Page 554 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 554
528 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 35: Aplastic Anemia: Acquired and Inherited 529
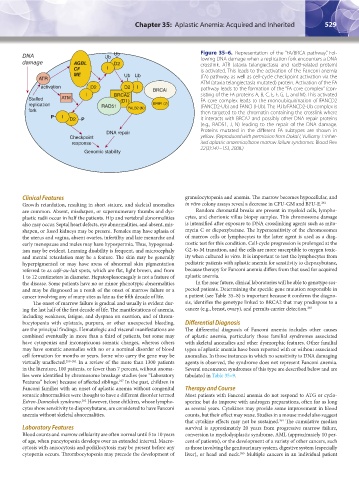
DNA Ub Ub Figure 35–6. Representation of the “FA/BRCA pathway.” Fol-
lowing DNA damage when a replication fork encounters a DNA
damage AGBL D2 crosslink, ATR (ataxia telangiectasia and rad3-related protein)
CF I is activated. This leads to the activation of the Fanconi anemia
ME Ub Ub (FA) pathway, as well as cell-cycle checkpoint activation via the
ATR
ATM (ataxia telangiectasia mutated) protein. Activation of the FA
activation D2 D2 I BRCAI pathway leads to the formation of the “FA core complex” (con-
I BRCA2 sisting of the FA proteins A, B, C, E, F, G, L, and M). This activated
Stalled ATM (D1) FA core complex leads to the monoubiquitination of FANCD2
replication RAD51 BRIPI (J) (FANCD2-Ub) and FANCI (I-Ub). The I-Ub/FANCD2-Ub complex is
fork PALB2 (N) then targeted to the chromatin containing the crosslink where
P I it interacts with BRCA2 and possibly other DNA repair proteins
D2 P
(e.g., RAD51, J, N) leading to the repair of the DNA damage.
DNA repair Proteins mutated in the different FA subtypes are shown in
Checkpoint yellow. (Reproduced with permission from Dokal I, Vulliamy T: Inher-
response ited aplastic anaemias/bone marrow failure syndromes. Blood Rev
22(3):141–153, 2008.)
Genomic stability
Clinical Features granulocytopenia and anemia. The marrow becomes hypocellular, and
Growth retardation, resulting in short stature, and skeletal anomalies in vitro colony assays reveal a decrease in CFU-GM and BFU-E. 261
are common. Absent, misshapen, or supernumerary thumbs and dys- Random chromatid breaks are present in myeloid cells, lympho-
plastic radii occur in half the patients. Hip and vertebral abnormalities cytes, and chorionic villus biopsy samples. This chromosome damage
also may occur. Septal heart defects, eye abnormalities, and absent, mis- is intensified after exposure to DNA crosslinking agents such as mito-
shapen, or fused kidneys may be present. Females may have aplasia of mycin C or diepoxybutane. The hypersensitivity of the chromosomes
the uterus and vagina, absent ovaries, infertility and late menarche and of marrow cells or lymphocytes to the latter agent is used as a diag-
early menopause and males may have hypospermia. Thus, hypogonad- nostic test for this condition. Cell-cycle progression is prolonged at the
ism may be evident. Learning disability is frequent, and microcephaly G2-to-M transition, and the cells are more susceptible to oxygen toxic-
and mental retardation may be a feature. The skin may be generally ity when cultured in vitro. It is important to test the lymphocytes from
hyperpigmented or may have areas of abnormal skin pigmentation pediatric patients with aplastic anemia for sensitivity to diepoxybutane,
referred to as café-au-lait spots, which are flat, light brown, and from because therapy for Fanconi anemia differs from that used for acquired
1 to 12 centimeters in diameter. Hepatosplenomegaly is not a feature of aplastic anemia.
the disease. Some patients have no or minor phenotypic abnormalities In the near future, clinical laboratories will be able to genotype sus-
and may be diagnosed as a result of the onset of marrow failure or a pected patients. Determining the specific gene mutation responsible in
cancer involving any of many sites as late as the fifth decade of life. a patient (see Table 35–8) is important because it confirms the diagno-
The onset of marrow failure is gradual and usually is evident dur- sis, identifies the genotype linked to BRCA2 that may predispose to a
ing the last half of the first decade of life. The manifestations of anemia, cancer (e.g., breast, ovary), and permits carrier detection. 263
including weakness, fatigue, and dyspnea on exertion, and of throm-
bocytopenia with epistaxis, purpura, or other unexpected bleeding, Differential Diagnosis
are the principal findings. Hematologic and visceral manifestations are The differential diagnosis of Fanconi anemia includes other causes
combined eventually in more than a third of patients, but some may of aplastic anemia, particularly those familial syndromes associated
have cytopenias and inconspicuous somatic changes, whereas others with skeletal anomalies and other dysmorphic features. Other familial
may have somatic anomalies with no or a nominal disorder of blood types of aplastic anemia have been reported with or without associated
cell formation for months or years. Some who carry the gene may be anomalies. In those instances in which no sensitivity to DNA damaging
virtually unaffected. 259–261 In a review of the more than 1300 patients agents is observed, the syndrome does not represent Fanconi anemia.
in the literature, 100 patients, or fewer than 7 percent, without anoma- Several uncommon syndromes of this type are described below and are
lies were identified by chromosome breakage studies (see “Laboratory tabulated in Table 35–9.
Features” below) because of affected siblings. In the past, children in
227
Fanconi families with an onset of aplastic anemia without congenital Therapy and Course
somatic abnormalities were thought to have a different disorder termed Most patients with Fanconi anemia do not respond to ATG or cyclo-
Estren-Dameshek syndrome. However, these children, whose lympho- sporine but do improve with androgen preparations, often for as long
262
cytes show sensitivity to diepoxybutane, are considered to have Fanconi as several years. Cytokines may provide some improvement in blood
anemia without skeletal abnormalities. counts, but their effect may wane. Studies in a mouse model also suggest
that cytokine effects may not be sustained. The cumulative median
264
Laboratory Features survival is approximately 20 years from progressive marrow failure,
Blood counts and marrow cellularity are often normal until 5 to 10 years conversion to myelodysplastic syndrome, AML (approximately 10 per-
of age, when pancytopenia develops over an extended interval. Macro- cent of patients), or the development of a variety of other cancers, such
cytosis with anisocytosis and poikilocytosis may be present before any as those involving the genitourinary system, digestive system (especially
cytopenia occurs. Thrombocytopenia may precede the development of liver), or head and neck. Multiple cancers in an individual patient
265
Kaushansky_chapter 35_p0513-0538.indd 529 9/19/15 12:24 AM