Page 1607 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1607
1582 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 95: General Considerations for Lymphomas 1583
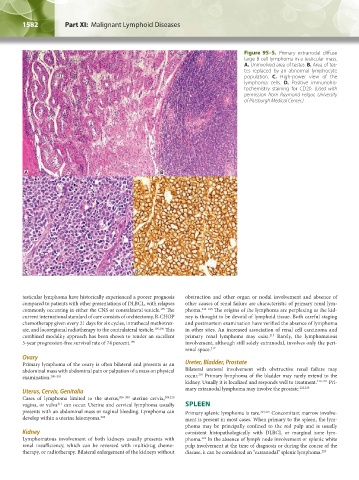
Figure 95–5. Primary extranodal diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma in a testicular mass.
A. Uninvolved area of testes. B. Area of tes-
tes replaced by an abnormal lymphocyte
population. C. High-power view of the
lymphoma cells. D. Positive immunohis-
tochemistry staining for CD20. (Used with
permission from Raymond Felgar, University
of Pittsburgh Medical Center.)
A B
C D
testicular lymphoma have historically experienced a poorer prognosis obstruction and other organ or nodal involvement and absence of
compared to patients with other presentations of DLBCL, with relapses other causes of renal failure are characteristic of primary renal lym-
commonly occurring in either the CNS or contralateral testicle. The phoma. 212–216 The origins of the lymphoma are perplexing as the kid-
199
current international standard of care consists of orchiectomy, R-CHOP ney is thought to be devoid of lymphoid tissue. Both careful staging
chemotherapy given every 21 days for six cycles, intrathecal methotrex- and postmortem examination have verified the absence of lymphoma
ate, and locoregional radiotherapy to the contralateral testicle. 195,196 This in other sites. An increased association of renal cell carcinoma and
combined modality approach has been shown to render an excellent primary renal lymphoma may exist. Rarely, the lymphomatous
215
5-year progression-free survival rate of 74 percent. 196 involvement, although still solely extranodal, involves only the peri-
renal space. 217
Ovary
Primary lymphoma of the ovary is often bilateral and presents as an Ureter, Bladder, Prostate
abdominal mass with abdominal pain or palpation of a mass on physical Bilateral ureteral involvement with obstructive renal failure may
218
examination. 200–205 occur. Primary lymphoma of the bladder may rarely extend to the
kidney. Usually it is localized and responds well to treatment. 219–221 Pri-
Uterus, Cervix, Genitalia mary extranodal lymphoma may involve the prostate. 222,223
Cases of lymphoma limited to the uterus, 206–208 uterine cervix, 209,210
vagina, or vulva can occur. Uterine and cervical lymphoma usually SPLEEN
211
presents with an abdominal mass or vaginal bleeding. Lymphoma can Primary splenic lymphoma is rare. 224,225 Concomitant marrow involve-
develop within a uterine leiomyoma. 208 ment is present in most cases. When primary to the spleen, the lym-
phoma may be principally confined to the red pulp and is usually
Kidney consistent histopathologically with DLBCL or marginal zone lym-
Lymphomatous involvement of both kidneys usually presents with phoma. In the absence of lymph node involvement or splenic white
224
renal insufficiency, which can be reversed with multidrug chemo- pulp involvement at the time of diagnosis or during the course of the
therapy, or radiotherapy. Bilateral enlargement of the kidneys without disease, it can be considered an “extranodal” splenic lymphoma. 225
Kaushansky_chapter 95_p1569-1586.indd 1582 9/21/15 12:17 PM