Page 979 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 979
862 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
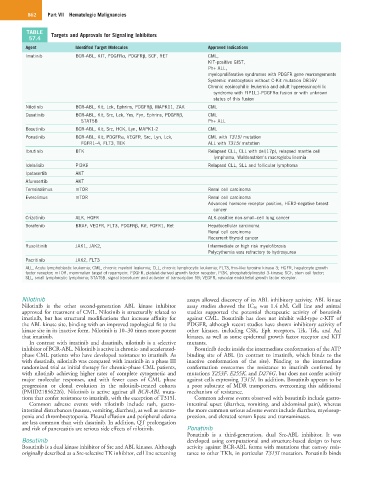
TABLE Targets and Approvals for Signaling Inhibitors
57.4
Agent Identified Target Molecules Approved Indications
Imatinib BCR-ABL, KIT, PDGFRα, PDGFRβ, SCF, RET CML,
KIT-positive GIST,
Ph+ ALL,
myeloproliferative syndromes with PDGFR gene rearrangements
Systemic mastocytosis without C-Kit mutation D816V
Chronic eosinophilic leukemia and adult hypereosinophilic
syndrome with FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion or with unknown
status of this fusion
Nilotinib BCR-ABL, Kit, Lck, Ephrins, PDGFRβ, MAPK11, ZAK CML
Dasatinib BCR-ABL, Kit, Src, Lck, Yes, Fyn, Ephrins, PDGFRβ, CML
STAT5B Ph+ ALL
Bosutinib BCR-ABL, Kit, Src, HCK, Lyn, MAPK1-2 CML
Ponatinib BCR-ABL, Kit, PDGFRα, VEGFR, Src, Lyn, Lck, CML with T315I mutation
FGFR1–4, FLT3, TEK ALL with T315I mutation
Ibrutinib BTK Relapsed CLL, CLL with del(17p), relapsed mantle cell
lymphoma, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia
Idelalisib PI3Kδ Relapsed CLL, SLL and follicular lymphoma
Ipatasertib AKT
Afuresertib AKT
Temsirolimus mTOR Renal cell carcinoma
Everolimus mTOR Renal cell carcinoma
Advanced hormone receptor positive, HER2-negative breast
cancer
Crizotinib ALK, HGFR ALK-positive non-small–cell lung cancer
Sorafenib BRAF, VEGFR, FLT3, PDGFRβ, Kit, FGFR1, Ret Hepatocellular carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma
Recurrent thyroid cancer
Ruxolitinib JAK1, JAK2, Intermediate or high risk myelofibrosis
Polycythemia vera refractory to hydroxyurea
Pacritinib JAK2, FLT3
ALL, Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; FLT3, fms-like tyrosine kinase 3; HGFR, hepatocyte growth
factor receptor; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor, PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; SCF, stem cell factor;
SLL, small lymphocytic lymphoma; STAT5B, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5B; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
Nilotinib assays allowed discovery of its ABL inhibitory activity. ABL kinase
Nilotinib is the other second-generation ABL kinase inhibitor assay studies showed the IC 50 was 1.4 nM. Cell line and animal
approved for treatment of CML. Nilotinib is structurally related to studies supported the potential therapeutic activity of bosutinib
imatinib, but has structural modifications that increase affinity for against CML. Bosutinib has does not inhibit wild-type c-KIT of
the ABL kinase site, binding with an improved topological fit to the PDGFR, although recent studies have shown inhibitory activity of
kinase site in its inactive form. Nilotinib is 10–30 times more potent other kinases, including CSK, Eph receptors, Trk, Tek, and Axl
that imatinib. kinases, as well as some epidermal growth factor receptor and KIT
In contrast with imatinib and dasatinib, nilotinib is a selective mutants.
inhibitor of BCR-ABL. Nilotinib is active in chronic- and accelerated- Bosutinib docks inside the intermediate conformation of the ATP
phase CML patients who have developed resistance to imatinib. As binding site of ABL (in contrast to imatinib, which binds to the
with dasatinib, nilotinib was compared with imatinib in a phase III inactive conformation of the site). Binding to the intermediate
randomized trial as initial therapy for chronic-phase CML patients, conformation overcomes the resistance to imatinib conferred by
with nilotinib achieving higher rates of complete cytogenetic and mutations Y253F, E255K, and D276G, but does not confer activity
major molecular responses, and with fewer cases of CML phase against cells expressing T315I. In addition, Bosutinib appears to be
progression or clonal evolution in the nilotinib-treated cohorts a poor substrate of MDR transporters, overcoming this additional
(PMID21856226). Nilotinib is active against all BCR-ABL muta- mechanism of resistance.
tions that confer resistance to imatinib, with the exception of T315I. Common adverse events observed with bosutinib include gastro-
Common adverse events with nilotinib include rash, gastro- intestinal upset (diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain), whereas
intestinal disturbances (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), as well as neutro- the more common serious adverse events include diarrhea, myelosup-
penia and thrombocytopenia. Pleural effusion and peripheral edema pression, and elevated serum lipase and transaminases.
are less common than with dasatinib. In addition, QT prolongation
and risk of pancreatitis are serious side effects of nilotinib. Ponatinib
Ponatinib is a third-generation, dual Src-ABL inhibitor. It was
Bosutinib developed using computational and structure-based design to have
Bosutinib is a dual kinase inhibitor of Src and ABL kinases. Although activity against BCR-ABL forms with mutations that convey resis-
originally described as a Src-selective TK inhibitor, cell line screening tance to other TKIs, in particular T315I mutation. Ponatinib binds