Page 2311 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2311
Chapter 138 Structure, Biology, and Genetics of von Willebrand Factor 2053
5 10 28 45 52
Multimerization Dimerization
B1–3
NH 2 COOH
D1 D2 D’ D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 C1 C2 CK
Pre Pro (741 AA) Mature subunit (2050 AA)
(22 AA)
1 23 763 2813
B1–3
NH 2 COOH
D’ D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 C1 C2 CK
FVIII Gplb Collagen
A Collagen αllbβ3
GP1b Collagen
FVIII GPIIb-IIIa
D’D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 CK
Multimerization Dimerization
B ADAMTS13
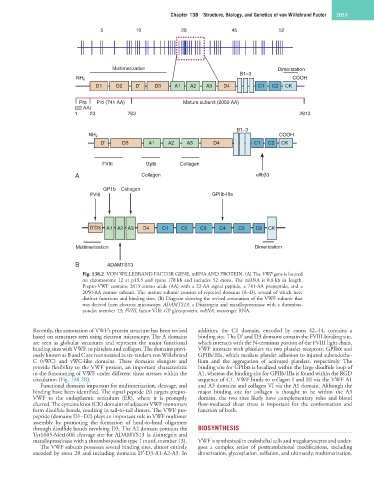
Fig. 138.2 VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR GENE, mRNA AND PROTEIN. (A) The VWF gene is located
on chromosome 12 at p13.3 and spans 178 kb and includes 52 exons. The mRNA is 8.8 kb in length.
Prepro-VWF contains 2813 amino acids (AA) with a 22-AA signal peptide, a 741-AA propeptide, and a
2050-AA mature subunit. The mature subunit consists of repeated domains (A–D), several of which have
distinct functions and binding sites. (B) Diagram showing the revised annotation of the VWF subunit that
was derived from electron microscopy. ADAMTS13, a Disintegrin and metalloproteinase with a thrombos-
pondin member 13; FVIII, factor VIII; GP, glycoprotein, mRNA, messenger RNA.
Recently, the annotation of VWF’s protein structure has been revised addition, the C1 domain, encoded by exons 42–44, contains a
based on structures seen using electron microscopy. The A domains binding site. The D′ and D3 domains contain the FVIII-binding site,
are seen as globular structures and represent the major functional which interacts with the N-terminus portion of the FVIII light chain.
binding sites with VWF, to platelets and collagen. The domains previ- VWF interacts with platelets via two platelet receptors; GPIbα and
ously known as B and C are reannotated as six-tandem von Willebrand GPIIb/IIIa, which mediate platelet adhesion to injured subendothe-
C (vWC) and vWC-like domains. These domains elongate and lium and the aggregation of activated platelets, respectively. The
provide flexibility to the VWF protein, an important characteristic binding site for GPIbα is localized within the large disulfide loop of
to the functioning of VWF under different shear stresses within the A1, whereas the binding site for GPIIb/IIIa is found within the RGD
circulation (Fig. 138.2B). sequence of C1. VWF binds to collagen I and III via the VWF A1
Functional domains important for multimerization, cleavage, and and A3 domains and collagen VI via the A1 domain. Although the
binding have been identified. The signal peptide (S) targets prepro- major binding site for collagen is thought to be within the A3
VWF to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where it is promptly domain, the two sites likely have complementary roles and blood
cleaved. The cysteine knot (CK) domains of adjacent VWF monomers flow-mediated shear stress is important for the conformation and
form disulfide bonds, resulting in tail-to-tail dimers. The VWF pro- function of both.
peptide (domains D1–D2) plays an important role in VWF multimer
assembly by promoting the formation of head-to-head oligomers
through disulfide bonds involving D3. The A2 domain contains the BIOSYNTHESIS
Tyr1605-Met1606 cleavage site for ADAMTS13 (a disintegrin and
metalloproteinase with a thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13). VWF is synthesized in endothelial cells and megakaryocytes and under-
The VWF subunit possesses several binding sites, almost entirely goes a complex series of posttranslational modifications, including
encoded by exon 28 and including domains D′-D3-A1-A2-A3. In dimerization, glycosylation, sulfation, and ultimately, multimerization.