Page 307 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 307
282 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 19: The Inflammatory Response 283
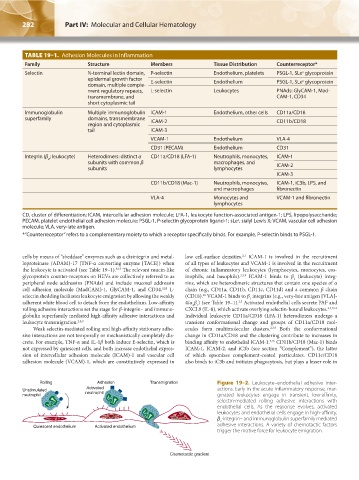
TABLE 19–1. Adhesion Molecules in Inflammation
Family Structure Members Tissue Distribution Counterreceptor*
Selectin N-terminal lectin domain, P-selectin Endothelium, platelets PSGL-1, SLe glycoprotein
x
epidermal growth factor E-selectin Endothelium PSGL-1, SLe glycoprotein
x
domain, multiple comple-
ment regulatory repeats, L-selectin Leukocytes PNAds: GlyCAM-1, Mad-
transmembrane, and CAM-1, CD34
short cytoplasmic tail
Immunoglobulin Multiple immunoglobulin ICAM-1 Endothelium, other cells CD11a/CD18
superfamily domains, transmembrane ICAM-2 CD11b/CD18
region and cytoplasmic
tail ICAM-3
VCAM-1 Endothelium VLA-4
CD31 (PECAM) Endothelium CD31
Integrin (β ; leukocyte) Heterodimers: distinct α CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1) Neutrophils, monocytes, ICAM-1
2
subunits with common β macrophages, and ICAM-2
subunits lymphocytes
ICAM-3
CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1) Neutrophils, monocytes, ICAM-1, iC3b, LPS, and
and macrophages fibronectin
VLA-4 Monocytes and VCAM-1 and fibronectin
lymphocytes
CD, cluster of differentiation; ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule; LFA-1, leukocyte function-associated antigen-1; LPS, lipopolysaccharide;
PECAM, platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule; PSGL-1, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1; sLe , sialyl Lewis X; VCAM, vascular cell adhesion
x
molecule; VLA, very-late antigen.
*”Counterreceptor” refers to a complementary moiety to which a receptor specifically binds. For example, P-selectin binds to PSGL-1.
cells by means of “sheddase” enzymes such as a disintegrin and metal- low cell-surface densities. ICAM-1 is involved in the recruitment
2,3
loproteinase (ADAM)-17 (TNF-α converting enzyme [TACE]) when of all types of leukocytes and VCAM-1 is involved in the recruitment
the leukocyte is activated (see Table 19–1). The relevant mucin-like of chronic inflammatory leukocytes (lymphocytes, monocytes, eos-
3,15
glycoprotein counter-receptors on HEVs are collectively referred to as inophils, and basophils). 2,3,9 ICAM-1 binds to β (leukocyte) integ-
2
peripheral node addressins (PNAds) and include mucosal addressin rins, which are heterodimeric structures that contain one species of α
cell adhesion molecule (MadCAM)-1, GlyCAM-1, and CD34. L- chain (e.g., CD11a, CD11b, CD11c, CD11d) and a common β chain
3,15
selectin shedding facilitates leukocyte emigration by allowing the weakly (CD18). VCAM-1 binds to β integrins (e.g., very-late antigen [VLA]-
16
1
adherent white blood cell to detach from the endothelium. Low-affinity 4/α β ) (see Table 19–1). Activated endothelial cells secrete PAF and
2,3
4 1
rolling adhesive interactions set the stage for β-integrin– and immuno- CXCL8 (IL-8), which activate overlying selectin-bound leukocytes. 2,3,9,16
globulin superfamily mediated high-affinity adhesive interactions and Individual leukocyte CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1) heterodimers undergo a
leukocyte transmigration. 2,3,9 transient conformational change and groups of CD11a/CD18 mol-
Weak selectin-mediated rolling and high-affinity stationary adhe- ecules form multimolecular clusters. 2,3,9 Both the conformational
sive interactions are not temporally or mechanistically completely dis- change in CD11a/CD18 and the clustering contribute to increases in
crete. For example, TNF-α and IL-1β both induce E-selectin, which is binding affinity to endothelial ICAM-1. CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1) binds
3,16
not expressed by quiescent cells, and both increase endothelial expres- ICAM-1, ICAM-2, and iC3b (see section “Complement”), the latter
sion of intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 and vascular cell of which opsonizes complement-coated particulates. CD11c/CD18
adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1, which are constitutively expressed in also binds to iC3b and initiates phagocytosis, but plays a lesser role in
Rolling Adhesion Transmigration Figure 19–2. Leukocyte–endothelial adhesive inter-
Activated
Unstimulated neutrophil actions. Early in the acute inflammatory response, mar-
neutrophil ginated leukocytes engage in transient, low-affinity,
selectin-mediated rolling adhesive interactions with
endothelial cells. As the response evolves, activated
leukocytes and endothelial cells engage in high-affinity,
β -integrin– and immunoglobulin superfamily mediated
2
adhesive interactions. A variety of chemotactic factors
Quiescent endothelium Activated endothelium
trigger the motive force for leukocyte emigration.
Chemotactic gradient
Kaushansky_chapter 19_p0279-0292.indd 282 9/17/15 5:51 PM