Page 2603 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2603
2316 Part XIII Consultative Hematology
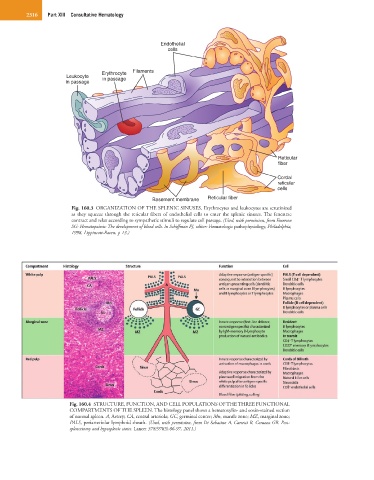
Endothelial
cells
Erythrocyte Filaments
Leukocyte in passage
in passage
Reticular
fiber
Cordal
reticular
cells
Basement membrane Reticular fiber
Fig. 160.3 ORGANIZATION OF THE SPLENIC SINUSES. Erythrocytes and leukocytes are scrutinized
as they squeeze through the reticular fibers of endothelial cells to enter the splenic sinuses. The fenestrae
contract and relax according to sympathetic stimuli to regulate cell passage. (Used, with permission, from Emerson
SG: Hematopoiesis: The development of blood cells. In Schiffman FJ, editor: Hematologic pathophysiology, Philadelphia,
1998, Lippincott-Raven, p 13.)
Fig. 160.4 STRUCTURE, FUNCTION, AND CELL POPULATIONS OF THE THREE FUNCTIONAL
COMPARTMENTS OF THE SPLEEN. The histology panel shows a hematoxylin- and eosin-stained section
of normal spleen. A, Artery; CA, central arteriola; GC, germinal center; Mn, mantle zone; MZ, marginal zone;
PALS, periarteriolar lymphoid sheath. (Used, with permission, from Di Sabatino A, Carsetti R, Corazza GR. Post-
splenectomy and hyposplenic states. Lancet 378(9785):86-97, 2011.)