Page 71 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 71
Chapter 4 Regulation of Gene Expression, Transcription, Splicing, and RNA Metabolism 43
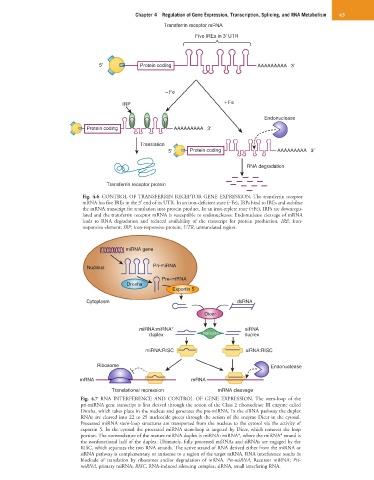
Transferrin receptor mRNA
Five IREs in 3 UTR
5 Protein coding AAAAAAAAA 3
− Fe
IRP + Fe
Endonuclease
Protein coding AAAAAAAAA 3
Translation
5 Protein coding AAAAAAAAA 3
RNA degradation
Transferrin receptor protein
Fig. 4.6 CONTROL OF TRANSFERRIN RECEPTOR GENE EXPRESSION. The transferrin receptor
mRNA has five IREs in the 3′ end of its UTR. In an iron-deficient state (−Fe), IRPs bind to IREs and stabilize
the mRNA transcript for translation into protein product. In an iron-replete state (+Fe), IRPs are downregu-
lated and the transferrin receptor mRNA is susceptible to endonucleases. Endonuclease cleavage of mRNA
leads to RNA degradation and reduced availability of the transcript for protein production. IRE, Iron-
responsive element; IRP, iron-responsive protein; UTR, untranslated region.
miRNA gene
Nucleus Pri-miRNA
Pre-miRNA
Drosha
Exportin 5
Cytoplasm dsRNA
Dicer
miRNA:miRNA* siRNA
duplex helicase duplex
miRNA:RISC siRNA:RISC
Ribosome Endonuclease
mRNA mRNA
Translational repression mRNA cleavage
Fig. 4.7 RNA INTERFERENCE AND CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION. The stem-loop of the
pri-miRNA gene transcript is first cleaved through the action of the Class 2 ribonuclease III enzyme called
Drosha, which takes place in the nucleus and generates the pre-miRNA. In the siRNA pathway the duplex
RNAs are cleaved into 22 to 25 nucleotide pieces through the action of the enzyme Dicer in the cytosol.
Processed miRNA stem-loop structures are transported from the nucleus to the cytosol via the activity of
exportin 5. In the cytosol the processed miRNA stem-loop is targeted by Dicer, which removes the loop
portion. The nomenclature of the mature miRNA duplex is miRNA : miRNA*, where the miRNA* strand is
the nonfunctional half of the duplex. Ultimately, fully processed miRNAs and siRNAs are engaged by the
RISC, which separates the two RNA strands. The active strand of RNA derived either from the miRNA or
siRNA pathway is complementary or antisense to a region of the target mRNA. RNA interference results in
blockade of translation by ribosomes and/or degradation of mRNA. Pre-miRNA, Recursor miRNA; Pri-
miRNA, primary miRNA; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex; siRNA, small interfering RNA.