Page 255 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 255
Chapter 19 Overview and Compartmentalization of the Immune System 207
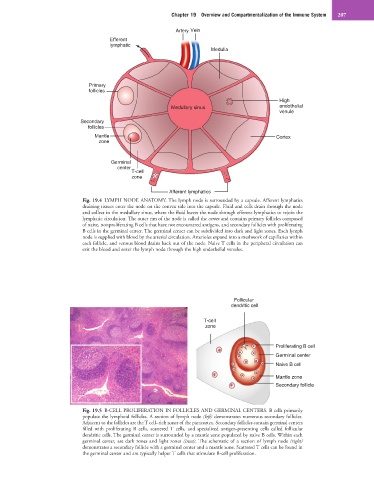
Artery Vein
Efferent
lymphatic
Medulla
Primary
follicles
High
Medullary sinus endothelial
venule
Secondary
follicles
Mantle Cortex
zone
Germinal
center
T-cell
zone
Afferent lymphatics
Fig. 19.4 LYMPH NODE ANATOMY. The lymph node is surrounded by a capsule. Afferent lymphatics
draining tissues enter the node on the convex side into the capsule. Fluid and cells drain through the node
and collect in the medullary sinus, where the fluid leaves the node through efferent lymphatics to rejoin the
lymphatic circulation. The outer rim of the node is called the cortex and contains primary follicles composed
of naive, nonproliferating B cells that have not encountered antigens, and secondary follicles with proliferating
B cells in the germinal center. The germinal center can be subdivided into dark and light zones. Each lymph
node is supplied with blood by the arterial circulation. Arterioles expand into a meshwork of capillaries within
each follicle, and venous blood drains back out of the node. Naive T cells in the peripheral circulation can
exit the blood and enter the lymph node through the high endothelial venules.
Follicular
dendritic cell
T-cell
zone
Proliferating B cell
Germinal center
Naive B cell
Mantle zone
Secondary follicle
Fig. 19.5 B-CELL PROLIFERATION IN FOLLICLES AND GERMINAL CENTERS. B cells primarily
populate the lymphoid follicles. A section of lymph node (left) demonstrates numerous secondary follicles.
Adjacent to the follicles are the T cell–rich zones of the paracortex. Secondary follicles contain germinal centers
filled with proliferating B cells, scattered T cells, and specialized antigen-presenting cells called follicular
dendritic cells. The germinal center is surrounded by a mantle zone populated by naive B cells. Within each
germinal center, are dark zones and light zones (inset). The schematic of a section of lymph node (right)
demonstrates a secondary follicle with a germinal center and a mantle zone. Scattered T cells can be found in
the germinal center and are typically helper T cells that stimulate B-cell proliferation.