Page 124 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 124
100 Part III: Epochal Hematology Chapter 7: Hematology of the Fetus and Newborn 101
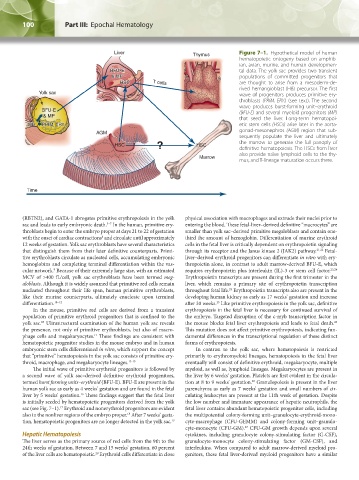
Liver Thymus Figure 7–1. Hypothetical model of human
hematopoietic ontogeny based on amphib-
ian, avian, murine, and human developmen-
BFU-E tal data. The yolk sac provides two transient
& MP populations of committed progenitors that
HSC T cells are thought to arise from a mesoderm-de-
rived hemangioblast (HB) precursor. The first
Yolk sac wave of progenitors produces primitive ery-
throblasts (PRIM. ERY.) (see text). The second
wave produces burst-forming unit–erythroid
BFU-E (BFU-E) and several myeloid progenitors (MP)
& MP that seed the liver. Long-term hematopoi-
HB PRIM. ERY. etic stem cells (HSCs) arise later in the aorta-
AGM gonad-mesonephros (AGM) region that sub-
sequently populate the liver and ultimately
? the marrow to generate the full panoply of
HSC HSC definitive hematopoiesis. The HSCs from liver
also provide naïve lymphoid cells to the thy-
Marrow
mus, and T-lineage maturation occurs there.
Time
(RBTN2), and GATA-1 abrogates primitive erythropoiesis in the yolk physical association with macrophages and extrude their nuclei prior to
sac and leads to early embryonic death. In the human, primitive ery- entering the blood. These fetal-liver–derived definitive “macrocytes” are
5–7
throblasts begin to enter the embryo proper at days 21 to 22 of gestation smaller than yolk sac–derived primitive megaloblasts and contain one-
with the onset of cardiac contractions and circulate until approximately third the amount of hemoglobin. Differentiation of murine erythroid
8
12 weeks of gestation. Yolk sac erythroblasts have several characteristics cells in the fetal liver is critically dependent on erythropoietin signaling
that distinguish them from their later definitive counterparts. Primi- through its receptor and the Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) pathway. 21,22 Fetal-
tive erythroblasts circulate as nucleated cells, accumulating embryonic liver–derived erythroid progenitors can differentiate in vitro with ery-
hemoglobins and completing terminal differentiation within the vas- thropoietin alone, in contrast to adult marrow-derived BFU-E, which
cular network. Because of their extremely large size, with an estimated requires erythropoietin plus interleukin (IL)-3 or stem cell factor. 23,24
9
MCV of >400 fL/cell, yolk sac erythroblasts have been termed meg- Erythropoietin transcripts are present during the first trimester in the
aloblasts. Although it is widely assumed that primitive red cells remain liver, which remains a primary site of erythropoietin transcription
nucleated throughout their life span, human primitive erythroblasts, throughout fetal life. Erythropoietin transcripts also are present in the
25
like their murine counterparts, ultimately enucleate upon terminal developing human kidney as early as 17 weeks’ gestation and increase
differentiation. 10–12 after 30 weeks. Like primitive erythropoiesis in the yolk sac, definitive
25
In the mouse, primitive red cells are derived from a transient erythropoiesis in the fetal liver is necessary for continued survival of
population of primitive erythroid progenitors that is confined to the the embryo. Targeted disruption of the c-myb transcription factor in
yolk sac. Ultrastructural examination of the human yolk sac reveals the mouse blocks fetal liver erythropoiesis and leads to fetal death.
26
13
the presence, not only of primitive erythroblasts, but also of macro- This mutation does not affect primitive erythropoiesis, indicating fun-
phage cells and megakaryocytes. These findings are consistent with damental differences in the transcriptional regulation of these distinct
11
hematopoietic progenitor studies in the mouse embryo and in human forms of erythropoiesis.
embryonic stem cells differentiated in vitro, which support the concept In contrast to the yolk sac, where hematopoiesis is restricted
that “primitive” hematopoiesis in the yolk sac consists of primitive ery- primarily to erythromyeloid lineages, hematopoiesis in the fetal liver
throid, macrophage, and megakaryocyte lineages. 13-15 eventually will consist of definitive erythroid, megakaryocyte, multiple
The initial wave of primitive erythroid progenitors is followed by myeloid, as well as, lymphoid lineages. Megakaryocytes are present in
a second wave of yolk sac–derived definitive erythroid progenitors, the liver by 6 weeks’ gestation. Platelets are first evident in the circula-
termed burst forming units–erythroid (BFU-E). BFU-E are present in the tion at 8 to 9 weeks’ gestation. Granulopoiesis is present in the liver
20
human yolk sac as early as 4 weeks’ gestation and are found in the fetal parenchyma as early as 7 weeks’ gestation and small numbers of cir-
liver by 5 weeks’ gestation. These findings suggest that the fetal liver culating leukocytes are present at the 11th week of gestation. Despite
16
is initially seeded by hematopoietic progenitors derived from the yolk the low number and immature appearance of hepatic neutrophils, the
sac (see Fig. 7–1). Erythroid and nonerythroid progenitors are evident fetal liver contains abundant hematopoietic progenitor cells, including
17
also in the nonliver regions of the embryo proper. After 7 weeks’ gesta- the multipotential colony-forming unit–granulocyte-erythroid-mono-
18
tion, hematopoietic progenitors are no longer detected in the yolk sac. 19 cyte-macrophage (CFU-GEMM) and colony-forming unit–granulo-
cyte-monocyte (CFU-GM). CFU-GM growth depends upon several
27
Hepatic Hematopoiesis cytokines, including granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF),
The liver serves as the primary source of red cells from the 9th to the granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and
24th weeks of gestation. Between 7 and 15 weeks’ gestation, 60 percent interleukins. When compared to adult marrow-derived myeloid pro-
of the liver cells are hematopoietic. Erythroid cells differentiate in close genitors, these fetal liver-derived myeloid progenitors have a similar
20
Kaushansky_chapter 07_p0097-0118.indd 100 9/18/15 10:13 PM