Page 333 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 333
Chapter 24 Complement and Immunoglobulin Biology Leading to Clinical Translation 275
IgG3
V H
IgG1 IgG2 V L IgG4
V H V H C L Cγ 1 V H
3
V L V L V L
C L C L C L
Cγ 1 Cγ 1 Cγ 1
1
2
2
2 2 2 2
Cγ 1 Cγ 2 Cγ 3 Cγ 4
A Cγ 1 3 Cγ 2 3 Cγ 3 3 Cγ 4 3
V H Cµ1
V L
Cα1
C L V H V L
Cµ3 Cµ2 C
Cµ4 L
Cα2
Cα3
J chain
J chain
Secretory
component
B C
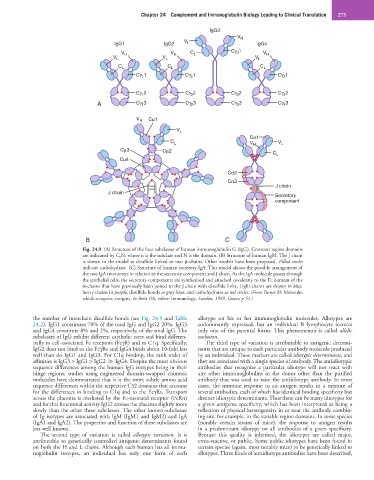
Fig. 24.9 (A) Structure of the four subclasses of human immunoglobulin G (IgG). Constant region domains
are indicated by C nN, where n is the subclass and N is the domain. (B) Structure of human IgM. The J chain
is shown in the model as disulfide linked to two µ-chains. Other models have been proposed. Filled circles
indicate carbohydrate. (C) Structure of human secretory IgA. This model shows the possible arrangement of
the two IgA monomers in relation to the secretory component and J chain. As the IgA molecule passes through
the epithelial cells, the secretory components are synthesized and attached covalently to the Fc domain of the
α-chains that have previously been joined to the J chain with disulfide links. Light chains are shown in blue,
heavy chains in purple, disulfide bonds as gray lines, and carbohydrates as red circles. (From Turner M: Molecules
which recognize antigens. In Roitt DK, editor: Immunology, London, 1989, Gower, p 51.)
the number of interchain disulfide bonds (see Fig. 24.9 and Table allotype on his or her immunoglobulin molecules. Allotypes are
24.2). IgG1 constitutes 70% of the total IgG and IgG2 20%. IgG3 codominantly expressed, but an individual B lymphocyte secretes
and IgG4 constitute 8% and 2%, respectively, of the total IgG. The only one of the parental forms. This phenomenon is called allelic
subclasses of IgG exhibit different catabolic rates and bind differen- exclusion.
tially to cell-associated Fc receptors (FcγR) and to C1q. Specifically, The third type of variation is attributable to antigenic determi-
IgG2 does not bind to the FcγRs and IgG4 binds about 10-fold less nants that are unique to each particular antibody molecule produced
well than do IgG1 and IgG3. For C1q binding, the rank order of by an individual. These markers are called idiotypic determinants, and
affinities is IgG3 > IgG1 > IgG2 ≫ IgG4. Despite the most obvious they are associated with a single species of antibody. The antiidiotypic
sequence differences among the human IgG isotypes being in their antibodies that recognize a particular idiotype will not react with
hinge regions, studies using engineered domain-swapped chimeric any other immunoglobulins in the donor other than the purified
molecules have demonstrated that it is the more subtle amino acid antibody that was used to raise the antiidiotype antibody. In most
sequence differences within the respective Cγ2 domains that account cases, the immune response to an antigen results in a mixture of
for the differences in binding to C1q and to the FcγRs. Transport several antibodies, each of which has identical binding specificity but
across the placenta is mediated by the Fc-neonatal receptor (FcRn) distinct idiotypic determinants. Thus there can be many idiotypes for
and for this functional activity IgG2 crosses the placenta slightly more a given antigenic specificity, which has been interpreted as being a
slowly than the other three subclasses. The other known subclasses reflection of physical heterogeneity in or near the antibody combin-
of Ig isotypes are associated with IgM (IgM1 and IgM2) and IgA ing site, for example, in the variable region domains. In some species
(IgA1 and IgA2). The properties and function of these subclasses are (notably certain strains of mice), the response to antigen results
less well known. in a predominant idiotype on all antibodies of a given specificity.
The second type of variation is called allotypic variation. It is Because this quality is inherited, the idiotypes are called major,
attributable to genetically controlled antigenic determinants found cross-reactive, or public. Some public idiotypes have been found in
on both the H and L chains. Although each human has all immu- certain species (again, most notably mice) to be genetically linked to
noglobulin isotypes, an individual has only one form of each allotypes. Three kinds of antiidiotype antibodies have been described,