Page 694 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 694
586 Part V Red Blood Cells
100
80
60
Hb F (%)
40 Sickle cell disease
20
Normal
0
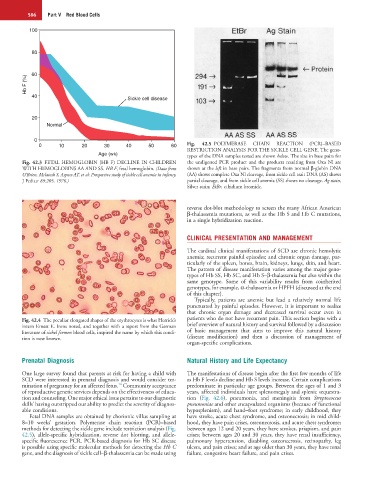
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Fig. 42.5 POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (PCR)–BASED
RESTRICTION ANALYSIS FOR THE SICKLE CELL GENE. The geno-
Age (wk) types of the DNA samples tested are shown below. The size in base pairs for
Fig. 42.3 FETAL HEMOGLOBIN (HB F) DECLINE IN CHILDREN the undigested PCR product and the products resulting from Oxa Nl are
WITH HEMOGLOBINS AA AND SS. HB F, fetal hemoglobin. (Data from shown at the left in base pairs. The fragments from normal β-globin DNA
O’Brien, Mclatosh S, Aspnes AT, et al: Prospective study of sickle cell anemia in infancy. (AA) shows complete Oxa Nl cleavage, from sickle cell trait DNA (AS) shows
J Pediatr 89:205, 1976.) partial cleavage, and from sickle cell anemia (SS) shows no cleavage. Ag stain,
Silver stain; EtBr, ethidium bromide.
reverse dot-blot methodology to screen the many African American
β-thalassemia mutations, as well as the Hb S and Hb C mutations,
in a single hybridization reaction.
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND MANAGEMENT
The cardinal clinical manifestations of SCD are chronic hemolytic
anemia; recurrent painful episodes; and chronic organ damage, par-
ticularly of the spleen, bones, brain, kidneys, lungs, skin, and heart.
The pattern of disease manifestation varies among the major geno-
types of Hb SS, Hb SC, and Hb S–β-thalassemia but also within the
same genotype. Some of this variability results from coinherited
genotypes, for example, α-thalassemia or HPFH (discussed at the end
of this chapter).
Typically, patients are anemic but lead a relatively normal life
punctuated by painful episodes. However, it is important to realize
that chronic organ damage and decreased survival occur even in
Fig. 42.4 The peculiar elongated shapes of the erythrocytes is what Herrick’s patients who do not have recurrent pain. This section begins with a
intern Ernest E. Irons noted, and together with a report from the German brief overview of natural history and survival followed by a discussion
literature of sichel formen blood cells, inspired the name by which this condi- of basic management that aims to improve this natural history
tion is now known. (disease modification) and then a discussion of management of
organ-specific complications.
Prenatal Diagnosis Natural History and Life Expectancy
One large survey found that parents at risk for having a child with The manifestations of disease begin after the first few months of life
SCD were interested in prenatal diagnosis and would consider ter- as Hb F levels decline and Hb S levels increase. Certain complications
14
mination of pregnancy for an affected fetus. Community acceptance predominate in particular age groups. Between the ages of 1 and 3
of reproductive genetic services depends on the effectiveness of educa- years, affected individuals have splenomegaly and splenic sequestra-
tion and counseling. One major ethical issue pertains to our diagnostic tion (Fig. 42.6), pneumonia, and meningitis from Streptococcus
skills’ having outstripped our ability to predict the severity of diagnos- pneumoniae and other encapsulated organisms (because of functional
able conditions. hyposplenism), and hand–foot syndrome; in early childhood, they
Fetal DNA samples are obtained by chorionic villus sampling at have stroke, acute chest syndrome, and osteonecrosis; in mid child-
8–10 weeks’ gestation. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)–based hood, they have pain crises, osteonecrosis, and acute chest syndrome;
methods for detecting the sickle gene include restriction analysis (Fig. between ages 12 and 20 years, they have strokes, priapism, and pain
42.5), allele-specific hybridization, reverse dot blotting, and allele- crises; between ages 20 and 30 years, they have renal insufficiency,
specific fluorescence PCR. PCR-based diagnosis for Hb SC disease pulmonary hypertension, disabling osteonecrosis, retinopathy, leg
is possible using specific molecular methods for detecting the Hb C ulcers, and pain crises; and at age older than 30 years, they have renal
gene, and the diagnosis of sickle cell–β-thalassemia can be made using failure, congestive heart failure, and pain crises.