Page 542 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 542
516 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 35: Aplastic Anemia: Acquired and Inherited 517
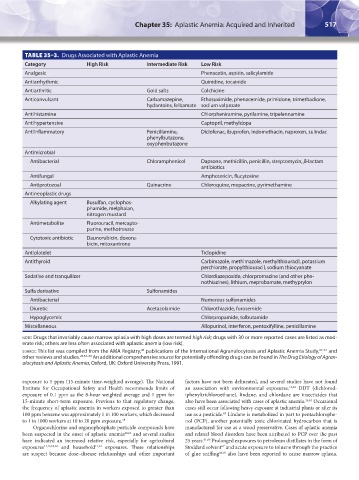
TABLE 35–3. Drugs Associated with Aplastic Anemia
Category High Risk Intermediate Risk Low Risk
Analgesic Phenacetin, aspirin, salicylamide
Antiarrhythmic Quinidine, tocainide
Antiarthritic Gold salts Colchicine
Anticonvulsant Carbamazepine, Ethosuximide, phenacemide, primidone, trimethadione,
hydantoins, felbamate sodium valproate
Antihistamine Chlorpheniramine, pyrilamine, tripelennamine
Antihypertensive Captopril, methyldopa
Antiinflammatory Penicillamine, Diclofenac, ibuprofen, indomethacin, naproxen, sulindac
phenylbutazone,
oxyphenbutazone
Antimicrobial
Antibacterial Chloramphenicol Dapsone, methicillin, penicillin, streptomycin, β-lactam
antibiotics
Antifungal Amphotericin, flucytosine
Antiprotozoal Quinacrine Chloroquine, mepacrine, pyrimethamine
Antineoplastic drugs
Alkylating agent Busulfan, cyclophos-
phamide, melphalan,
nitrogen mustard
Antimetabolite Fluorouracil, mercapto-
purine, methotrexate
Cytotoxic antibiotic Daunorubicin, doxoru-
bicin, mitoxantrone
Antiplatelet Ticlopidine
Antithyroid Carbimazole, methimazole, methylthiouracil, potassium
perchlorate, propylthiouracil, sodium thiocyanate
Sedative and tranquilizer Chlordiazepoxide, chlorpromazine (and other phe-
nothiazines), lithium, meprobamate, methyprylon
Sulfa derivative Sulfonamides
Antibacterial Numerous sulfonamides
Diuretic Acetazolamide Chlorothiazide, furosemide
Hypoglycemic Chlorpropamide, tolbutamide
Miscellaneous Allopurinol, interferon, pentoxifylline, penicillamine
note: Drugs that invariably cause marrow aplasia with high doses are termed high risk; drugs with 30 or more reported cases are listed as mod-
erate risk; others are less often associated with aplastic anemia (low risk).
46
source: This list was compiled from the AMA Registry, publications of the International Agranulocytosis and Aplastic Anemia Study, 47–51 and
other reviews and studies. 26,52–54 An additional comprehensive source for potentially offending drugs can be found in The Drug Etiology of Agran-
ulocytosis and Aplastic Anemia, Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 1991.
exposure to 5 ppm (15-minute time-weighted average). The National factors have not been delineated, and several studies have not found
Institute for Occupational Safety and Health recommends limits of an association with environmental exposures. 12,64 DDT (dichlorod-
exposure of 0.1 ppm as the 8-hour weighted average and 1 ppm for iphenyltrichloroethane), lindane, and chlordane are insecticides that
15-minute short-term exposure. Previous to that regulatory change, also have been associated with cases of aplastic anemia. 16,61 Occasional
the frequency of aplastic anemia in workers exposed to greater than cases still occur following heavy exposure at industrial plants or after its
100 ppm benzene was approximately 1 in 100 workers, which decreased use as a pesticide. Lindane is metabolized in part to pentachlorophe-
65
to 1 in 1000 workers at 10 to 20 ppm exposure. 58 nol (PCP), another potentially toxic chlorinated hydrocarbon that is
Organochlorine and organophosphate pesticide compounds have manufactured for use as a wood preservative. Cases of aplastic anemia
been suspected in the onset of aplastic anemia 60,61 and several studies and related blood disorders have been attributed to PCP over the past
have indicated an increased relative risk, especially for agricultural 25 years. 61,66 Prolonged exposures to petroleum distillates in the form of
exposures 11,16,62,63 and household 11,63 exposures. These relationships Stoddard solvent and acute exposure to toluene through the practice
67
are suspect because dose–disease relationships and other important of glue sniffing 68,69 also have been reported to cause marrow aplasia.
Kaushansky_chapter 35_p0513-0538.indd 517 9/19/15 12:23 AM