Page 249 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 249
Chapter 19 Overview and Compartmentalization of the Immune System 201
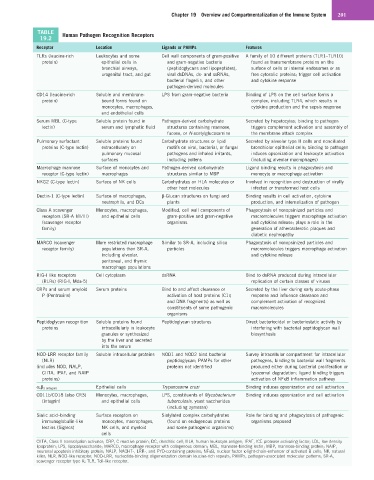
TABLE Human Pathogen Recognition Receptors
19.2
Receptor Location Ligands or PAMPs Features
TLRs (leucine-rich Leukocytes and some Cell wall components of gram-positive A family of 10 different proteins (TLR1–TLR10)
protein) epithelial cells in and gram-negative bacteria found as transmembrane proteins on the
bronchial airways, (peptidoglycans and lipopeptides), surface of cells or internal endosomes or as
urogenital tract, and gut viral dsDNAs, ds- and ssRNAs, free cytosolic proteins; trigger cell activation
bacterial flagellin, and other and cytokine response
pathogen-derived molecules
CD14 (leucine-rich Soluble and membrane- LPS from gram-negative bacteria Binding of LPS on the cell surface forms a
protein) bound forms found on complex, including TLR4, which results in
monocytes, macrophages, cytokine production and the sepsis response
and endothelial cells
Serum MBL (C-type Soluble protein found in Pathogen-derived carbohydrate Secreted by hepatocytes; binding to pathogen
lectin) serum and lymphatic fluid structures containing mannose, triggers complement activation and assembly of
fucose, or N-acetylglucosamine the membrane attack complex
Pulmonary surfactant Soluble proteins found Carbohydrate structures or lipid Secreted by alveolar type II cells and nonciliated
proteins (C-type lectin) extracellularly on motifs on viral, bacterial, or fungal bronchiolar epithelial cells; binding to pathogen
pulmonary mucosal pathogens and inhaled irritants, induces opsonization and leukocyte activation
surfaces including pollens (including alveolar macrophages)
Macrophage mannose Surface of monocytes and Pathogen-derived carbohydrate Ligand binding results in phagocytosis and
receptor (C-type lectin) macrophages structures similar to MBP monocyte or macrophage activation
NKG2 (C-type lectin) Surface of NK cells Carbohydrates on HLA molecules or Involved in recognition and destruction of virally
other host molecules infected or transformed host cells
Dectin-1 (C-type lectin) Surface of macrophages, β-Glucan structures on fungi and Binding results in cell activation, cytokine
neutrophils, and DCs plants production, and internalization of pathogen
Class A scavenger Monocytes, macrophages, Modified, cell wall components of Phagocytosis of nonopsinized particles and
receptors (SR-A I/II/III) and epithelial cells gram-positive and gram-negative macromolecules triggers macrophage activation
(scavenger receptor organisms and cytokine release; plays a role in the
family) generation of atherosclerotic plaques and
diabetic nephropathy
MARCO (scavenger More restricted macrophage Similar to SR-A, including silica Phagocytosis of nonopsinized particles and
receptor family) populations than SR-A, particles macromolecules triggers macrophage activation
including alveolar, and cytokine release
peritoneal, and thymic
macrophage populations
RIG-I like receptors Cell cytoplasm dsRNA Bind to dsRNA produced during intracellular
(RLRs) (RIG-I, Mda-5) replication of certain classes of viruses
CRPs and serum amyloid Serum proteins Bind to and affect clearance or Secreted by the liver during early acute-phase
P (Pentraxins) activation of host proteins (C1q response and influence clearance and
and DNA fragments) as well as complement activation of recognized
constituents of some pathogenic macromolecules
organisms
Peptidoglycan recognition Soluble proteins found Peptidoglycan structures Direct bacteriocidal or bacteriostatic activity by
proteins intracellularly in leukocyte interfering with bacterial peptidoglycan wall
granules or synthesized biosynthesis
by the liver and secreted
into the serum
NOD-LRR receptor family Soluble intracellular proteins NOD1 and NOD2 bind bacterial Survey intracellular compartment for intracellular
(NLR) peptidoglycan; PAMPs for other pathogens, binding to bacterial wall fragments
(includes NOD, NALP, proteins not identified produced either during bacterial proliferation or
CIITA, IPAF, and NAIP lysozomal degradation; ligand binding triggers
proteins) activation of NFκB inflammation pathway
Epithelial cells Trypanosome cruzi Binding induces opsonization and cell activation
α v β 3 (integrin)
CD11b/CD18 (also CR3) Monocytes, macrophages, LPS, constituents of Mycobacterium Binding induces opsonization and cell activation
(integrin) and epithelial cells tuberculosis, yeast saccharides
(including zymosan)
Sialic acid–binding Surface receptors on Sialylated complex carbohydrates Role for binding and phagocytosis of pathogenic
immunoglobulin-like monocytes, macrophages, (found on endogenous proteins organisms proposed
lectins (Siglecs) NK cells, and myeloid and some pathogenic organisms)
cells
CIITA, Class II transcription activator; CRP, C-reactive protein; DC, dendritic cell; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; IPAF, ICE-protease activating factor; LDL, low-density
lipoprotein; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MARCO, macrophage receptor with collagenous domain; MBL, mannose-binding lectin; MBP, mannose-binding protein; NAIP,
neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein; NALP, NACHT-, LRR-, and PYD-containing proteins; NFκB, nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NK, natural
killer; NLR, NOD-like receptor; NOD-LRR, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain leucine-rich repeats; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; SR-A,
scavenger receptor type A; TLR, Toll-like receptor.