Page 768 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 768
Chapter 46 Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia 655
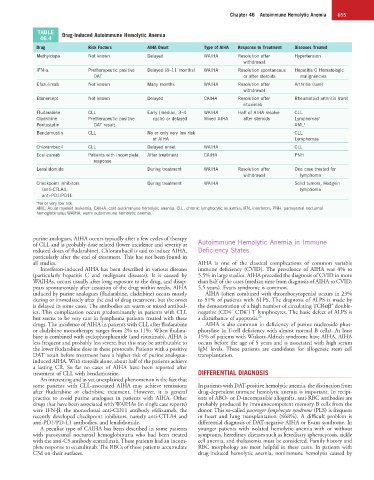
TABLE Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
46.4
Drug Risk Factors AIHA Onset Type of AIHA Response to Treatment Diseases Treated
Methyldopa Not known Delayed WAIHA Resolution after Hypertension
withdrawal
IFN-α Pretherapeutic positive Delayed (8–11 months) WAIHA Resolution spontaneous Hepatitis C Hematologic
DAT or after steroids malignancies
Efazulimab Not known Many months WAIHA Resolution after Arthritis (rare)
withdrawal
Etanercept Not known Delayed CAIHA Resolution after Rheumatoid arthritis (rare)
rituximab
Fludarabine CLL Early (median, 3–4 WAIHA Half of AIHA resolve CLL
Cladribine Pretherapeutic positive cycle) or delayed Mixed AIHA after steroids Lymphomas a
Pentostatin DAT result AML a
Bendamustin CLL No or only very low risk CLL
of AIHA Lymphomas
Chlorambucil CLL Delayed onset WAIHA CLL
Eculizumab Patients with incomplete After treatment CAIHA PNH
response
Lenalidomide During treatment WAIHA Resolution after One case treated for
withdrawal lymphoma
Checkpoint inhibitors During treatment WAIHA Solid tumors, Hodgkin
(anti-CTLA4, lymphoma
anti-PD1/PD1L
a No or very low risk.
AML, Acute myeloid leukemia; CAIHA, cold autoimmune hemolytic anemia; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; IFN, interferon; PNH, paroxysmal nocturnal
hemoglobinuria; WAIHA, warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
purine analogues, AIHA occurs typically after a few cycles of therapy
of CLL and is probably dose related (lower incidence and severity at Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia in Immune
reduced doses of fludarabine). Chlorambucil is said to induce AIHA, Deficiency States
particularly after the end of treatment. This has not been found in
all studies. AIHA is one of the classical complications of common variable
Interferon-induced AIHA has been described in various diseases immune deficiency (CVID). The prevalence of AIHA was 4% to
(particularly hepatitis C and malignant diseases). It is caused by 5.5% in large studies. AIHA preceded the diagnosis of CVID in more
WAIHAs, occurs usually after long exposure to the drug, and disap- than half of the cases (median time from diagnosis of AIHA to CVID:
pears spontaneously after cessation of the drug within weeks. AIHA 5.5 years). Evans syndrome is common.
induced by purine analogues (fludarabine, cladribine) occurs mostly AIHA (often combined with thrombocytopenia) occurs in 23%
during or immediately after the end of drug treatment, but the onset to 51% of patients with ALPS. The diagnosis of ALPS is made by
+
is delayed in some cases. The antibodies are warm or mixed antibod- the demonstration of a high number of circulating TCRαβ double-
–
–
ies. This complication occurs predominantly in patients with CLL negative (CD4 CD8 ) T lymphocytes. The basic defect of ALPS is
but seems to be very rare in lymphoma patients treated with these a disturbance of apoptosis. 26
drugs. The incidence of AIHA in patients with CLL after fludarabine AIHA is also common in deficiency of purine nucleoside phos-
or cladribine monotherapy ranges from 2% to 11%. When fludara- phorylase (a T-cell deficiency with almost normal B cells). At least
bine is combined with cyclophosphamide (and rituximab), AIHA is 15% of patients with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome have AIHA. AIHA
less frequent and probably less severe, but this may be attributable to occurs before the age of 5 years and is associated with high serum
the lower fludarabine dose in these protocols. Patients with a positive IgM levels. These patients are candidates for allogeneic stem cell
DAT result before treatment have a higher risk of purine analogue- transplantation.
induced AIHA. With steroids alone, about half of the patients achieve
a lasting CR. So far no cases of AIHA have been reported after
treatment of CLL with bendamustine. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
An interesting and as yet unexplained phenomenon is the fact that
some patients with CLL-associated AIHA may achieve remissions In patients with DAT-positive hemolytic anemia, the distinction from
after fludarabine or cladribine treatment. However, it is general drug-dependent immune hemolytic anemia is important. In recipi-
practice to avoid purine analogues in patients with AIHA. Other ents of ABO- or D-incompatible allografts, anti-RBC antibodies are
drugs that have been associated with WAIHAs (in single case reports) probably produced by immunocompetent memory B cells from the
were IFN-β, the monoclonal anti-CD11 antibody efalizumab, the donor. This so-called passenger lymphocyte syndrome (PLS) is frequent
recently developed checkpoint inhibitors, namely anti-CTLA4 and in heart and lung transplantation (≤68%). A difficult problem is
anti-PD1/PD-L1 antibodies, and lenalidomide. differential diagnosis of DAT-negative AIHA or Evans syndrome. In
A peculiar type of CAIHA has been described in some patients younger patients with isolated hemolytic anemia with or without
with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria who had been treated symptoms, hereditary diseases such as hereditary spherocytosis, sickle
with the anti-C5 antibody ecuzulimab. These patients had an incom- cell anemia, and thalassemia must be considered. Family history and
plete response to ecuzulimab. The RBCs of these patients accumulate RBC morphology are most helpful in these cases. In patients with
C3d on their surfaces. drug-induced hemolytic anemia, nonimmune hemolysis caused by