Page 2243 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2243
1990 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
A B
C D
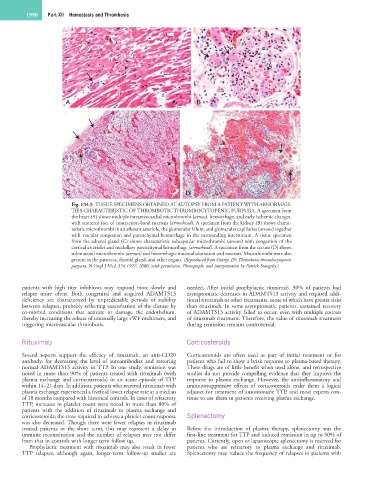
Fig. 134.5 TISSUE SPECIMENS OBTAINED AT AUTOPSY FROM A PATIENT WITH ABNORMALI-
TIES CHARACTERISTIC OF THROMBOTIC THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA. A specimen from
the heart (A) shows multiple intramyocardial microthrombi (arrow), hemorrhage, and early ischemic changes,
with scattered foci of contraction-band necrosis (arrowhead). A specimen from the kidney (B) shows charac-
teristic microthrombi in an afferent arteriole, the glomerular hilum, and glomerular capillaries (arrows) together
with vascular congestion and parenchymal hemorrhage in the surrounding interstitium. A tissue specimen
from the adrenal gland (C) shows characteristic subcapsular microthrombi (arrows) with congestion of the
cortical arterioles and medullary parenchymal hemorrhage (arrowhead). A specimen from the cecum (D) shows
submucosal microthrombi (arrows) and hemorrhagic mucosal ulceration and necrosis. Microthrombi were also
present in the pancreas, thyroid gland, and other organs. (Reproduced from George, JN: Thrombotic thrombocytopenic
purpura. N Engl J Med 354:1927, 2006, with permission. Photographs and interpretation by Patrick Stangeby.)
patients with high titer inhibitors may respond more slowly and needed. After initial prophylactic rituximab, 30% of patients had
relapse more often. Both congenital and acquired ADAMTS13 asymptomatic decreases in ADAMTS13 activity and required addi-
deficiency are characterized by unpredictable periods of stability tional rituximab or other treatments, some of which have greater risks
between relapses, probably reflecting exacerbation of the disease by than rituximab. In some asymptomatic patients, sustained recovery
co-morbid conditions that activate or damage the endothelium, of ADAMTS13 activity failed to occur, even with multiple courses
thereby increasing the release of unusually large vWF multimers, and of rituximab treatment. Therefore, the value of rituximab treatment
triggering microvascular thrombosis. during remission remains controversial.
Rituximab Corticosteroids
Several reports support the efficacy of rituximab, an anti-CD20 Corticosteroids are often used as part of initial treatment or for
antibody, for decreasing the level of autoantibodies and restoring patients who fail to show a brisk response to plasma-based therapy.
normal ADAMTS13 activity in TTP. In one study, remission was These drugs are of little benefit when used alone, and retrospective
noted in more than 90% of patients treated with rituximab (with studies do not provide compelling evidence that they improve the
plasma exchange and corticosteroids) in an acute episode of TTP response to plasma exchange. However, the antiinflammatory and
within 14–21 days. In addition, patients who received rituximab with immunosuppressive effects of corticosteroids make them a logical
plasma exchange experienced a fivefold lower relapse rate at a median adjunct for treatment of autoimmune TTP, and most experts con-
of 18 months compared with historical controls. In cases of refractory tinue to use them in patients receiving plasma exchange.
TTP, increases in platelet count were noted in more than 80% of
patients with the addition of rituximab to plasma exchange and
corticosteroids; the time required to achieve a platelet count response Splenectomy
was also decreased. Though there were fewer relapses in rituximab
treated patients in the short term, this may represent a delay in Before the introduction of plasma therapy, splenectomy was the
immune reconstitution and the number of relapses may not differ first-line treatment for TTP and induced remission in up to 50% of
from that in controls with longer term follow up. patients. Currently, open or laparoscopic splenectomy is reserved for
Prophylactic treatment with rituximab may also result in fewer patients who are refractory to plasma exchange and rituximab.
TTP relapses, although again, longer-term follow-up studies are Splenectomy may reduce the frequency of relapses in patients with