Page 320 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 320
294 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 20: Innate Immunity 295
discovery of an LPS-sensing function for TLR4, a homologue of Toll, Structure of the Toll-Like Receptors
made evolutionary sense. The TLRs are single-spanning transmembrane proteins with leucine-rich
Other molecules of microbial origin (for example, di- and tri- repeat (LRR) motifs in their extracellular domains and a characteris-
acylated lipopeptides and lipoproteins, lipoteichoic acid, unmethy- tic TIR (Toll/interleukin [IL]-1 receptor) motif in their cytoplasmic
lated DNA bearing CpG dinucleotides in a particular context, flagellin, domains. The TIR domain is based on an ancient protein fold evident
25
and double-stranded RNA [dsRNA]) were known to elicit responses in cytosolic plant disease resistance proteins (where it often is repre-
qualitatively similar to those elicited by LPS. The other TLR paralogs sented together with a nucleotide binding sequence [NBS] and/or LRR
seemed excellent candidate receptors for these molecules. Reverse motifs), in proteins of the IL-1 and IL-18 receptor family, in the adapter
genetic methods established that each of these molecules is indeed rec- proteins that carry signals from TLRs, and in the TLRs themselves.
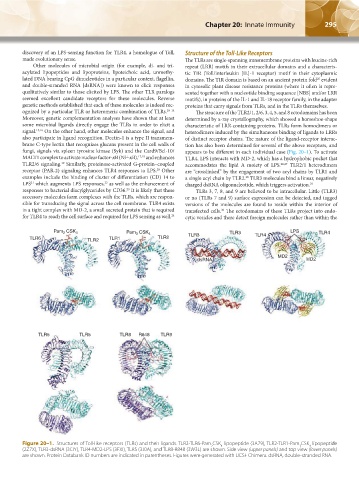
ognized by a particular TLR or heteromeric combination of TLRs. 10–14 The structure of the TLR2/1, 2/6, 3, 4, 5, and 8 ectodomains has been
Moreover, genetic complementation analyses have shown that at least determined by x-ray crystallography, which showed a horseshoe-shape
some microbial ligands directly engage the TLRs in order to elicit a characteristic of LRR-containing proteins. TLRs form homodimers or
signal. 15,16 On the other hand, other molecules enhance the signal, and heterodimers induced by the simultaneous binding of ligands to LRRs
also participate in ligand recognition. Dectin-1 is a type II transmem- of distinct receptor chains. The nature of the ligand-receptor interac-
brane C-type lectin that recognizes glucans present in the cell walls of tion has also been determined for several of the above receptors, and
fungi, signals via spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) and the Card9/Bcl-10/ appears to be different in each individual case (Fig. 20–1). To activate
MALT1 complex to activate nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), 17,18 and enhances TLR4, LPS interacts with MD-2, which has a hydrophobic pocket that
19
TLR2/6 signaling. Similarly, proteinase-activated G-protein–coupled accommodates the lipid A moiety of LPS. 26,27 TLR2/1 heterodimers
20
receptor (PAR-2) signaling enhances TLR4 responses to LPS. Other are “crosslinked” by the engagement of two acyl chains by TLR1 and
examples include the binding of cluster of differentiation (CD) 14 to a single acyl chain by TLR2. TLR3 molecules bind a linear, negatively
28
22
LPS which augments LPS responses, as well as the enhancement of charged dsRNA oligonucleotide, which triggers activation. 29
21
responses to bacterial diacylglycerides by CD36. It is likely that these TLRs 3, 7, 8, and 9 are believed to be intracellular. Little (TLR3)
23
accessory molecules form complexes with the TLRs, which are respon- or no (TLRs 7 and 9) surface expression can be detected, and tagged
sible for transducing the signal across the cell membrane. TLR4 exists versions of the molecules are found to reside within the interior of
in a tight complex with MD-2, a small secreted protein that is required transfected cells. The ectodomains of these TLRs project into endo-
30
for TLR4 to reach the cell surface and required for LPS sensing as well. 24 cytic vesicles and there detect foreign molecules rather than within the
Pam 2 CSK 4 Pam 3 CSK 4 TLR3 LPS TLR4
TLR6 TLR2 TLR1 TLR2 TLR3 TLR4
MD2
dsRNA MD2
TLR5 TLR5 TLR8 R848 TLR8
Figure 20–1. Structures of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and their ligands. TLR2-TLR6-Pam CSK lipopeptide (3A79), TLR2-TLR1-Pam CSK lipopeptide
4
3
2
4
(2Z7X), TLR3-dsRNA (3CIY), TLR4-MD2-LPS (3FXI), TLR5 (3J0A), and TLR8-R848 (3W3L) are shown. Side view (upper panels) and top view (lower panels)
are shown. Protein Databank ID numbers are indicated in parentheses. Figures were generated with UCSF Chimera. dsRNA, double-stranded RNA.
Kaushansky_chapter 20_p0293-0306.indd 295 9/17/15 5:51 PM