Page 2605 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2605
2318 Part XIII Consultative Hematology
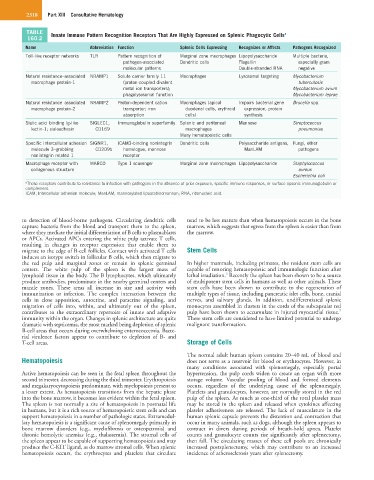
TABLE Innate Immune Pattern Recognition Receptors That Are Highly Expressed on Splenic Phagocytic Cells a
160.2
Name Abbreviation Function Splenic Cells Expressing Recognizes or Affects Pathogens Recognized
Toll-like receptor networks TLR Pattern recognition of Marginal zone macrophages Lipopolysaccharide Multiple bacteria,
pathogen-associated Dendritic cells Flagellin especially gram
molecular patterns Double-stranded RNA negative
Natural resistance–associated NRAMP1 Solute carrier family 11 Macrophages Lysosomal targeting Mycobacterium
macrophage protein-1 (proton-coupled divalent tuberculosis
metal ion transporters); Mycobacterium avium
phagolysosomal function Mycobacterium leprae
Natural resistance–associated NRAMP2 Proton-dependent cation Macrophages (apical Impairs bacterial gene Brucella spp.
macrophage protein-2 transporter; iron duodenal cells, erythroid expression, protein
absorption cells) synthesis
Sialic acid–binding Ig-like SIGLEC1, Immunoglobulin superfamily Splenic and peritoneal Mannose Streptococcus
lectin-1; sialoadhesin CD169 macrophages pneumoniae
Many hematopoietic cells
Specific intercellular adhesion SIGNR1, ICAM3-binding nonintegrin Dendritic cells Polysaccharide antigens, Fungi, other
molecule 3–grabbing CD209b homologue, mannose ManLAM pathogens
nonintegrin related 1 receptor
Macrophage receptor with MARCO Type 1 scavenger Marginal zone macrophages Lipopolysaccharide Staphylococcus
collagenous structure aureus
Escherichia coli
a These receptors contribute to resistance to infection with pathogens in the absence of prior exposure, specific immune responses, or surface opsonic immunoglobulin or
complement.
ICAM, Intercellular adhesion molecule; ManLAM, mannosylated lipoarabinomannan; RNA, ribonucleic acid.
to detection of blood-borne pathogens. Circulating dendritic cells tend to be less mature than when hematopoiesis occurs in the bone
capture bacteria from the blood and transport them to the spleen, marrow, which suggests that egress from the spleen is easier than from
where they mediate the initial differentiation of B cells to plasmablasts the marrow.
or APCs. Activated APCs entering the white pulp activate T cells,
resulting in changes in receptor expression that enable them to
migrate to the edge of B-cell follicles. Contact with activated T cells Stem Cells
induces an isotype switch in follicular B cells, which then migrate to
the red pulp and marginal zones or remain in splenic germinal In higher mammals, including primates, the resident stem cells are
centers. The white pulp of the spleen is the largest mass of capable of restoring hematopoietic and immunologic function after
6
lymphoid tissue in the body. The B lymphocytes, which ultimately lethal irradiation. Recently the spleen has been shown to be a source
produce antibodies, predominate in the nearby germinal centers and of multipotent stem cells in humans as well as other animals. These
mantle zones. These areas all increase in size and activity with stem cells have been shown to contribute to the regeneration of
immunization or infection. The complex interaction between the multiple types of tissue, including pancreatic islet cells, bone, cranial
cells in close apposition, autocrine, and paracrine signaling, and nerves, and salivary glands. In addition, undifferentiated splenic
migration of cells into, within, and ultimately out of the spleen, monocytes assembled in clusters in the cords of the subcapsular red
7
contributes to the extraordinary repertoire of innate and adaptive pulp have been shown to accumulate in injured myocardial tissue.
immunity within the organ. Changes in splenic architecture are quite These stem cells are considered to have limited potential to undergo
dramatic with septicemia, the most marked being depletion of splenic malignant transformation.
B-cell areas that occurs during overwhelming enterococcemia. Bacte-
rial virulence factors appear to contribute to depletion of B- and
T-cell areas. Storage of Cells
The normal adult human spleen contains 20–40 mL of blood and
Hematopoiesis does not serve as a reservoir for blood or erythrocytes. However, in
many conditions associated with splenomegaly, especially portal
Active hematopoiesis can be seen in the fetal spleen throughout the hypertension, the pulp cords widen to create an organ with more
second trimester, decreasing during the third trimester. Erythropoiesis storage volume. Vascular pooling of blood and formed elements
and megakaryocytopoiesis predominate, with myelopoiesis present to occurs, regardless of the underlying cause of the splenomegaly.
a lesser extent. As hematopoiesis transitions from the hepatic phase Platelets and granulocytes, however, are normally stored in the red
into the bone marrow, it becomes less evident within the fetal spleen. pulp of the spleen. As much as one-third of the total platelet mass
The spleen is not normally a site of hematopoiesis in postnatal life may be stored in the spleen and released when cytokines affecting
in humans, but it is a rich source of hematopoietic stem cells and can platelet adhesiveness are released. The lack of musculature in the
support hematopoiesis in a number of pathologic states. Extramedul- human splenic capsule prevents the distention and contraction that
lary hematopoiesis is a significant cause of splenomegaly primarily in occur in many animals, such as dogs, although the spleen appears to
bone marrow disorders (e.g., myelofibrosis or osteopetrosis) and contract in divers during periods of breath-hold apnea. Platelet
chronic hemolytic anemias (e.g., thalassemia). The stromal cells of counts and granulocyte counts rise significantly after splenectomy,
the spleen appear to be capable of supporting hematopoiesis and may then fall. The circulating masses of these cell pools are chronically
produce the C-KIT ligand, as do marrow stromal cells. When splenic increased postsplenectomy, which may contribute to an increased
hematopoiesis occurs, the erythrocytes and platelets that circulate incidence of atherosclerosis years after splenectomy.