH, CFI, CFB
• MCP expression • Anti-ADAMTS13 serology
• Anti CFH • Serial ADAMTS13
• Genetic testing • ADAMTS13 genetics
Complement, DGKε,
Thrombomodulin
Not TTP/aHUS aHUS: Acquired TTP: Hereditary TTP:
• Specific • Eculizumab • Plasma exchange • Plasma therapy
management • Rituximab (anti–CFH) • Steroid/Rituximab • rADAMTS13*
• Transplantation • Block GPIb-vWF*
Fig. 134.2 AN APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF THROMBOTIC MICROAN-
GIOPATHIES. ADAMTS13, A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with Thrombospondin type 1 motifs,
member 13; Ag, antigen; ANA, antinuclear antibody; APLA, antiphospholipid antibodies; BM, bone marrow;
CAPS, catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome; CFB, complement factor B; CFH, complement factor H;
CFI, complement factor I; DGKE, diacyl glycerol kinase ε; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation;
GP, glycoprotein; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HUS, hemolytic uremic syndrome; MAHA, mac-
roangiopathic hemolytic anemia; MCP, membrane cofactor protein; STEC, Shiga toxin-producing E. coli,
TMA, thrombotic microangiopathy; TTP, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; vWF, von Willebrand
factor. Bullet points are diagnoses or therapies. * indicates therapies under investigation.
the circulation and promote intravascular platelet aggregation. multimers between disease flairs in the plasma of patients with
Under high shear, vWF multimers elongate along the endothelium chronic relapsing TTP. He proposed that the patients lacked a plasma
and promote platelet adhesion through interactions with platelet enzyme that cleaves these unusually large multimers and that the
glycoprotein (GP) Ib; shear stress–induced conformational changes abnormal multimers then caused uncontrolled intravascular platelet
also enhance the susceptibility of vWF to enzymatic cleavage. aggregation, thrombosis, and tissue infarction. Subsequently, a plasma
ADAMTS13 regulates the activity of vWF by cleaving the most metalloprotease was discovered that degrades vWF multimers by
hemostatically active high-molecular-weight multimers; failure of cleaving the Tyr 1605 -Met 1606 bond in the vWF A2 domain. This metal-
this feedback mechanism may lead to the microvascular thrombosis, loprotease is lacking in patients with Upshaw-Schülman syndrome.
tissue ischemia, and infarction characteristic of TTP. However, the When the vWF-degrading protease was isolated from plasma and
factors that trigger sporadic episodes of TTP by causing endothelial cloned, it was found to be a member of the ADAMTS family of
damage or activation remain undefined. Moreover, some patients metalloproteases (Fig. 134.3). Genome-wide linkage analysis showed
develop TTP despite normal levels of circulating ADAMTS13, while that Upshaw-Schülman syndrome is caused by mutations in the
patients with congenital deficiencies of ADAMTS13 may not develop ADAMTS13 gene on chromosome 9q34.
TTP until adulthood, or not at all. The latter observations suggest ADAMTS13 is mainly synthesized by hepatic stellate cells but also
that ADAMTS13 deficiency should be considered an important in vascular endothelial cells and renal glomerular podocytes. Small
predisposing factor, but not the sole cause of this syndrome. This amounts of functional ADAMTS13 are present in platelets. More
concept is supported by studies of ADAMTS13-deficient mice, in than 150 mutations that can cause Upshaw-Schülman syndrome have
which a TTP-like syndrome develops spontaneously in some genetic been reported, and they have been found in almost all structural
backgrounds (high vWF levels) but requires a triggering factor, such domains of ADAMTS13 (see Fig. 134.3). The majority of these
as Shiga toxin, in other strains. mutations, approximately 60%, are single amino acid missense sub-
stitutions. Mutations affecting the highly conserved N-terminal
domains of ADAMTS13 are associated with lower residual enzyme
Inherited ADAMTS13 Deficiency activity, more severe clinical phenotype, and probably presentation of
disease earlier in life. Expression studies have shown that missense
Upshaw-Schülman syndrome is an autosomal recessive form of TTP mutations usually prevent the secretion of ADAMTS13, although
first linked to vWF by Moake, who found unusually large vWF some also impair catalytic activity.