Page 320 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 320
262 Part III Immunologic Basis of Hematology
Classical pathway
Ig Clq, r, s C4 C2 C3
Ag Convertase
C4a C2b (classical or C3a
Classical C3 alternative)
convertase
Lectin pathway
C5
MBL MASP C4 C2
*
C5
convertase C5a
C4a C2b
Classical C3 C6 Lytic pathway
convertase C7
Alternative pathway C8
C3 Factor B Factor D
C9
Out
* C3a Ba
Alternative In
C3 convertase
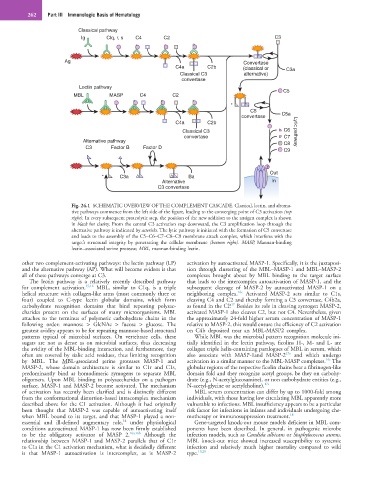
Fig. 24.1 SCHEMATIC OVERVIEW OF THE COMPLEMENT CASCADE. Classical, lectin, and alterna-
tive pathways commence from the left side of the figure, leading to the converging point of C3 activation (top
right). In every subsequent proteolytic step, the position of the new addition to the antigen complex is shown
in black for clarity. From the central C3 activation step downward, the C3 amplification loop through the
alternative pathway is indicated by asterisks. The lytic pathway is initiated with the formation of C5 convertase
and leads to the assembly of the C5–C6–C7–C8–C9 membrane attack complex, which interferes with the
target’s structural integrity by penetrating the cellular membrane (bottom right). MASP, Mannan-binding
lectin–associated serine protease; MBL, mannan-binding lectin.
other two complement-activating pathways: the lectin pathway (LP) activation by autoactivated MASP-1. Specifically, it is the juxtaposi-
and the alternative pathway (AP). What will become evident is that tion through clustering of the MBL–MASP-1 and MBL–MASP-2
all of these pathways converge at C3. complexes brought about by MBL binding to the target surface
The lectin pathway is a relatively recently described pathway that leads to the intercomplex autoactivation of MASP-1, and the
for complement activation. 15,16 MBL, similar to C1q, is a triple subsequent cleavage of MASP-2 by autoactivated MASP-1 on a
16c
helical structure with collagen-like arms (most commonly three or neighboring complex. Activated MASP-2 acts similar to C1s,
four) coupled to C-type lectin globular domains, which form cleaving C4 and C2 and thereby forming a C3 convertase, C4b2a,
17
carbohydrate recognition domains that bind repeating polysac- as found in the CP. Besides its role in cleaving zymogen MASP-2,
charides present on the surfaces of many microorganisms. MBL activated MASP-1 also cleaves C2, but not C4. Nevertheless, given
attaches to the terminus of polymeric carbohydrate chains in the the approximately 24-fold higher serum concentration of MASP-1
following order: mannose > GlcNAc > fucose > glucose. The relative to MASP-2, this would ensure the efficiency of C2 activation
greatest avidity appears to be for repeating mannose-based structural on C4b deposited near an MBL-MASP2 complex.
patterns typical of microbial surfaces. On vertebrate cells, these While MBL was the microbial pattern recognition molecule ini-
sugars are not as dense as on microbial surfaces, thus decreasing tially identified in the lectin pathway, ficolins H-, M- and L- are
the avidity of the MBL-binding interaction, and furthermore, they collagen triple helix-containing paralogues of MBL in serum, which
17a
often are covered by sialic acid residues, thus limiting recognition also associate with MASP-1and MASP-2 and which undergo
16c
by MBL. The MBL-associated serine proteases MASP-1 and activation in a similar manner to the MBL-MASP complexes. The
MASP-2, whose domain architecture is similar to C1r and C1s, globular regions of the respective ficolin chains bear a fibrinogen-like
predominantly bind as homodimeric zymogens to separate MBL domain fold and they recognize acetyl groups, be they on carbohy-
oligomers. Upon MBL binding to polysaccharides on a pathogen drate (e.g., N-acetylglucosamine), or non carbohydrate entities (e.g.,
surface, MASP-1 and MASP-2 become activated. The mechanism N-acetyl-glycine or acetylcholine). 17a
of activation has recently been clarified and is distinctly different MBL serum concentration can differ by up to 1000-fold among
from the conformational distortion-based intracomplex mechanism individuals, with those having low circulating MBL apparently more
described above for the C1 activation. Although it had originally vulnerable to infections. MBL insufficiency appears to be a particular
been thought that MASP-2 was capable of autoactivating itself risk factor for infections in infants and individuals undergoing che-
when MBL bound to its target, and that MASP-1 played a non- motherapy or immunosuppression treatment. 18
14
essential and ill-defined augmentary role, under physiological Gene-targeted knock-out mouse models deficient in MBL com-
conditions autoactivated MASP-1 has now been firmly established ponents have been described. In general, in pathogenic microbe
to be the obligatory activator of MASP 2. 16a,16b Although the infection models, such as Candida albicans or Staphylococcus aureus,
relationship between MASP-1 and MASP-2 parallels that of C1r MBL knock-out mice showed increased susceptibility to systemic
to C1s in the C1 activation mechanism, what is decidedly different infection and relatively much higher mortality compared to wild
is that MASP-1 autoactivation is intercomplex, as is MASP-2 type. 19,20