Page 745 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 745
632 Part V Red Blood Cells
ing the amount of EMA binding, is analyzed by flow cytometry. The
intensity of EMA binding is decreased in HS erythrocytes (Fig. 45.4).
Although defects of band 3 protein are only found in ~25% of typical
282 HS patients, decreased EMA fluorescence is also observed in HS
erythrocytes with primary defects in ankyrin and spectrin, thought
HS Control to be caused by transmission of long range effects of varying protein
defects across the membrane, influencing EMA binding. EMA
Counts 188 binding has high sensitivity and specificity. In laboratories with the
ability to perform fluorescence-activated cell sorting-based studies, it
is simple and rapidly performed, even on samples after shipment or
94 storage.
Like osmotic fragility, EMA binding struggles in the diagnosis of
mild HS where results may be normal or indeterminate. Other
8 erythrocyte abnormalities such as defects of erythrocyte hydration
10 0 10 1 10 2 and variants of dyserythropoietic anemia can also yield abnormal
EMA results.
100 Autohemolysis and Other Tests
Severe HS
Tail RBC autohemolysis, the spontaneous hemolysis of RBCs incubated
Typical HS under sterile conditions without glucose, was previously advocated as
80 a sensitive test for the detection of HS. This test is being used less
frequently and is probably no more sensitive than the incubated
osmotic fragility test. Other tests described in the literature such as
the glycerol lysis test, the pink test, hypertonic cryohemolysis, and
the skeleton gelation test are infrequently performed in diagnostic
60
Percent lysis laboratories in the United States. The former two tests, which use
glycerol to retard the osmotic swelling of RBCs, are preferred by some
laboratories because they are easy to perform and can be adapted to
microsamples. Cryohemolysis testing in particular remains popular
40
in Europe.
Detection of the Underlying Molecular Defect
20 Control
Because the most common finding in erythrocytes of patients with
HS is a deficiency of one or more of the membrane proteins, molecu-
0 lar studies often include sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel
0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) solubilized RBC membrane proteins
followed by densitometric quantitation. The results are expressed as
NaCl concentration (%)
ratios of individual red cell membrane proteins to band 3. This
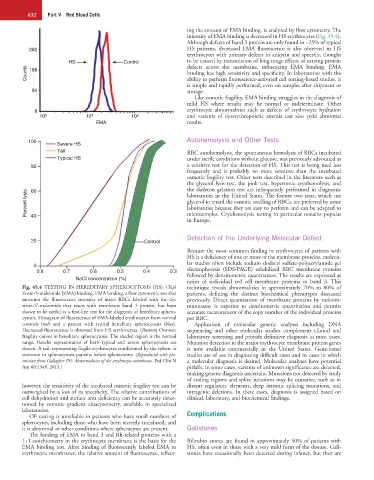
Fig. 45.4 TESTING IN HEREDITARY SPHEROCYTOSIS (HS). (Top) technique reveals abnormalities in approximately 70% to 80% of
Eosin-5-maleimide (EMA) binding. EMA binding, a flow cytometric test that patients, defining the distinct biochemical phenotypes discussed
measures the fluorescence intensity of intact RBCs labeled with the dye previously. Direct quantitation of membrane proteins by radioim-
eosin-5′-maleimide that reacts with membrane band 3 protein, has been munoassay is superior to densitometric quantitation and permits
shown to be useful as a first-line test for the diagnosis of hereditary sphero- accurate measurement of the copy number of the individual proteins
cytosis. Histogram of fluorescence of EMA-labeled erythrocytes from normal per RBC.
controls (red) and a patient with typical hereditary spherocytosis (blue). Application of molecular genetic analyses including DNA
Decreased fluorescence is observed from HS erythrocytes. (Bottom) Osmotic sequencing and other molecular studies complement clinical and
fragility curves in hereditary spherocytosis. The shaded region is the normal laboratory screening and provide definitive diagnosis in most cases.
range. Results representative of both typical and severe spherocytosis are Mutation detection in the major erythrocyte membrane protein genes
shown. A tail, representing fragile erythrocytes conditioned by the spleen, is is now available commercially in the United States. Gene-based
common in spherocytosis patients before splenectomy. (Reproduced with per- studies are of use in diagnosing difficult cases and in cases in which
mission from Gallagher PG: Abnormalities of the erythrocyte membrane. Ped Clin N a molecular diagnosis is desired. Molecular analyses have potential
Am 60:1349, 2013.) pitfalls. In some cases, variants of unknown significance are detected,
making genetic diagnosis uncertain. Mutations not detected by study
of coding regions and splice junctions may be causative, such as in
however, the sensitivity of the incubated osmotic fragility test can be distant regulatory elements, deep intronic splicing mutations, and
outweighed by a loss of its specificity. The relative contributions of intragenic deletions. In these cases, diagnosis is assigned based on
cell dehydration and surface area deficiency can be accurately deter- clinical, laboratory, and biochemical findings.
mined by osmotic gradient ektacytometry, available in specialized
laboratories.
OF testing is unreliable in patients who have small numbers of Complications
spherocytes, including those who have been recently transfused, and
it is abnormal in other conditions where spherocytes are present. Gallstones
The binding of EMA to band 3 and Rh-related proteins with a
1 : 1 stoichiometry in the erythrocyte membrane is the basis for the Bilirubin stones are found in approximately 50% of patients with
EMA binding test. After binding of fluorescently labeled EMA to HS, often even in those with a very mild form of the disease. Gall-
erythrocyte membranes, the relative amount of fluorescence, reflect- stones have occasionally been detected during infancy, but they are