Page 539 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 539
514 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 35: Aplastic Anemia: Acquired and Inherited 515
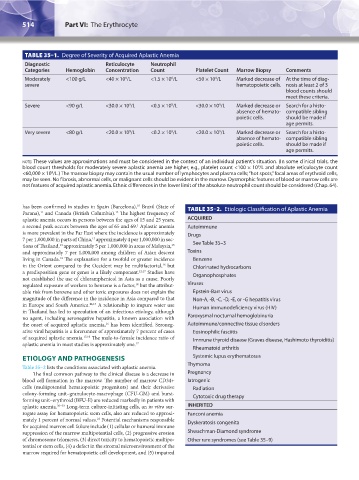
TABLE 35–1. Degree of Severity of Acquired Aplastic Anemia
Diagnostic Reticulocyte Neutrophil
Categories Hemoglobin Concentration Count Platelet Count Marrow Biopsy Comments
Moderately <100 g/L <40 × 10 /L <1.5 × 10 /L <50 × 10 /L Marked decrease of At the time of diag-
9
9
9
severe hematopoietic cells. nosis at least 2 of 3
blood counts should
meet these criteria.
Severe <90 g/L <30.0 × 10 /L <0.5 × 10 /L <30.0 × 10 /L Marked decrease or Search for a histo-
9
9
9
absence of hemato- compatible sibling
poietic cells. should be made if
age permits.
Very severe <80 g/L <20.0 × 10 /L <0.2 × 10 /L <20.0 × 10 /L Marked decrease or Search for a histo-
9
9
9
absence of hemato- compatible sibling
poietic cells. should be made if
age permits.
note: These values are approximations and must be considered in the context of an individual patient’s situation. (In some clinical trials, the
blood count thresholds for moderately severe aplastic anemia are higher, e.g., platelet count <100 × 10 /L and absolute reticulocyte count
9
<60,000 × 10 /L.) The marrow biopsy may contain the usual number of lymphocytes and plasma cells; “hot spots,” focal areas of erythroid cells,
9
may be seen. No fibrosis, abnormal cells, or malignant cells should be evident in the marrow. Dysmorphic features of blood or marrow cells are
not features of acquired aplastic anemia. Ethnic differences in the lower limit of the absolute neutrophil count should be considered (Chap. 64).
has been confirmed in studies in Spain (Barcelona), Brazil (State of TABLE 35–2. Etiologic Classification of Aplastic Anemia
10
Parana), and Canada (British Columbia). The highest frequency of
12
11
aplastic anemia occurs in persons between the ages of 15 and 25 years; ACQUIRED
a second peak occurs between the ages of 65 and 69. Aplastic anemia Autoimmune
1
is more prevalent in the Far East where the incidence is approximately Drugs
7 per 1,000,000 in parts of China, approximately 4 per 1,000,000 in sec-
13
tions of Thailand, approximately 5 per 1,000,000 in areas of Malaysia, See Table 35–3
15
14
and approximately 7 per 1,000,000 among children of Asian descent Toxins
living in Canada. The explanation for a twofold or greater incidence Benzene
12
in the Orient compared to the Occident may be multifactorial, but Chlorinated hydrocarbons
16
a predisposition gene or genes is a likely component. 12,17 Studies have
not established the use of chloramphenicol in Asia as a cause. Poorly Organophosphates
regulated exposure of workers to benzene is a factor, but the attribut- Viruses
18
able risk from benzene and other toxic exposures does not explain the Epstein-Barr virus
magnitude of the difference in the incidence in Asia compared to that Non-A, -B, -C, -D, -E, or -G hepatitis virus
in Europe and South America. 16,17 A relationship to impure water use Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
in Thailand has led to speculation of an infectious etiology, although
no agent, including seronegative hepatitis, a known association with Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
the onset of acquired aplastic anemia, has been identified. Seroneg- Autoimmune/connective tissue disorders
16
ative viral hepatitis is a forerunner of approximately 7 percent of cases Eosinophilic fasciitis
of acquired aplastic anemia. 17,19 The male-to-female incidence ratio of Immune thyroid disease (Graves disease, Hashimoto thyroiditis)
aplastic anemia in most studies is approximately one. 17
Rheumatoid arthritis
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS Systemic lupus erythematosus
Table 35–2 lists the conditions associated with aplastic anemia. Thymoma
The final common pathway to the clinical disease is a decrease in Pregnancy
blood cell formation in the marrow. The number of marrow CD34+ Iatrogenic
cells (multipotential hematopoietic progenitors) and their derivative Radiation
colony-forming unit–granulocyte-macrophage (CFU-GM) and burst- Cytotoxic drug therapy
forming unit–erythroid (BFU-E) are reduced markedly in patients with
aplastic anemia. 20–23 Long-term culture-initiating cells, an in vitro sur- INHERITED
rogate assay for hematopoietic stem cells, also are reduced to approxi- Fanconi anemia
23
mately 1 percent of normal values. Potential mechanisms responsible Dyskeratosis congenita
for acquired marrow cell failure include (1) cellular or humoral immune
suppression of the marrow multipotential cells, (2) progressive erosion Shwachman-Diamond syndrome
of chromosome telomeres, (3) direct toxicity to hematopoietic multipo- Other rare syndromes (see Table 35–9)
tential or stem cells, (4) a defect in the stromal microenvironment of the
marrow required for hematopoietic cell development, and (5) impaired
Kaushansky_chapter 35_p0513-0538.indd 514 9/19/15 12:23 AM