Page 2542 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2542
Chapter 157 Hematologic Manifestations of HIV/AIDS 2265
A B C D
E F G H I
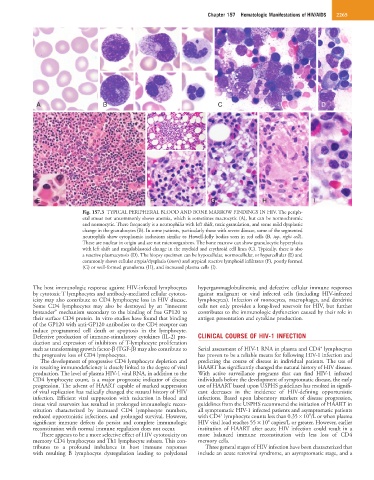
Fig. 157.3 TYPICAL PERIPHERAL BLOOD AND BONE MARROW FINDINGS IN HIV. The periph-
eral smear not uncommonly shows anemia, which is sometimes macrocytic (A), but can be normochromic
and normocytic. There frequently is a neutrophilia with left shift, toxic granulation, and some mild dysplastic
change in the granulocytes (B). In some patients, particularly those with severe disease, some of the segmented
neutrophils show cytoplasmic inclusions similar to Howell-Jolly bodies seen in red cells (B, top, right cell).
These are nuclear in origin and are not microorganisms. The bone marrow can show granulocytic hyperplasia
with left shift and megaloblastoid change in the myeloid and erythroid cell lines (C). Typically, there is also
a reactive plasmacytosis (D). The biopsy specimen can be hypocellular, normocellular, or hypercellular (E) and
commonly shows cellular atypia/dysplasia (insert) and atypical reactive lymphoid infiltrates (F), poorly formed
(G) or well-formed granuloma (H), and increased plasma cells (I).
The host immunologic response against HIV-infected lymphocytes hypergammaglobulinemia and defective cellular immune responses
by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and antibody-mediated cellular cytotox- against malignant or viral infected cells (including HIV-infected
icity may also contribute to CD4 lymphocyte loss in HIV disease. lymphocytes). Infection of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic
Some CD4 lymphocytes may also be destroyed by an “innocent cells not only provides a long-lived reservoir for HIV, but further
bystander” mechanism secondary to the binding of free GP120 to contributes to the immunologic dysfunction caused by their role in
their surface CD4 protein. In vitro studies have found that binding antigen presentation and cytokine production.
of the GP120 with anti-GP120 antibodies to the CD4 receptor can
induce programmed cell death or apoptosis in the lymphocyte.
Defective production of immune-stimulatory cytokines (IL-2) pro- CLINICAL COURSE OF HIV-1 INFECTION
duction and expression of inhibitors of T-lymphocyte proliferation
+
such as transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) may also contribute to Serial assessment of HIV-1 RNA in plasma and CD4 lymphocytes
the progressive loss of CD4 lymphocytes. has proven to be a reliable means for following HIV-1 infection and
The development of progressive CD4 lymphocyte depletion and predicting the course of disease in individual patients. The use of
its resulting immunodeficiency is closely linked to the degree of viral HAART has significantly changed the natural history of HIV disease.
production. The level of plasma HIV-1 viral RNA, in addition to the With active surveillance programs that can find HIV-1 infected
CD4 lymphocyte count, is a major prognostic indicator of disease individuals before the development of symptomatic disease, the early
progression. The advent of HAART capable of marked suppression use of HAART based upon USPHS guidelines has resulted in signifi-
of viral replication has radically changed the natural history of HIV cant decreases in the incidence of HIV-defining opportunistic
infection. Efficient viral suppression with reduction in blood and infections. Based upon laboratory markers of disease progression,
tissue viral reservoirs has resulted in prolonged immunologic recon- guidelines from the USPHS recommend the initiation of HAART in
stitution characterized by increased CD4 lymphocyte numbers, all symptomatic HIV-1 infected patients and asymptomatic patients
+
9
reduced opportunistic infections, and prolonged survival. However, with CD4 lymphocyte counts less than 0.35 × 10 /L or when plasma
6
significant immune defects do persist and complete immunologic HIV viral load reaches 55 × 10 copies/L or greater. However, earlier
reconstitution with normal immune regulation does not occur. institution of HAART after acute HIV infection could result in a
There appears to be a more selective effect of HIV cytotoxicity on more balanced immune reconstitution with less loss of CD4
memory CD4 lymphocytes and Th1 lymphocyte subsets. This con- memory cells.
tributes to a profound imbalance in host immune responses Three general stages of HIV infection have been characterized that
with resulting B lymphocyte dysregulation leading to polyclonal include an acute retroviral syndrome, an asymptomatic stage, and a