Page 2440 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2440
2178 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
protamine sulfate. Consequently, patients at high risk for bleeding may half-life is about 17 hours. The drug is given subcutaneously once
be more safely treated with continuous intravenous unfractionated daily. Because fondaparinux is cleared unchanged via the kidneys, it
heparin than with subcutaneous LMWH. In addition to the potential is contraindicated in patients with a creatinine clearance less than
for complete reversal with protamine sulfate, the short half-life of 30 mL/min, and it should be used with caution in those with a
intravenous heparin also is an advantage if major bleeding occurs. creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min.
Fondaparinux produces a predictable anticoagulant response after
Thrombocytopenia administration in fixed doses because it does not bind to plasma
The risk of HIT is about fivefold lower with LMWH than with proteins. The drug is given at a dose of 2.5 mg once daily for preven-
heparin. LMWH binds less avidly to platelets and causes less PF4 tion of venous thromboembolism. For initial treatment of established
release. Furthermore, with lower affinity for PF4 than heparin, venous thromboembolism, fondaparinux is given at a dose of 7.5 mg
LMWH is less likely to induce the conformational changes in PF4 once daily. The dose can be reduced to 5 mg once daily for those
that trigger the formation of HIT antibodies. LMWH should not be weighing less than 50 kg and increased to 10 mg for those weighing
used to treat patients with HIT, because most HIT antibodies exhibit more than 100 kg. When given in these doses, fondaparinux is as
cross-reactivity with LMWH, and there are case reports of thrombosis effective as heparin or LMWH for initial treatment of patients with
when patients with HIT were treated with LMWH. deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism and produces similar
rates of bleeding.
Osteoporosis Although not licensed for this indication in the United States,
The risk of osteoporosis is lower with long-term LMWH than with fondaparinux has been used in place of heparin or LMWH in patients
heparin. For extended treatment, therefore, LMWH is a better choice with acute coronary syndrome. When the prophylactic dose of
than heparin because of the lower risk of both osteoporosis and HIT. fondaparinux (2.5 mg daily) was compared with treatment doses of
enoxaparin in patients with non–ST-segment elevation acute coro-
nary syndrome, there was no difference in the rate of cardiovascular
Fondaparinux death, myocardial infarction, or stroke at 9 days. However, the rate
17
of major bleeding was 50% lower with fondaparinux than with
A synthetic analogue of the antithrombin-binding pentasaccharide enoxaparin, a difference that likely reflects the fact that the dose of
sequence, fondaparinux differs from LMWH in several ways (Table fondaparinux was lower than that of enoxaparin. In patients with
149.6). Fondaparinux is licensed for (1) thromboprophylaxis in acute coronary syndrome who require PCI, there is a risk of catheter
medical, general surgical, and high-risk orthopedic patients and (2) thrombosis with fondaparinux unless adjunctive heparin is given.
as an alternative to heparin or LMWH for initial treatment of patients
with established venous thromboembolism. In some countries,
fondaparinux also is approved as an alternative to heparin or LMWH Side Effects
for treatment of patients with acute coronary syndromes.
Fondaparinux does not cause HIT, and, in contrast to LMWH, there
is no cross-reactivity of fondaparinux with HIT antibodies. Interest-
Mechanism of Action ingly, fondaparinux induces the formation of HIT antibodies to the
same extent as LMWH. In contrast to heparin or LMWH, however,
As a synthetic analogue of the antithrombin-binding pentasaccharide fondaparinux is too short to cluster PF4 tetramers together, which is
sequence found in heparin and LMWH, fondaparinux has a molecu- a prerequisite for HIT antibody binding. This phenomenon explains
lar weight of 1728. Fondaparinux binds only to antithrombin (see not only why HIT antibodies do not cross-react with fondaparinux
Fig. 149.4) and is too short to bridge thrombin to antithrombin. but also why fondaparinux does not cause HIT despite the fact that
Consequently, fondaparinux catalyzes factor Xa inhibition by anti- it induces the formation of HIT antibodies. Although fondaparinux
thrombin and does not enhance the rate of thrombin inhibition. has been used successfully for HIT treatment, large clinical trials are
lacking, and the drug is not licensed for this indication.
The major side effect of fondaparinux is bleeding. There is no
Pharmacology antidote for fondaparinux. Protamine sulfate has no effect on the
anticoagulant activity of fondaparinux, because it fails to bind to the
Fondaparinux exhibits complete bioavailability after subcutaneous drug. Recombinant activated factor VII reverses the anticoagulant
injection. With no binding to endothelial cells or plasma proteins, effects of fondaparinux in volunteers, but it is unknown whether this
the clearance of fondaparinux is dose independent, and its plasma agent will control fondaparinux-induced bleeding.
Parenteral Direct Thrombin Inhibitors
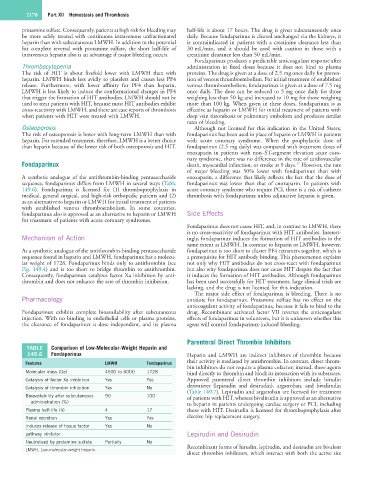
TABLE Comparison of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin and
149.6 Fondaparinux Heparin and LMWH are indirect inhibitors of thrombin because
Features LMWH Fondaparinux their activity is mediated by antithrombin. In contrast, direct throm-
bin inhibitors do not require a plasma cofactor; instead, these agents
Molecular mass (Da) 4500 to 6000 1728 bind directly to thrombin and block its interaction with its substrates.
Catalysis of factor Xa inhibition Yes Yes Approved parenteral direct thrombin inhibitors include hirudin
Catalysis of thrombin inhibition Yes No derivatives (lepirudin and desirudin), argatroban, and bivalirudin
(Table 149.7). Lepirudin and argatroban are licensed for treatment
Bioavailability after subcutaneous 90 100 of patients with HIT, whereas bivalirudin is approved as an alternative
administration (%) to heparin in patients undergoing cardiac surgery or PCI, including
Plasma half-life (h) 4 17 those with HIT. Desirudin is licensed for thromboprophylaxis after
Renal excretion Yes Yes elective hip replacement surgery.
Induces release of tissue factor Yes No
pathway inhibitor Lepirudin and Desirudin
Neutralized by protamine sulfate Partially No
LMWH, Low-molecular-weight heparin. Recombinant forms of hirudin, lepirudin, and desirudin are bivalent
direct thrombin inhibitors, which interact with both the active site