Page 2541 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2541
2264 Part XIII Consultative Hematology
degradation of the viral RNA by ribonuclease H activity of p66. The
Virion reverse transcriptase then acts as a DNA polymerase forming a
double-stranded DNA provirus. The reverse transcriptase of HIV has
a significant rate of base substitution errors, estimated as high as 1 in
Binding CD4 Chemokine 1700 to 1 in 2000 nucleoside bases, resulting in an average of 5 to
Penetration receptor 10 nucleoside mutations for each replication cycle. This explains the
high degree of genomic diversity observed between HIV-1 viral
RNA isolates.
Reverse A linear form of the provirus is integrated into the host DNA by
transcription the viral integrase. In kinetic studies of HIV-1 infection, viral DNA
Single-stranded DNA
Replication is present in the cytoplasm within 2 to 3 hours of infection, and viral
Double-stranded DNA nuclear DNA has been detected by 24 hours. The gene product of
Translocation VPR assists in transport of the viral pro-DNA into the nucleus for
subsequent integration. After integration of the viral genome, the
Circularization Circular viral DNA HIV-1 infected cell may develop either a latent or persistent form of
infection.
HIV-1 does not replicate readily in resting lymphocytes and
Integration Host Host macrophages. Cellular transactivation by, for example, nuclear factor
DNA DNA Provirus kappa-B (NFκB) can enhance proviral transcription. HIV-1 proviral
Transcription transcription leads to the expression of regulatory proteins tat, rev,
Viral RNAs
Transport/translation [regulatory proteins] and nef. Tat is a protein essential for HIV replication and in
[structural proteins] conjunction with the cellular proteins TAK (Tat associated kinase)
and Cyc T (cyclin T) promotes viral RNA elongation resulting in a
1000-fold increase in HIV-1 expression. Rev is a viral protein that is
Viral RNA
Processing [genomic] also essential for replication by regulating nuclear export of unspliced
viral RNA. Nef and vpu proteins modulate the downregulation of
cellular CD4.
The structural proteins of the GAG, POL, and ENV genes are
Assembly expressed as precursor proteins and subsequently cleaved by viral
protease yielding mature viral proteins. This final step in protein
processing is essential for the assembly of mature infectious virus. For
Budding
this reason, inhibition of the viral protease has proven a fruitful target
for HAART. The products of the ENV gene, GP120 and GP 41, are
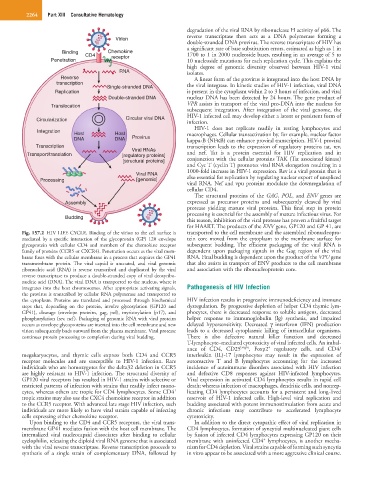
Fig. 157.2 HIV LIFE CYCLE. Binding of the virion to the cell surface is transported to the cell membrane and the assembled ribonucleopro-
mediated by a specific interaction of the glycoprotein (GP) 120 envelope tein core moved from the cytoplasm to the membrane surface for
glycoprotein with cellular CD4 and members of the chemokine receptor subsequent budding. The efficient packaging of the viral RNA is
family of proteins (CCR5 or CXCR4). Penetration occurs as the viral mem- dependent upon packaging signals in the Gag region of the viral
brane fuses with the cellular membrane in a process that requires the GP41 RNA. Final budding is dependent upon the product of the VPU gene
transmembrane protein. The viral capsid is uncoated, and viral genomic that also assists in transport of ENV products to the cell membrane
ribonucleic acid (RNA) is reverse transcribed and duplicated by the viral and association with the ribonucleoprotein core.
reverse transcriptase to produce a double-stranded copy of viral deoxyribo-
nucleic acid (DNA). The viral DNA is transported to the nucleus, where it
integrates into the host chromosomes. After appropriate activating signals, Pathogenesis of HIV Infection
the provirus is transcribed by cellular RNA polymerase and transported to
the cytoplasm. Proteins are translated and processed through biochemical HIV infection results in progressive immunodeficiency and immune
steps that, depending on the protein, involve glycosylation (GP120 and dysregulation. By progressive depletion of helper CD4 thymic lym-
GP41), cleavage (envelope proteins, gag, pol), myristoylation (p17), and phocytes, there is decreased response to soluble antigens, decreased
phosphorylation (rev, nef). Packaging of genomic RNA with viral proteins helper response to immunoglobulin (Ig) synthesis, and impaired
occurs as envelope glycoproteins are inserted into the cell membrane and new delayed hypersensitivity. Decreased γ interferon (IFN) production
virion subsequently buds outward from the plasma membrane. Viral protease leads to a decreased cytoplasmic killing of intracellular organisms.
continues protein processing to completion during viral budding. There is also defective natural killer function and decreased
T-lymphocyte–mediated cytotoxicity of viral infected cells. An imbal-
+
ance of CD4, CD25 bright , Foxp2 regulatory cells, and CD4/
megakaryocytes, and thymic cells express both CD4 and CCR5 interleukin (IL)-17 lymphocytes may result in the expression of
receptor molecules and are susceptible to HIV-1 infection. Rare autoreactive T and B lymphocytes accounting for the increased
individuals who are homozygotes for the delta32 deletion in CCR5 incidence of autoimmune disorders associated with HIV infection
are highly resistant to HIV-1 infection. The structural diversity of and defective CD8 responses against HIV-infected lymphocytes.
GP120 viral receptors has resulted in HIV-1 strains with selective or Viral expression in activated CD4 lymphocytes results in rapid cell
restricted patterns of infection with strains that readily infect mono- death; whereas infection of macrophages, dendritic cells, and nonrep-
+
cytes, whereas others are tropic for CD4 lymphocytes. Some CD4 licating CD4 lymphocytes accounts for a persistent and long-lived
tropic strains may also use the CXC4 chemokine receptor in addition reservoir of HIV-1 infected cells. High-level viral replication and
to the CCR5 receptor. With advanced late stage HIV infection, such budding associated with potent immunostimulation from acute and
individuals are more likely to have viral strains capable of infecting chronic infections may contribute to accelerated lymphocyte
cells expressing either chemokine receptor. cytotoxicity.
Upon binding to the CD4 and CCR5 receptors, the viral trans- In addition to the direct cytopathic effect of viral replication in
membrane GP41 mediates fusion with the host cell membrane. The CD4 lymphocytes, formation of syncytial multinucleated giant cells
internalized viral nucleocapsid dissociates after binding to cellular by fusion of infected CD4 lymphocytes expressing GP120 on their
+
cyclophilin, releasing the diploid viral RNA genome that is associated membrane with uninfected CD4 lymphocytes, is another mecha-
with the viral reverse transcriptase. Reverse transcription proceeds to nism for CD4 depletion. Viral strains capable of forming such syncytia
synthesis of a single strain of complementary DNA, followed by in vitro appear to be associated with a more aggressive clinical course.