Page 1334 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1334
1308 Part X: Malignant Myeloid Diseases Chapter 85: Essential Thrombocythemia 1309
A
B
C
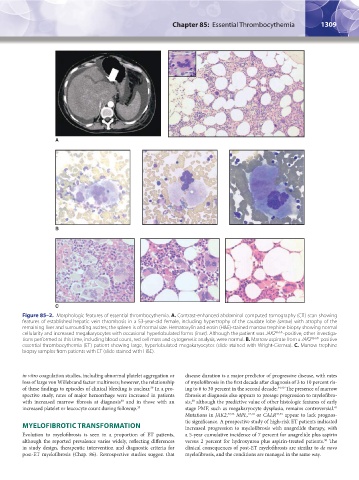
Figure 85–2. Morphologic features of essential thrombocythemia. A. Contrast-enhanced abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan showing
features of established hepatic vein thrombosis in a 53-year-old female, including hypertrophy of the caudate lobe (arrow) with atrophy of the
remaining liver and surrounding ascites; the spleen is of normal size. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained marrow trephine biopsy showing normal
cellularity and increased megakaryocytes with occasional hyperlobulated forms (inset). Although the patient was JAK2 V617F -positive, other investiga-
tions performed at this time, including blood count, red cell mass and cytogenetic analysis, were normal. B. Marrow aspirate from a JAK2 V617F -positive
essential thrombocythemia (ET) patient showing large, hyperlobulated megakaryocytes (slide stained with Wright-Giemsa). C. Marrow trephine
biopsy samples from patients with ET (slide stained with H&E).
in vitro coagulation studies, including abnormal platelet aggregation or disease duration is a major predictor of progressive disease, with rates
loss of large von Willebrand factor multimers; however, the relationship of myelofibrosis in the first decade after diagnosis of 3 to 10 percent ris-
of these findings to episodes of clinical bleeding is unclear. In a pro- ing to 6 to 30 percent in the second decade. 34,40 The presence of marrow
39
spective study, rates of major hemorrhage were increased in patients fibrosis at diagnosis also appears to presage progression to myelofibro-
with increased marrow fibrosis at diagnosis and in those with an sis, although the predictive value of other histologic features of early
38
38
increased platelet or leucocyte count during followup. 35 stage PMF, such as megakaryocyte dysplasia, remains controversial.
41
Mutations in JAK2, 42,43 MPL, 17,18 or CALR 44,45 appear to lack prognos-
tic significance. A prospective study of high-risk ET patients indicated
MYELOFIBROTIC TRANSFORMATION increased progression to myelofibrosis with anagrelide therapy, with
Evolution to myelofibrosis is seen in a proportion of ET patients, a 5-year cumulative incidence of 7 percent for anagrelide plus aspirin
although the reported prevalence varies widely, reflecting differences versus 2 percent for hydroxyurea plus aspirin-treated patients. The
30
in study design, therapeutic intervention and diagnostic criteria for clinical consequences of post-ET myelofibrosis are similar to de novo
post-ET myelofibrosis (Chap. 86). Retrospective studies suggest that myelofibrosis, and the conditions are managed in the same way.
Kaushansky_chapter 85_p1307-1318.indd 1309 9/21/15 11:08 AM