Page 771 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 771
658 Part V Red Blood Cells
TABLE Treatment Options for Primary and Secondary Warm Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia and Cold Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
46.5
Disease or Condition First Line Second Line Beyond Second Line Last Resort
Primary AIHA Steroids (+ rituximab) Splenectomy Azathioprine, MMF, High-dose cyclophos-
Rituximab cyclosporine, phamide, alemtuzumab
cyclophosphamide
B- and T-cell NHL Steroids Chemotherapy +/− rituximab Other anti-CD20 antibodies,
(splenectomy in SMZL) ibrutinib
Hodgkin lymphoma Steroids Chemotherapy
Solid tumors Steroids
Surgery
Ovarian dermoid cyst Ovariectomy
SLE Steroids Azathioprine MMF Rituximab
Autologous SCT
Ulcerative colitis Steroids Azathioprine Total colectomy
CVID Steroids + IgG replacement
ALPD Steroids MMF Sirolimus
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome Steroids Allogeneic SCT
Allogeneic SCT Steroids Rituximab a Splenectomy
T-cell infusion
Organ transplantation Reduction of
immunosuppression,
steroids
Drug induced Withdrawal Steroids
b
Primary CAD Protection from cold Rituximab Fludarabine + rituximab Ecuzulimab bortezomid b
exposure Chlorambucil
PCH Supportive treatment Rituximab (chronic)
a
(postinfectious)
a Early second-line treatment because of known poor response to steroids.
b Off-label use in single cases.
AIHA, Autoimmune hemolytic anemia; ALPD, autoimmune lymphoproliferative disorders; CAD, cold agglutinin disease; CVID, common variable immune deficiency;
IgG, immunoglobulin G; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; NHL, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma; PCH, paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria; SCT, stem cell transplantation; SLE,
systemic lupus erythematosus; SMZL, splenic marginal zone lymphoma.
C
A B D
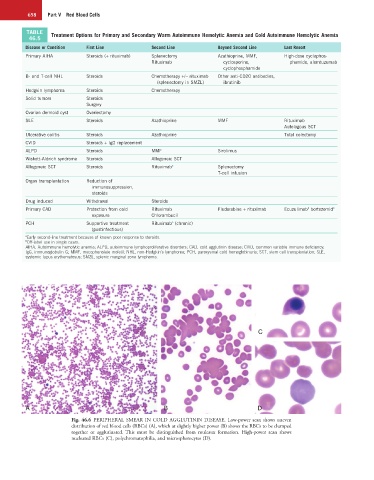
Fig. 46.6 PERIPHERAL SMEAR IN COLD AGGLUTININ DISEASE. Low-power scan shows uneven
distribution of red blood cells (RBCs) (A), which at slightly higher power (B) shows the RBCs to be clumped
together or agglutinated. This must be distinguished from rouleaux formation. High-power scan shows
nucleated RBCs (C), polychromatophilia, and microspherocytes (D).