Page 41 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 41
Chapter 1 Anatomy and Physiology of the Gene 13
to complete their life cycle. The proviral genomes often carry with other similar fragments, generating artificially recombined, or recom-
them nearby bits of the genomic DNA in which they sat. If the binant, DNA molecules. These ligated gene fragments can then be
retrovirus infects the DNA of another individual at another site, it inserted into bacteria to produce more copies of the recombinant
will insert this genomic bit. Through many cycles of infection, the molecules or to express the cloned genes. While still useful in a
virus will act as a transposon, scattering its attached sequence number of contexts, restriction enzyme analysis is increasingly being
throughout the genome. These types of sequences are called long supplanted by direct DNA sequence analysis.
interspersed elements. They represent footprints of ancient viral
infections.
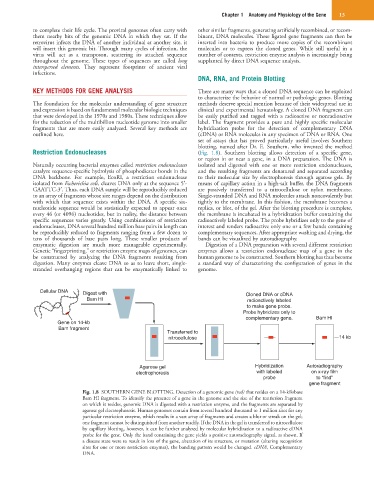
DNA, RNA, and Protein Blotting
KEY METHODS FOR GENE ANALYSIS There are many ways that a cloned DNA sequence can be exploited
to characterize the behavior of normal or pathologic genes. Blotting
The foundation for the molecular understanding of gene structure methods deserve special mention because of their widespread use in
and expression is based on fundamental molecular biologic techniques clinical and experimental hematology. A cloned DNA fragment can
that were developed in the 1970s and 1980s. These techniques allow be easily purified and tagged with a radioactive or nonradioactive
for the reduction of the multibillion nucleotide genome into smaller label. The fragment provides a pure and highly specific molecular
fragments that are more easily analyzed. Several key methods are hybridization probe for the detection of complementary DNA
outlined here. (cDNA) or RNA molecules in any specimen of DNA or RNA. One
set of assays that has proved particularly useful involves Southern
blotting, named after Dr. E. Southern, who invented the method
Restriction Endonucleases (Fig. 1.8). Southern blotting allows detection of a specific gene,
or region in or near a gene, in a DNA preparation. The DNA is
Naturally occurring bacterial enzymes called restriction endonucleases isolated and digested with one or more restriction endonucleases,
catalyze sequence-specific hydrolysis of phosphodiester bonds in the and the resulting fragments are denatured and separated according
DNA backbone. For example, EcoRI, a restriction endonuclease to their molecular size by electrophoresis through agarose gels. By
isolated from Escherichia coli, cleaves DNA only at the sequence 5′- means of capillary action in a high-salt buffer, the DNA fragments
GAATTC-3′. Thus, each DNA sample will be reproducibly reduced are passively transferred to a nitrocellulose or nylon membrane.
to an array of fragments whose size ranges depend on the distribution Single-stranded DNA and RNA molecules attach noncovalently but
with which that sequence exists within the DNA. A specific six- tightly to the membrane. In this fashion, the membrane becomes a
nucleotide sequence would be statistically expected to appear once replica, or blot, of the gel. After the blotting procedure is complete,
every 46 (or 4096) nucleotides, but in reality, the distance between the membrane is incubated in a hybridization buffer containing the
specific sequences varies greatly. Using combinations of restriction radioactively labeled probe. The probe hybridizes only to the gene of
endonucleases, DNA several hundred million base pairs in length can interest and renders radioactive only one or a few bands containing
be reproducibly reduced to fragments ranging from a few dozen to complementary sequences. After appropriate washing and drying, the
tens of thousands of base pairs long. These smaller products of bands can be visualized by autoradiography.
enzymatic digestion are much more manageable experimentally. Digestion of a DNA preparation with several different restriction
Genetic “fingerprinting,” or restriction enzyme maps of genomes, can enzymes allows a restriction endonuclease map of a gene in the
be constructed by analyzing the DNA fragments resulting from human genome to be constructed. Southern blotting has thus become
digestion. Many enzymes cleave DNA so as to leave short, single- a standard way of characterizing the configuration of genes in the
stranded overhanging regions that can be enzymatically linked to genome.
Cellular DNA Digest with Cloned DNA or cDNA
Bam HI radioactively labeled
to make gene probe.
Probe hybridizes only to
complementary gene. Bam HI
Gene on 14-kb
Bam fragment
Transferred to
nitrocellulose 14 kb
Agarose gel Hybridization Autoradiography
electrophoresis with labeled on x-ray film
probe to “find”
gene fragment
Fig. 1.8 SOUTHERN GENE BLOTTING. Detection of a genomic gene (red) that resides on a 14-kilobase
Bam HI fragment. To identify the presence of a gene in the genome and the size of the restriction fragment
on which it resides, genomic DNA is digested with a restriction enzyme, and the fragments are separated by
agarose gel electrophoresis. Human genomes contain from several hundred thousand to 1 million sites for any
particular restriction enzyme, which results in a vast array of fragments and creates a blur or streak on the gel;
one fragment cannot be distinguished from another readily. If the DNA in the gel is transferred to nitrocellulose
by capillary blotting, however, it can be further analyzed by molecular hybridization to a radioactive cDNA
probe for the gene. Only the band containing the gene yields a positive autoradiography signal, as shown. If
a disease state were to result in loss of the gene, alteration of its structure, or mutation (altering recognition
sites for one or more restriction enzymes), the banding pattern would be changed. cDNA, Complementary
DNA.