Page 2310 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2310
2052 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
P
P P P P
P P
P P P
FVIII bound P
VWF FVIII to N-terminus Platelets
multimers P
of VWF
Resting Activated
P P P
P P
P P
P P P P
P P P
With injury, VWF adheres to vessel With shear, VWF multimers uncoil, platelets adhere and
subendothelial matrix. become activated.
Activated platelets expose phosphatidyl Bleeding ceases by platelet-fibrin plug sealing vascular
serine and bind FVIII to facilitate clotting. injury and is followed by thrombolysis and tissue repair.
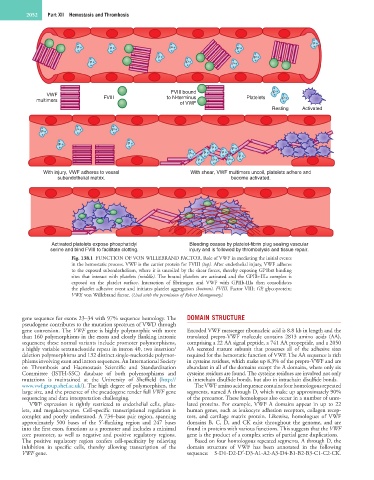
Fig. 138.1 FUNCTION OF VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR. Role of VWF in mediating the initial events
in the hemostatic process. VWF is the carrier protein for FVIII (top). After endothelial injury, VWF adheres
to the exposed subendothelium, where it is uncoiled by the shear forces, thereby exposing GP1bα binding
sites that interact with platelets (middle). The bound platelets are activated and the GPIIb-IIIa complex is
exposed on the platelet surface. Interaction of fibrinogen and VWF with GPIIb-IIIa then consolidates
the platelet adhesive event and initiates platelet aggregation (bottom). FVIII, Factor VIII; GP, glycoprotein;
VWF, von Willebrand factor. (Used with the permission of Robert Montgomery).
gene sequence for exons 23–34 with 97% sequence homology. The DOMAIN STRUCTURE
pseudogene contributes to the mutation spectrum of VWD through
gene conversion. The VWF gene is highly polymorphic with more Encoded VWF messenger ribonucleic acid is 8.8 kb in length and the
than 160 polymorphisms in the exons and closely flanking intronic translated prepro-VWF molecule contains 2813 amino acids (AA),
sequences; these normal variants include promoter polymorphisms, comprising a 22 AA signal peptide, a 741 AA propeptide, and a 2050
a highly variable tetranucleotide repeat in intron 40, two insertion/ AA secreted mature subunit that possesses all of the adhesive sites
deletion polymorphisms and 132 distinct single-nucleotide polymor- required for the hemostatic function of VWF. The AA sequence is rich
phisms involving exon and intron sequences. An International Society in cysteine residues, which make up 8.3% of the prepro-VWF and are
on Thrombosis and Haemostasis Scientific and Standardization abundant in all of the domains except the A domains, where only six
Committee (ISTH-SSC) database of both polymorphisms and cysteine residues are found. The cysteine residues are involved not only
mutations is maintained at the University of Sheffield (http:// in interchain disulfide bonds, but also in intrachain disulfide bonds.
www.vwf.group.shef.ac.uk/). The high degree of polymorphism, the The VWF amino acid sequence contains four homologous repeated
large size, and the presence of the pseudogene render full VWF gene segments, named A through D, which make up approximately 90%
sequencing and data interpretation challenging. of the precursor. These homologues also occur in a number of unre-
VWF expression is tightly restricted to endothelial cells, plate- lated proteins. For example, VWF A domains appear in up to 22
lets, and megakaryocytes. Cell-specific transcriptional regulation is human genes, such as leukocyte adhesion receptors, collagen recep-
complex and poorly understood. A 734–base pair region, spanning tors, and cartilage matrix protein. Likewise, homologues of VWF
approximately 500 bases of the 5′-flanking region and 247 bases domains B, C, D, and CK exist throughout the genome, and are
into the first exon, functions as a promoter and includes a minimal found in proteins with various functions. This suggests that the VWF
core promoter, as well as negative and positive regulatory regions. gene is the product of a complex series of partial gene duplications.
The positive regulatory region confers cell-specificity by relieving Based on four homologous repeated segments, A through D, the
inhibition in specific cells, thereby allowing transcription of the domain structure of VWF has been annotated in the following
VWF gene. sequence: S-D1-D2-D′-D3-A1-A2-A3-D4-B1-B2-B3-C1-C2-CK.