Page 764 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 764
Chapter 46 Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia 651
Among methodologic diagnostic problems, reticulocyte counting reliable, and probably more sensitive (Fig. 46.4). In the indirect
is the biggest, because in many laboratories low-precision microscopic antiglobulin test (IAT), patient plasma or serum is incubated with
counts are still performed. Automatic flow cytometric methods are test RBCs, and (after washing) RBC-bound IgG is detected with
more precise, reliable, and convenient. With flow cytometry, the the DAT. IAT is usually not required for the diagnosis of AIHA
number of highly fluorescent reticulocytes (which are increased in except when a drug-dependent antibody is suspected. For the dif-
AIHA but are low in hereditary spherocytosis) can also be measured. ferentiation of drug-dependent antibodies and autoantibodies, an
Falsely very high mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and mean cor- acid eluate of the patient’s RBCs should be made and tested in the
puscular Hb concentration occur in some cases of CAIHA because IAT. If the IAT result is positive, the patient has autoantibodies.
RBC counts are falsely low because of agglutination of RBC at room The severity of AIHA does not correlate with the strength of the
temperature. If a CAIHA is suspected, blood samples should be sent DAT but rather with the immunoglobulin subclass of the antibody
to the laboratory in warmed containers. (IgG 1 or IgG 3). The result of the DAT is not a reliable marker
All of the findings of the pentad are not always present. Reticu- of treatment success because patients with a complete hematologic
locytosis is often (in ≈25%) not present at the onset of AIHA. remission may remain DAT positive, and DAT positivity or negativ-
This is mostly because of a delayed initial bone marrow response of ity has only limited value to predict the duration of hematologic
erythropoiesis. After 1 week, most of these patients have reticulocy- remission.
tosis. In other patients (particularly in secondary cases), absence of
reticulocytosis may be attributable to impairment of erythropoiesis
caused by bone marrow infiltration or blunted erythropoiesis caused Falsely Negative and Positive Direct Antiglobulin
by an acute-phase reaction. If the reticulocyte count is very low, Test Results Without Hemolysis or Anemia
pure RBC aplasia (PRCA), either immune mediated or induced by a
parvovirus (or HHV6) infection, should be suspected. Haptoglobin If the conventional DAT test result is negative, hemolytic anemia
may be falsely normal or even increased, particularly in patients is defined as DAT negative. However, AIHA cannot be definitely
with malignant or immune diseases, because haptoglobin is an excluded because about 5% (2% to 11%) of AIHA patients are
acute-phase protein. Haptoglobin may be falsely low in patients DAT negative. If AIHA is suspected for clinical grounds despite a
with a haplotype H 0 H 0 and in patients with severe liver disease. negative DAT result, more sensitive quantitative tests are required to
Both increased bilirubin and elevated LDH have a limited specificity determine the amount of IgG on the RBCs. The threshold of positiv-
for AIHA. ity of the conventional DAT is 100–200 IgG molecules per RBC,
but in some AIHA patients, the RBC IgG is less than this amount.
In about one-third of DAT-negative cases, one of the more sensitive
Step 2: Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia? test results (e.g., immunoradiometric tests) will be positive. However,
the relationship between the amount of RBC IgG and hemolysis is
23
The next step is to find out whether the hemolytic anemia is an AIHA. not clear cut, and there is no “hemolysis threshold.” The reasons
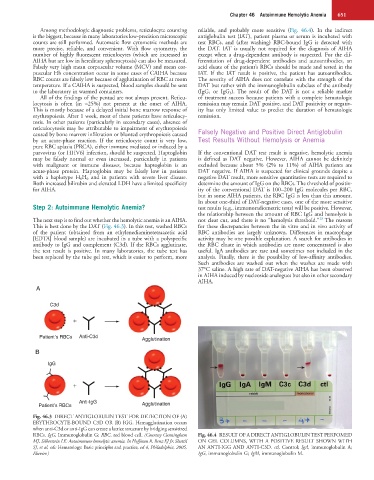
This is best done by the DAT (Fig. 46.3). In this test, washed RBCs for these discrepancies between the in vitro and in vivo activity of
of the patient (obtained from an ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid RBC antibodies are largely unknown. Differences in macrophage
[EDTA] blood sample) are incubated in a tube with a polyspecific activity may be one possible explanation. A search for antibodies in
antibody to IgG and complement (C3d). If the RBCs agglutinate, the RBC eluate in which antibodies are more concentrated is also
the test result is positive. In many laboratories, the tube test has useful. IgA antibodies are rare and sometimes not included in the
been replaced by the tube gel test, which is easier to perform, more analysis. Finally, there is the possibility of low-affinity antibodies.
Such antibodies are washed out when the washes are made with
37°C saline. A high rate of DAT-negative AIHA has been observed
in AIHA induced by nucleoside analogues but also in other secondary
AIHA.
A
C3d
+
Patient’s RBCs Anti-C3d Agglutination
B
IgG
+
Anti-IgG
Patient’s RBCs Agglutination
Fig. 46.3 DIRECT ANTIGLOBULIN TEST FOR DETECTION OF (A)
ERYTHROCYTE-BOUND C3D OR (B) IGG. Hemagglutination occurs
when anti-C3d or anti-IgG can create a lattice structure by bridging sensitized
RBCs. IgG, Immunoglobulin G; RBC, red blood cell. (Courtesy Cunningham Fig. 46.4 RESULT OF A DIRECT ANTIGLOBULIN TEST PERFOMED
MJ, Silberstein LE: Autoimmune hemolytic anemia. In Hoffman R, Benz EJ Jr, Shattil ON GEL COLUMNS, WITH A POSITIVE RESULT SHOWN WITH
SJ, et al, eds: Hematology: Basic principles and practice, ed 4, Philadelphia, 2005, AN ANTI-IGG AND ANTI-C3D. ctl, Control; IgA, immunoglobulin A;
Elsevier.) IgG, immunoglobulin G; IgM, immunoglobulin M.