Page 34 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 34
6 Part I Molecular and Cellular Basis of Hematology
Coding Noncoding
sequence (intervening 3 coding
5 (exon) sequence, intron) strand
DNA
3 5 noncoding
Transcription
mRNA 5 Exon Intron strand
precursor 3
5 CAP 3 Poly (A), modification
and shortening of
Processing transcript
Nucleus
Processed 5 CAP Poly (A)-3
mRNA
transcript 5 CAP Poly (A)-3
mRNA
Transport to
cytoplasm
Nuclear “pore”
Cytoplasm
Initiation factors
tRNA, ribosomes
Translation
5 CAP Poly (A)-3
Completed
Protein apoprotein
Cofactors
other subunits
Microsomes
Golgi, etc.
Completed functioning protein
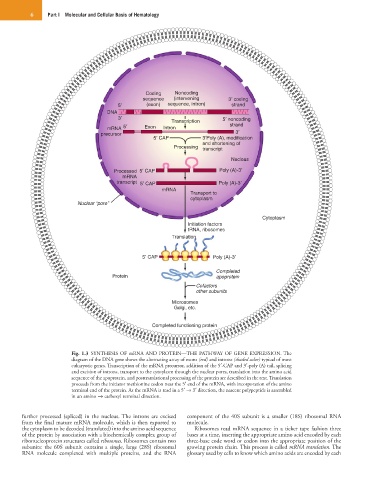
Fig. 1.3 SYNTHESIS OF mRNA AND PROTEIN—THE PATHWAY OF GENE EXPRESSION. The
diagram of the DNA gene shows the alternating array of exons (red) and introns (shaded color) typical of most
eukaryotic genes. Transcription of the mRNA precursor, addition of the 5′-CAP and 3′-poly (A) tail, splicing
and excision of introns, transport to the cytoplasm through the nuclear pores, translation into the amino acid
sequence of the apoprotein, and posttranslational processing of the protein are described in the text. Translation
proceeds from the initiator methionine codon near the 5′ end of the mRNA, with incorporation of the amino
terminal end of the protein. As the mRNA is read in a 5′ → 3′ direction, the nascent polypeptide is assembled
in an amino → carboxyl terminal direction.
further processed (spliced) in the nucleus. The introns are excised component of the 40S subunit is a smaller (18S) ribosomal RNA
from the final mature mRNA molecule, which is then exported to molecule.
the cytoplasm to be decoded (translated) into the amino acid sequence Ribosomes read mRNA sequence in a ticker tape fashion three
of the protein by association with a biochemically complex group of bases at a time, inserting the appropriate amino acid encoded by each
ribonucleoprotein structures called ribosomes. Ribosomes contain two three-base code word or codon into the appropriate position of the
subunits: the 60S subunit contains a single, large (28S) ribosomal growing protein chain. This process is called mRNA translation. The
RNA molecule complexed with multiple proteins, and the RNA glossary used by cells to know which amino acids are encoded by each