Page 201 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 201
176 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 13: Cytogenetics and Genetic Abnormalities 177
A
Centromere 9q34.1 Telomere
LSI-ASS-ABL1
LSI-BCR Dual Fusion
A B
Centromere 11q23.3 Telomere
T3D Exon 1 Exon 4 Exon 6 Exon 8 Exon 15 Exon 37 ARCN1 D11S614
5' 3'
BCR
~350 kb
~190 kb
LSI-KMT2A/MLL Dual Color, Break Apart
C D
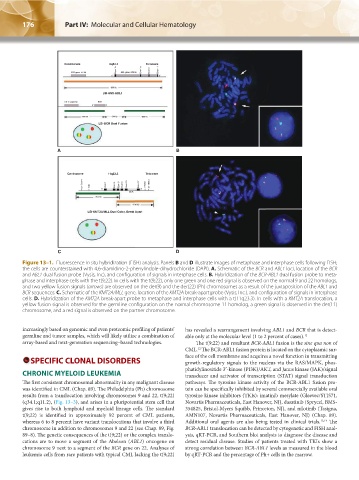
Figure 13–1. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis. Panels B and D illustrate images of metaphase and interphase cells following FISH;
the cells are counterstained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole-dihydrochloride (DAPI). A. Schematic of the BCR and ABL1 loci, location of the BCR
and ABL1 dual fusion probe (Vysis, Inc), and configuration of signals in interphase cells. B. Hybridization of the BCR-ABL1 dual fusion probe to meta-
phase and interphase cells with the t(9;22). In cells with the t(9;22), only one green and one red signal is observed on the normal 9 and 22 homologs,
and two yellow fusion signals (arrows) are observed on the der(9) and the der(22) (Ph) chromosomes as a result of the juxtaposition of the ABL1 and
BCR sequences. C. Schematic of the KMT2A/MLL gene, location of the KMT2A break-apart probe (Vysis, Inc.), and configuration of signals in interphase
cells. D. Hybridization of the KMT2A break-apart probe to metaphase and interphase cells with a t(11q23.3). In cells with a KMT2A translocation, a
yellow fusion signal is observed for the germline configuration on the normal chromosome 11 homolog, a green signal is observed in the der(11)
chromosome, and a red signal is observed on the partner chromosome.
increasingly based on genomic and even proteomic profiling of patients’ has revealed a rearrangement involving ABL1 and BCR that is detect-
germline and tumor samples, which will likely utilize a combination of able only at the molecular level (1 to 2 percent of cases). 12
array-based and next-generation sequencing–based technologies. The t(9;22) and resultant BCR-ABL1 fusion is the sine qua non of
12
CML. The BCR-ABL1 fusion protein is located on the cytoplasmic sur-
SPECIFIC CLONAL DISORDERS face of the cell membrane and acquires a novel function in transmitting
growth-regulatory signals to the nucleus via the RAS/MAPK, phos-
phatidylinositide 3′-kinase (PI3K)/AKT, and Janus kinase (JAK)/signal
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signal transduction
The first consistent chromosomal abnormality in any malignant disease pathways. The tyrosine kinase activity of the BCR-ABL1 fusion pro-
was identified in CML (Chap. 89). The Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome tein can be specifically inhibited by several commercially available oral
results from a translocation involving chromosomes 9 and 22, t(9;22) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs): imatinib mesylate (Gleevec/STI571,
(q34.1;q11.2), (Fig. 13–3), and arises in a pluripotential stem cell that Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ), dasatinib (Sprycel, BMS-
gives rise to both lymphoid and myeloid lineage cells. The standard 354825, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ), and nilotinib (Tasigna,
t(9;22) is identified in approximately 92 percent of CML patients, AMN107, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ) (Chap. 89).
whereas 6 to 8 percent have variant translocations that involve a third Additional oral agents are also being tested in clinical trials. 13,14 The
chromosome in addition to chromosomes 9 and 22 (see Chap. 89, Fig. BCR-ABL1 translocation can be detected by cytogenetic and FISH anal-
89–8). The genetic consequences of the t(9;22) or the complex translo- ysis, qRT-PCR, and Southern blot analysis to diagnose the disease and
cations are to move a segment of the Abelson (ABL1) oncogene on detect residual disease. Studies of patients treated with TKIs show a
chromosome 9 next to a segment of the BCR gene on 22. Analyses of strong correlation between BCR-ABL1 levels as measured in the blood
leukemia cells from rare patients with typical CML lacking the t(9;22) by qRT-PCR and the percentage of Ph+ cells in the marrow.
Kaushansky_chapter 13_p0173-0190.indd 176 17/09/15 6:32 pm