Page 2386 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2386
2128 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
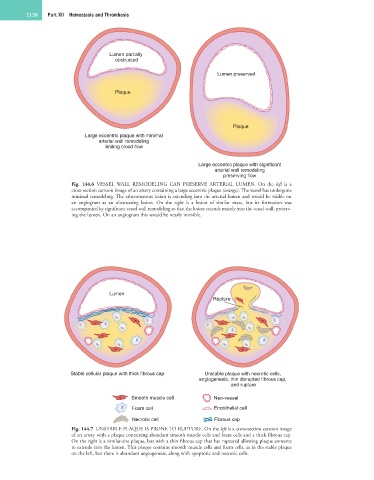
Lumen partially
obstructed
Lumen preserved
Plaque
Plaque
Large eccentric plaque with minimal
arterial wall remodeling
limiting blood flow
Large eccentric plaque with significant
arterial wall remodeling
preserving flow
Fig. 144.6 VESSEL WALL REMODELING CAN PRESERVE ARTERIAL LUMEN. On the left is a
cross-section cartoon image of an artery containing a large eccentric plaque (orange). The vessel has undergone
minimal remodeling. The atheromatous lesion is extending into the arterial lumen and would be visible on
an angiogram as an obstructing lesion. On the right is a lesion of similar mass, but its formation was
accompanied by significant vessel wall remodeling so that the lesion extends mainly into the vessel wall, preserv-
ing the lumen. On an angiogram this would be nearly invisible.
Lumen
Rupture
Stable cellular plaque with thick fibrous cap Unstable plaque with necrotic cells,
angiogenesis, thin disrupted fibrous cap,
and rupture
Smooth muscle cell Neo-vessel
Foam cell Endothelial cell
Necrotic cell Fibrous cap
Fig. 144.7 UNSTABLE PLAQUE IS PRONE TO RUPTURE. On the left is a cross-section cartoon image
of an artery with a plaque containing abundant smooth muscle cells and foam cells and a thick fibrous cap.
On the right is a similar-size plaque, but with a thin fibrous cap that has ruptured allowing plaque contents
to extrude into the lumen. This plaque contains smooth muscle cells and foam cells, as in the stable plaque
on the left, but there is abundant angiogenesis, along with apoptotic and necrotic cells.