Page 741 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 741
628 Part V Red Blood Cells
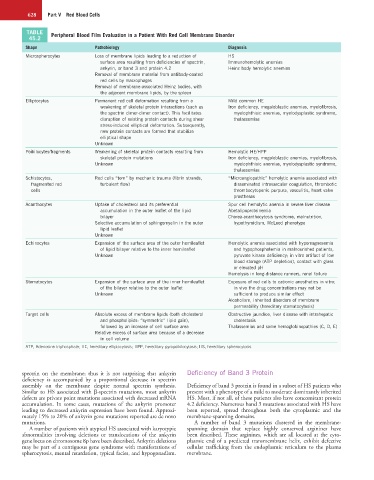
TABLE Peripheral Blood Film Evaluation in a Patient With Red Cell Membrane Disorder
45.2
Shape Pathobiology Diagnosis
Microspherocytes Loss of membrane lipids leading to a reduction of HS
surface area resulting from deficiencies of spectrin, Immunohemolytic anemias
ankyrin, or band 3 and protein 4.2 Heinz body hemolytic anemias
Removal of membrane material from antibody-coated
red cells by macrophages
Removal of membrane-associated Heinz bodies, with
the adjacent membrane lipids, by the spleen
Elliptocytes Permanent red cell deformation resulting from a Mild common HE
weakening of skeletal protein interactions (such as Iron deficiency, megaloblastic anemias, myelofibrosis,
the spectrin dimer-dimer contact). This facilitates myelophthisic anemias, myelodysplastic syndrome,
disruption of existing protein contacts during shear thalassemias
stress-induced elliptical deformation. Subsequently,
new protein contacts are formed that stabilize
elliptical shape
Unknown
Poikilocytes/fragments Weakening of skeletal protein contacts resulting from Hemolytic HE/HPP
skeletal protein mutations Iron deficiency, megaloblastic anemias, myelofibrosis,
Unknown myelophthisic anemias, myelodysplastic syndrome,
thalassemias
Schistocytes, Red cells “torn” by mechanic trauma (fibrin strands, “Microangiopathic” hemolytic anemia associated with
fragmented red turbulent flow) disseminated intravascular coagulation, thrombotic
cells thrombocytopenic purpura, vasculitis, heart valve
prostheses
Acanthocytes Uptake of cholesterol and its preferential Spur cell hemolytic anemia in severe liver disease
accumulation in the outer leaflet of the lipid Abetalipoproteinemia
bilayer Chorea-acanthocytosis syndrome, malnutrition,
Selective accumulation of sphingomyelin in the outer hypothyroidism, McLeod phenotype
lipid leaflet
Unknown
Echinocytes Expansion of the surface area of the outer hemileaflet Hemolytic anemia associated with hypomagnesemia
of lipid bilayer relative to the inner hemileaflet and hypophosphatemia in malnourished patients,
Unknown pyruvate kinase deficiency; in vitro artifact of low
blood storage (ATP depletion), contact with glass
or elevated pH
Hemolysis in long-distance runners, renal failure
Stomatocytes Expansion of the surface area of the inner hemileaflet Exposure of red cells to cationic anesthetics in vitro;
of the bilayer relative to the outer leaflet in vivo the drug concentrations may not be
Unknown sufficient to produce similar effect
Alcoholism, inherited disorders of membrane
permeability (hereditary stomatocytosis)
Target cells Absolute excess of membrane lipids (both cholesterol Obstructive jaundice, liver disease with intrahepatic
and phospholipids: “symmetric” lipid gain), cholestasis
followed by an increase of cell surface area Thalassemias and some hemoglobinopathies (C, D, E)
Relative excess of surface area because of a decrease
in cell volume
ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; HE, hereditary elliptocytosis; HPP, hereditary pyropoikilocytosis; HS, hereditary spherocytosis.
spectrin on the membrane; thus it is not surprising that ankyrin Deficiency of Band 3 Protein
deficiency is accompanied by a proportional decrease in spectrin
assembly on the membrane despite normal spectrin synthesis. Deficiency of band 3 protein is found in a subset of HS patients who
Similar to HS associated with β-spectrin mutations, most ankyrin present with a phenotype of a mild to moderate dominantly inherited
defects are private point mutations associated with decreased mRNA HS. Most, if not all, of these patients also have concomitant protein
accumulation. In some cases, mutations of the ankyrin promoter 4.2 deficiency. Numerous band 3 mutations associated with HS have
leading to decreased ankyrin expression have been found. Approxi- been reported, spread throughout both the cytoplasmic and the
mately 15% to 20% of ankyrin gene mutations reported are de novo membrane-spanning domains.
mutations. A number of band 3 mutations clustered in the membrane-
A number of patients with atypical HS associated with karyotypic spanning domain that replace highly conserved arginines have
abnormalities involving deletions or translocations of the ankyrin been described. These arginines, which are all located at the cyto-
gene locus on chromosome 8p have been described. Ankyrin deletions plasmic end of a predicted transmembrane helix, exhibit defective
may be part of a contiguous gene syndrome with manifestations of cellular trafficking from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma
spherocytosis, mental retardation, typical facies, and hypogonadism. membrane.