Page 698 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 698
590 Part V Red Blood Cells
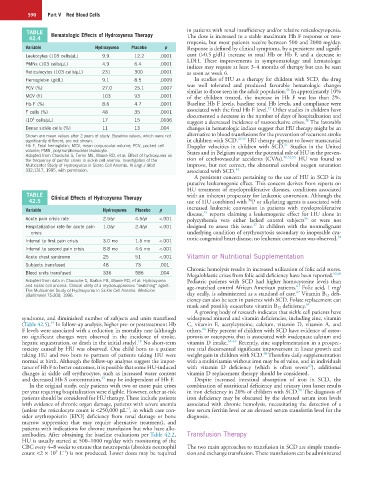
TABLE Hematologic Effects of Hydroxyurea Therapy in patients with renal insufficiency and/or relative reticulocytopenia.
42.4 The dose is increased to a stable maximum Hb F response or neu-
tropenia, but most patients receive between 500 and 2000 mg/day.
Variable Hydroxyurea Placebo p Response is defined by clinical symptoms, by a persistent and signifi-
Leukocytes (103 cells/µL) 9.9 12.2 .0001 cant (>0.5 g/dL) increase in total Hb or Hb F, and a decrease in
LDH. These improvements in symptomatology and hematologic
PMNs (103 cells/µL) 4.9 6.4 .0001
indices may require at least 3–4 months of therapy but can be seen
Reticulocytes (103 cells/µL) 231 300 .0001 as soon as week 6.
Hemoglobin (g/dL) 9.1 8.5 .0009 In studies of HU as a therapy for children with SCD, the drug
was well tolerated and produced favorable hematologic changes
PCV (%) 27.0 25.1 .0007 46
similar to those seen in the adult population. In approximately 10%
MCV (fl) 103 93 .0001 of the children treated, the increase in Hb F was less than 2%.
Hb F (%) 8.6 4.7 .0001 Baseline Hb F levels, baseline total Hb levels, and compliance were
47
F cells (%) 48 35 .0001 associated with the final Hb F level. Other studies in children have
documented a decrease in the number of days of hospitalization and
(10 cells/µL) 17 15 .0036 suggest a decreased incidence of vasoocclusive crises. The favorable
3
48
Dense sickle cells (%) 11 13 .004 changes in hematologic indices suggest that HU therapy might be an
Shown are mean values after 2 years of study. Baseline values, which were not alternative to blood transfusions for the prevention of recurrent stroke
49,50
significantly different, are not shown. in children with SCD. HU therapy appears to lower transcranial
51
Hb F, Fetal hemoglobin; MCV, mean corpuscular volume; PCV, packed cell Doppler velocities in children with SCD. Studies in the United
volume; PMN, polymorphonuclear leukocyte. States and in Belgium support the potential role of HU in the preven-
Adapted from Charache S, Terrin ML, Moore RD, et al: Effect of hydroxyurea on 50,52,53
the frequency of painful crises in sickle cell anemia. Investigators of the tion of cerebrovascular accidents (CVAs). HU was found to
Multicenter Study of Hydroxyurea in Sickle Cell Anemia. N Engl J Med improve, but not correct, the abnormal cerebral oxygen saturation
332:1317, 1995, with permission. associated with SCD. 54
A persistent concern pertaining to the use of HU in SCD is its
putative leukemogenic effect. This concern derives from reports on
HU treatment of myeloproliferative diseases, conditions associated
TABLE Clinical Effects of Hydroxyurea Therapy with an inherent propensity for leukemic conversion. Although the
42.5 use of HU combined with P or alkylating agents is associated with
36
Variable Hydroxyurea Placebo p increased leukemic conversion in patients with myeloproliferative
55
disease, reports claiming a leukemogenic effect for HU alone in
Acute pain crisis rate 2.5/yr 4.5/yr <.001 polycythemia vera either lacked control subjects or were not
56
57
Hospitalization rate for acute pain 1.0/yr 2.4/yr <.001 designed to assess this issue. In children with the nonmalignant
crisis underlying condition of erythrocytosis secondary to inoperable cya-
58
Interval to first pain crisis 3.0 mo 1.5 mo <.001 notic congenital heart disease, no leukemic conversion was observed.
Interval to second pain crisis 8.8 mo 4.6 mo <.001
Acute chest syndrome 25 51 <.001 Vitamin or Nutritional Supplementation
Subjects transfused 48 73 .001
Blood units transfused 336 586 .004 Chronic hemolysis results in increased utilization of folic acid stores.
59,60
Megaloblastic crises from folic acid deficiency have been reported.
Adapted from data in Charache S, Barton FB, Moore RD, et al: Hydroxyurea Pediatric patients with SCD had higher homocysteine levels than
and sickle cell anemia. Clinical utility of a myelosuppressive “switching” agent. age-matched control African American patients. Folic acid, 1 mg/
61
The Multicenter Study of Hydroxyurea in Sickle Cell Anemia. Medicine 62
(Baltimore) 75:300, 1996. day orally, is administered as a standard of care. Vitamin B 12 defi-
ciency can also be seen in patients with SCD. Folate replacement can
mask and possibly exacerbate vitamin B 12 deficiency. 63
A growing body of research indicates that sickle cell patients have
syndrome, and diminished number of subjects and units transfused widespread mineral and vitamin deficiencies, including zinc, vitamin
44
(Table 42.5). In follow-up analysis, higher pre- or posttreatment Hb C, vitamin E, acetylcysteine, calcium, vitamin D, vitamin A, and
64
F levels were associated with a reduction in mortality rate (although others. Fifty percent of children with SCD have evidence of osteo-
no significant changes were observed in the incidence of stroke, porosis or osteopenia that is associated with inadequate calcium and
18
hepatic sequestration, or death in the initial study). No short-term vitamin D intake. 65–67 Recently, zinc supplementation in a prospec-
toxicity caused by HU was observed. One child born to a patient tive trial documented significant improvement in linear growth and
68
taking HU and two born to partners of patients taking HU were weight gain in children with SCD. Therefore daily supplementation
normal at birth. Although the follow-up analyses suggest the impor- with a multivitamin without iron may be of value, and in individuals
69
tance of Hb F to better outcomes, it is possible that some HU-induced with vitamin D deficiency (which is often severe ), additional
changes in sickle cell erythrocytes, such as increased water content vitamin D replacement therapy should be considered.
45
and decreased Hb S concentration, may be independent of Hb F. Despite increased intestinal absorption of iron in SCD, the
In the original study, only patients with two or more pain crises combination of nutritional deficiency and urinary iron losses results
70
per year requiring hospitalization were eligible. However, other at-risk in iron deficiency in 20% of children with SCD. The diagnosis of
patients should be considered for HU therapy. These include patients iron deficiency may be obscured by the elevated serum iron levels
with evidence of chronic organ damage, patients with severe anemia associated with chronic hemolysis, necessitating the detection of a
−1
(unless the reticulocyte count is <250,000 µL , in which case con- low serum ferritin level or an elevated serum transferrin level for the
sider erythropoietin [EPO] deficiency from renal damage or bone diagnosis.
marrow suppression that may require alternative treatment), and
patients with indications for chronic transfusion but who have allo-
antibodies. After obtaining the baseline evaluations per Table 42.2, Transfusion Therapy
HU is usually started at 500–1000 mg/day with monitoring of the
CBC every 4–8 weeks to ensure that neutropenia (absolute neutrophil The two main approaches to transfusion in SCD are simple transfu-
−1
9
count <2 × 10 L ) is not produced. Lower doses may be required sion and exchange transfusion. These transfusions can be administered