Page 332 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 332
274 Part III Immunologic Basis of Hematology
correspondence in amino acids, position for position, to the carboxy- the total Ig in blood. It is present in normal adults at concentrations
terminus. The H chains exhibit a similar pattern and can be divided of 600 to 1500 mg/dL. IgG is designated γ2κ2 or γ2λ2. It is the only
likewise into V H and C H1, C H2, and C H3. Comparison of the amino class of Ig that crosses the placenta (Table 24.2). 142
acid sequence of many V L s has revealed that whereas certain parts of The isotype IgM is predominantly a pentamer consisting of five
the variable region exhibit excess variability, others are less variable. monomeric units disulfide linked at the C-terminus of the H chain.
The former regions are called hypervariable or complementarity- Each monomer of IgM is 180 kDa because of the presence of an
determining regions (CDRs). The latter framework regions function additional C H domain, specifically the Cµ2 domain, which replaces
as a structural scaffold to support the CDRs. Antigen binding is the hinge segment. The complete protein has a sedimentation coef-
mediated by six CDRs, three in each of the V H and V L domains. The ficient of 19 S, which corresponds to a molecular mass of 850 kDa.
combining site for antigen is a trough, cavity, or even flat surface IgM is designated (µ2κ2) 5 or (µ2λ2) 5. IgM also contains a 15-kDa
composed of parts of the hypervariable regions of both the H and L protein called the J chain. In the current structural model of IgM,
chains. It is a small region, representing only 25% of the antibody V the J chain forms a disulfide-bonded clasp at the C-terminus of two
region. The region that interacts directly with the epitope on the H chains (Fig. 24.9). 139
antigen is even smaller and is formed by the association of the CDR The structure of the other isotypes of immunoglobulins are sum-
regions, each of which consists of approximately 20 amino acids. marized as follows. The isotype IgA has a variable number of
Thus the variation in a few amino acids accounts for the specificity monomeric units and is designated (α2κ2) n or (α2λ2) n , where n =
and diversity of antibodies with respect to antigen binding. 141 1–5. Serum IgA constitutes 20% of the total serum immunoglobulin,
Immunoglobulins exhibit additional physical heterogeneity, and 80% of this is monomeric. The remainder exists as polymers,
which imparts to each immunoglobulin a special effector function where n = 2–5. The other form of IgA is found in external secretions
that is reflected in unique biologic properties independent of antigen- such as saliva, tracheobronchial secretions, colostrum, milk, and
binding activity. In the pregenome era of immunochemical research, genitourinary secretions. Secretory IgA consists of four components:
heterologous and autologous antisera raised against immunoglobulins a dimer of two monomeric molecules, a 70-kDa secretory component
were used to classify three types of physical heterogeneity. The first that binds noncovalently to the IgA dimer, and the 15-kDa J chain
kind is based on the antigenic heterogeneity exhibited by immuno- that is believed to form a disulfide-bonded clasp at the C-terminus
globulin when it is used as an immunogen in other species. This is of the H chains (see Fig. 24.9). The isotype IgD has a molecular mass
called class or isotypic variation. In humans, five isotypes can be dis- of 180 kDa. Its serum concentration is very low, approximately
tinguished based on unique antigenic (isotypic) determinants found 3 mg/dL. IgD apparently functions as a membrane molecule, being
on the H chain. These are designated by capital Roman letters as IgG, associated on mature but unstimulated B cells in association with
IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE. The H chain of each class is designated by IgM. IgE is the homocytotropic or reaginic Ig and mediates immedi-
the lower-case Greek letter corresponding to the Roman letter of the ate hypersensitivity. It has a molecular mass of 180 kDa and, similar
class. Thus the H chain for IgG is γ, for IgM is µ, for IgA is α, for to IgM, has four C domains. The Fc portion of IgE binds strongly
IgD is δ, and for IgE is ε. Some of the immunoglobulin classes are to a receptor on mast cells, FcεR, and this is how this immunoglobu-
composed of polymers of the basic monomer. In humans, the two lin exerts its particular activity. The overall properties of the immu-
antigenic varieties of the L chain are kappa (κ) and lambda (λ). Each noglobulins are summarized in Table 24.2.
Ig has two identical L chains; the κ and λ are shared by all classes. The Subclasses of isotypes IgG, IgA, and IgM have been identified.
monomeric form of any immunoglobulin is described by its chain The structural basis for this antigenic heterogeneity is variation in
structure. The molecular mass of the immunoglobulins can vary from amino acid sequence in the Fc portion of the H chain of a given class.
150 to 1000 kDa. This variation is attributable to polymerization of The subclasses of human IgG, called IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4,
the basic monomer form. None of the immunoglobulins are polymeric are the best characterized. Each has a slightly different structure, with
forms of another class. IgG is the most prevalent, constituting 75% of the most notable differences being in the length of the hinge and in
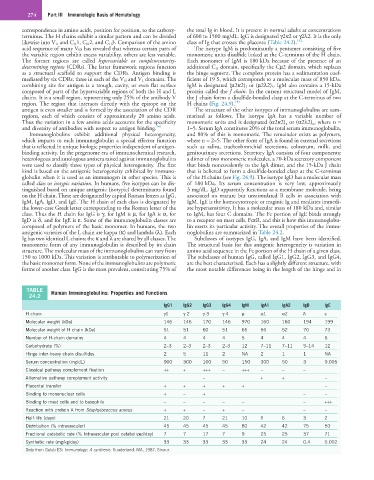
TABLE Human Immunoglobulins: Properties and Functions
24.2
IgG1 IgG2 IgG3 IgG4 IgM IgA1 IgA2 IgD IgE
H chain γ1 γ 2 γ 3 γ 4 µ α1 α2 δ ε
Molecular weight (kDa) 146 146 170 146 970 160 160 194 199
Molecular weight of H chain (kDa) 51 51 60 51 65 56 52 70 73
Number of H-chain domains 4 4 4 4 5 4 4 4 5
Carbohydrate (%) 2–3 2–3 2–3 2–3 12 7–11 7–11 9–14 12
Hinge inter-heavy chain disulfides 2 5 11 2 NA 2 1 1 NA
Serum concentration (mg/dL) 900 300 100 50 150 300 50 3 0.005
Classical pathway complement fixation ++ + +++ − +++ − − −
Alternative pathway complement activity − + + −
Placental transfer + + + + + −
Binding to mononuclear cells + − + − −
Binding to mast cells and to basophils − − − − − − +++
Reaction with protein A from Staphylococcus aureus + + − + − − −
Half-life (days) 21 20 7 21 10 6 6 3 2
Distribution (% intravascular) 45 45 45 45 80 42 42 75 50
Fractional catabolic rate (% Intravascular pool catabolized/day) 7 7 17 7 9 25 25 37 71
Synthetic rate (mg/kg/day) 33 33 33 33 33 24 24 0.4 0.002
Data from Golub ES: Immunology: A synthesis. Sunderland, MA, 1987, Sinaur.