Page 305 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 305
Chapter 23 Dendritic Cell Biology 253
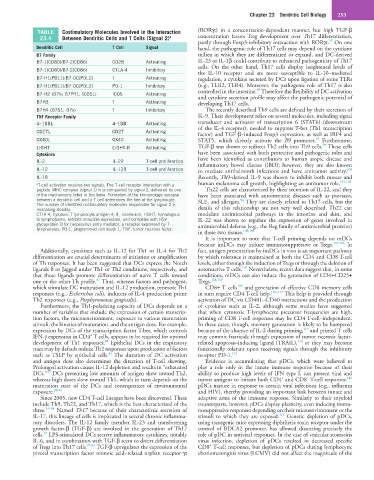
TABLE Costimulatory Molecules Involved in the Interaction (RORγt) in a concentration-dependent manner, but high TGF-β
23.4 Between Dendritic Cells and T Cells (Signal 2) a concentration favors Treg development over Th17 differentiation,
97
partly through Foxp3-inhibitory interaction with RORγt. On one
Dendritic Cell T Cell Signal hand, the pathogenic role of Th17 cells may depend on the cytokine
B7 Family milieu in which they are differentiated or expand, and DC-derived
B7-1(CD80)/B7-2(CD86) CD28 Activating IL-23 or IL-1β could contribute to enhanced pathogenicity of Th17
cells. On the other hand, Th17 cells display heightened levels of
B7-1(CD80)/B7-2(CD86) CTLA-4 Inhibitory
the IL-10 receptor and are more susceptible to IL-10–mediated
B7-H1(PDL1)/B7-DC(PDL2) ? Activating regulation, a cytokine secreted by DCs upon ligation of some TLRs
B7-H1(PDL1)/B7-DC(PDL2) PD-1 Inhibitory (e.g., TLR2, TLR4). Moreover, the pathogenic role of Th17 is also
98
controlled in the intestine. Therefore the flexibility of DC activation
B7-H2 (B7h; B7PR1; ICOSL) ICOS Activating
and cytokine secretion profile may affect the pathogenic potential of
B7H3 ? Activating developing Th17 cells.
B7H4 (B7S1; B7x) ? Inhibitory The recently described Th9 cells are defined by their secretion of
TNF Receptor Family IL-9. Their development relies on several molecules, including signal
4–1BBL 4–1BB Activating transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) (downstream
of the IL-4 receptor), needed to suppress T-bet (Th1 transcription
CD27L CD27 Activating
factor) and TGF-β–induced Foxp3 expression, as well as IRF4 and
92
OX40L OX40 Activating STAT5, which directly activate the Il9 promoter. Furthermore,
99
LIGHT LIGHT-R Activating TGF-β was shown to redirect Th2 cells into Th9 cells. These cells
Cytokines have been associated with both protective and pathogenic roles and
IL-2 IL-2R T-cell proliferation have been identified as contributors to human atopic disease and
inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); however, they are also known
IL-12 IL-12R T-cell proliferation to mediate antihelminth infections and have antitumor activity.
100
IL-18 Recently, Th9-derived IL-9 was shown to inhibit both mouse and
a T-cell activation requires two signals. The T-cell receptor interaction with a human melanoma cell growth, highlighting an antitumor role. 101,102
peptide–MHC complex (signal 1) is accompanied by signal 2, delivered by one Th22 cells are characterized by their secretion of IL-22, and they
of the mechanisms listed in this table. Formation of the immunologic synapse have been associated with autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis,
between a dendritic cell and a T cell determines the fate of the lymphocyte. SLE, and allergies. They are closely related to Th17 cells, but the
94
The number of identified costimulatory molecules responsible for signal 2 is
increasing steadily. details of this relationship are not very well described. Th22 can
CTLA-4, Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4; IL, interleukin; LIGHT, homologous modulate antimicrobial pathways in the intestine and skin, and
to lymphotoxins, exhibits inducible expression, and competes with HSV IL-22 was shown to regulate the expression of genes involved in
glycoprotein D for herpesvirus entry mediator, a receptor expressed by T antimicrobial defense (e.g., the Reg family of antimicrobial proteins)
lymphocytes; PD-1, programmed cell death 1; TNF, tumor necrosis factor. 103,104
in these two tissues.
It is important to note that T-cell priming depends on mDCs
because imDCs may induce immunosuppressive or Tregs. 105,106 In
Additionally, cytokines such as IL-12 for Th1 or IL-4 for Th2 fact, antigen presentation by imDCs in vivo is an important pathway
differentiation are crucial determinants of initiation or amplification by which tolerance is maintained at both the CD4 and CD8 T-cell
of Th responses. It has been suggested that DCs express the Notch levels, either through the induction of Tregs or through the deletion of
107
ligands δ or Jagged under Th1 or Th2 conditions, respectively, and autoreactive T cells. Nevertheless, recent data suggest that, in some
that these ligands promote differentiation of naive T cells toward conditions, mDCs can also induce the generation of CD4+CD25+
87
one or the other Th profile. Thus, whereas factors and pathogens, Tregs. 108,109
105
which stimulate DC maturation and IL-12 production, promote Th1 CD8+ T cells and generation of effective CD8 memory cells
responses (e.g., Escherichia coli), inducers of IL-4 production prime in turn require CD4 T-cell help. 110–112 This help is provided through
Th2 responses (e.g., Porphyromonas gingivalis). activation of DC via CD40L–CD40 interactions and the production
Furthermore, the Th1-polarizing capacity of DCs depends on a of cytokines such as IL-2, although some studies have suggested
number of variables that include the expression of certain transcrip- that when cytotoxic T-lymphocyte precursor frequencies are high,
tion factors, the microenvironment, exposure to various maturation priming of CD8 T-cell responses may be CD4 T-cell–independent.
stimuli, the kinetics of maturation, and the antigen dose. For example, In these cases, though, memory generation is likely to be hampered
113
expression by DCs of the transcription factor T-bet, which controls because of the absence of IL-2 during priming, and primed T cells
+
IFN-γ expression in CD4 T cells, appears to be required for optimal may commit fratricide through expression of tumor necrosis factor-
88
114
development of Th1 responses. Epithelial DCs in the respiratory related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), or they may become
tract may by default induce Th2 responses upon production of factors functionally tolerant upon receiving signals through the inhibitory
41
such as TSLP by epithelial cells. The duration of DC activation receptor PD-1. 115
and antigen dose also determines the direction of T-cell skewing. Evidence is accumulating that pDCs, which were believed to
Prolonged activation causes IL-12 depletion and results in “exhausted play a role only in the innate immune response because of their
37
DCs.” DCs presenting low amounts of antigen skew toward Th2, ability to produce high levels of IFN type I, can present viral and
+
+
116
whereas high doses skew toward Th1, which in turn depends on the tumor antigens to initiate both CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses.
maturation state of the DCs and consequences of environmental pDCs mature in response to certain viral infections (e.g., influenza
exposure. 89,90 and HIV), thereby providing an important link between innate and
Since 2005, new CD4 T-cell lineages have been discovered. These adaptive arms of the immune response. Similarly to their myeloid
include Th9, Th22, and Th17, which is the best characterized of the counterparts, however, pDCs display plasticity, even inducing immu-
three. 91–94 Named Th17 because of their characteristic secretion of nosuppressive responses depending on their microenvironment or the
117
IL-17, this lineage of cells is implicated in several chronic inflamma- stimuli to which they are exposed. Genetic depletion of pDCs,
tory disorders. The IL-12 family member IL-23 and transforming using transgenic mice expressing diphtheria toxin receptor under the
growth factor-β (TGF-β) are involved in the generation of Th17 control of BDCA2 promoter, has allowed dissecting precisely the
91
cells. LPS-stimulated DCs secrete inflammatory cytokines, notably role of pDC in antiviral responses. In the case of vesicular stomatitis
IL-6, and in combination with TGF-β seem to divert differentiation virus infection, depletion of pDCs resulted in decreased specific
+
of Tregs into Th17 cells. 95,96 TGF-β upregulates the expression of the CD8 T-cell responses, but depletion of pDCs during lymphocytic
pivotal transcription factor retinoic acid–related orphan receptor-γt choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) did not affect the magnitude of the