Page 553 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 553
528 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 35: Aplastic Anemia: Acquired and Inherited 529
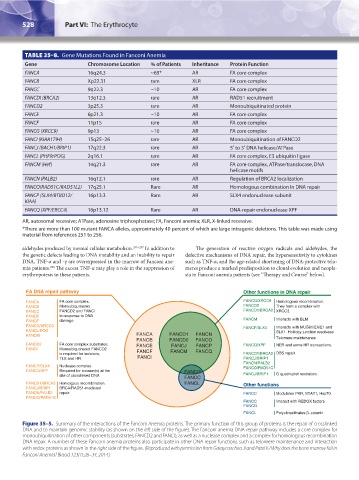
TABLE 35–8. Gene Mutations Found in Fanconi Anemia
Gene Chromosome Location % of Patients Inheritance Protein Function
FANCA 16q24.3 ~65* AR FA core complex
FANCB Xp22.31 rare XLR FA core complex
FANCC 9q22.3 ~10 AR FA core complex
FANCDI (BRCA2) 13q12.3 rare AR RAD51 recruitment
FANCD2 3p25.3 rare AR Monoubiquitinated protein
FANCE 6p21.3 ~10 AR FA core complex
FANCF 11p15 rare AR FA core complex
FANCG (XRCC9) 9p13 ~10 AR FA core complex
FANCI (KIAA1794) 15q25–26 rare AR Monoubiquitination of FANCD2
FANCJ (BACH1/BRIP1) 17q22.3 rare AR 5′ to 3′ DNA helicase/ATPase
FANCL (PHF9/POG) 2q16.1 rare AR FA core complex, E3 ubiquitin ligase
FANCM (Hef) 14q21.3 rare AR FA core complex, ATPase/translocase, DNA
helicase motifs
FANCN (PALB2) 16q12.1 rare AR Regulation of BRCA2 localization
FANCO(RAD51C/RAD51L2) 17q25.1 Rare AR Homologous combination In DNA repair
FANCP (SLX4/BTBD12/ 16p13.3 Rare AR SLX4 endonuclease subunit
KIAA)
FANCQ (XPF/ERCC4) 16p13.12 Rare AR DNA-repair endonuclease XPF
AR, autosomal recessive; ATPase, adenosine triphosphatase; FA, Fanconi anemia; XLR, X-linked recessive.
*There are more than 100 mutant FANCA alleles, approximately 40 percent of which are large intragenic deletions. This table was made using
material from references 251 to 256.
aldehydes produced by normal cellular metabolism. 255–257 In addition to The generation of reactive oxygen radicals and aldehydes, the
the genetic defects leading to DNA instability and an inability to repair defective mechanisms of DNA repair, the hypersensitivity to cytokines
DNA, TNF-α and -γ are overexpressed in the marrow of Fanconi ane- such as TNF-α, and the age-related shortening of DNA-protective telo-
mia patients. The excess TNF-α may play a role in the suppression of meres produce a marked predisposition to clonal evolution and neopla-
258
erythropoiesis in these patients. sia in Fanconi anemia patients (see “Therapy and Course” below).
FA DNA repair pathway Other functions in DNA repair
FANCA FA core complex. FANCG/XRCC9 Homologous recombination.
FANCB Monoubiqutinates FANCD2 They form a complex with
FANCC FANCD2 and FANCI FANCD1/BRCA2 XRCC3.
FANCE in response to DNA
FANCF damage FANCM Interacts with BLM
FANCG/XRCC9 FANCP/SLX4 Interacts with MUS81/EME1 and
FANCL/POG SLX1. Holliday junction resolvase
FANCM FANCA FANCD1 FANCN Telomere maintenance
FANCB FANCD2 FANCO
FANCD2 FA core complex substrates. FANCE FANCJ FANCP FANCQ/XPF NER and some HR transactions.
FANCI Monoubiqutinated FANCD2 FANCF FANCM FANCQ
is required for incisions, FANCD1/BRCA2 DBS repair.
TLS and HR FANCI FANCJ/BRIP1
FANCN/PALB2
FANCP/SLX4 Nuclease complex. FANCO/RAD51C
FANCQ/XPF Required for incision(s) at the FANCG
site of crosslinked DNA FANCC FANCJ/BRIP1 G quadruplet resolution.
FANCD1/BRCA2 Homolgous recombination. FANCL Other functions
FANCJ/BRIP1 BRCA/RAD51-mediated
FANCN/PALB2 repair. FANCC Modulates PKR, STAT1, Hsp70
FANCO/RAD51C
FANCC Interact with REDOX factors
FANCG
FANCL Polyubiquitinates β–catenin
Figure 35–5. Summary of the interactions of the Fanconi Anemia proteins. The primary function of this group of proteins is the repair of crosslinked
DNA and to maintain genomic stability (as shown on the left side of the figure). The Fanconi anemia DNA repair pathway includes a core complex for
monoubiquitination of other components (substrates, FANCD2 and FANCI), as well as a nuclease complex and a complex for homologous recombination
DNA repair. A number of these Fanconi anemia proteins also participate in other DNA repair functions such as telomere maintenance and interaction
with redox proteins as shown in the right side of the figure. (Reproduced with permission from Garaycoechea JI and Patel KJ Why does the bone marrow fail in
Fanconi Anemia? Blood 123(1):26–34, 2014.)
Kaushansky_chapter 35_p0513-0538.indd 528 9/19/15 12:24 AM