Page 724 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 724
Chapter 43 Hemoglobin Variants Associated With Hemolytic Anemia, Altered Oxygen Affinity, and Methemoglobinemias 611
not particularly acute or brisk. Thus Heinz bodies may not be strong evidence in support of the diagnosis. A normal electropho-
demonstrable at all times. Two provocative laboratory maneuvers are retogram, however, should never be regarded as strong evidence
used to aid detection, both of which unmask the tendency of unstable against the presence of a mutant hemoglobin, especially if the clini-
hemoglobins to precipitate: the heat instability test (heating of a cal picture or family history otherwise supports the diagnosis. Mass
hemoglobin solution to 50°C) or the isopropanol instability test spectrometry analysis of hemoglobin and direct globin gene sequenc-
(insolubility in 17% isopropanol). ing are supplanting electrophoresis as diagnostic strategies. They
Hemoglobin electrophoresis should be performed but should not usually provide unambiguous identification of a sequence abnormal-
be relied on as the major diagnostic criterion for ruling in or ruling out ity. However, electrophoresis is still in use in many clinical settings.
a hemoglobinopathy. Many amino acid substitutions that have a Thus the aforementioned precautions in interpretation are still
profound effect on solubility do not change the overall charge on the worth noting.
hemoglobin molecule. For example, Hb Köln, the most common of Additional sophisticated analyses of hemoglobin can be obtained
the unstable hemoglobin mutations, arises from a mutation chang- from reference laboratories if detailed characterization seems war-
ing the valine at position 98 to a methionine. This mutation is ranted. For example, abnormal hemoglobin or globin bands migrat-
electrically neutral; it does not alter electrophoretic mobility. There- ing to novel positions on an isoelectric focusing gel can result from
fore these variants do not form an abnormal band on an electropho- hemoglobin or globin moieties lacking heme in groups. When heme
resis gel. Demonstration of an abnormal band would clearly add is added to the sample and the proteins are reanalyzed, these bands
disappear. This behavior is nearly diagnostic of an unstable variant.
Detection of unstable hemoglobins is occasionally compromised
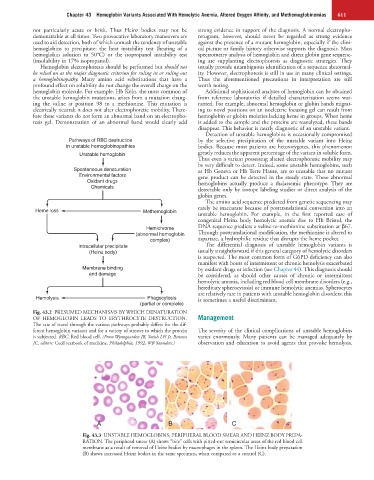
Pathways of RBC destruction by the selective precipitation of the unstable variant into Heinz
in unstable hemoglobinopathies bodies. Because most patients are heterozygotes, this phenomenon
Unstable hemoglobin greatly reduces the apparent percentage of the variant in soluble form.
Thus even a variant possessing altered electrophoretic mobility may
be very difficult to detect. Indeed, some unstable hemoglobins, such
Spontaneous denaturation as Hb Geneva or Hb Terre Haute, are so unstable that no mutant
Environmental factors gene product can be detected in the steady state. These abnormal
Oxidant drugs hemoglobins actually produce a thalassemic phenotype. They are
Chemicals detectable only by isotope labeling studies or direct analysis of the
globin genes.
The amino acid sequence predicted from genetic sequencing may
rarely be inaccurate because of posttranslational conversion into an
Heme loss Methemoglobin unstable hemoglobin. For example, in the first reported case of
congenital Heinz body hemolytic anemia due to Hb Bristol, the
Hemichrome DNA sequence predicts a valine-to-methionine substitution at β67.
(abnormal hemoglobin Through posttranslational modification, the methionine is altered to
complex) aspartate, a hydrophilic residue that disrupts the heme pocket.
Intracellular precipitate The differential diagnosis of unstable hemoglobin variants is
(Heinz body) usually straightforward if this general category of hemolytic disorders
is suspected. The most common form of G6PD deficiency can also
manifest with bouts of intermittent or chronic hemolysis exacerbated
Membrane binding by oxidant drugs or infection (see Chapter 44). This diagnosis should
and damage be considered, as should other causes of chronic or intermittent
hemolytic anemia, including red blood cell membrane disorders (e.g.,
hereditary spherocytosis) or immune hemolytic anemias. Spherocytes
are relatively rare in patients with unstable hemoglobin disorders; this
Hemolysis Phagocytosis is sometimes a useful discriminant.
(partial or complete)
Fig. 43.2 PRESUMED MECHANISMS BY WHICH DENATURATION
OF HEMOGLOBIN LEADS TO ERYTHROCYTE DESTRUCTION. Management
The rate of travel through the various pathways probably differs for the dif-
ferent hemoglobin variants and for a variety of stresses to which the protein The severity of the clinical complications of unstable hemoglobins
is subjected. RBC, Red blood cell. (From Wynngaarden JB, Smith LH Jr, Bennett varies enormously. Many patients can be managed adequately by
JC, editors: Cecil textbook of medicine, Philadelphia, 1992, WB Saunders.) observation and education to avoid agents that provoke hemolysis.
A B C
Fig. 43.3 UNSTABLE HEMOGLOBINS; PERIPHERAL BLOOD SMEAR AND HEINZ BODY PREPA-
RATION. The peripheral smear (A) shows “bite” cells with pitted-out semicircular areas of the red blood cell
membrane as a result of removal of Heinz bodies by macrophages in the spleen. The Heinz body preparation
(B) shows increased Heinz bodies in the same specimen, when compared to a control (C).