Page 610 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 610
584 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 41: Folate, Cobalamin, and Megaloblastic Anemias 585
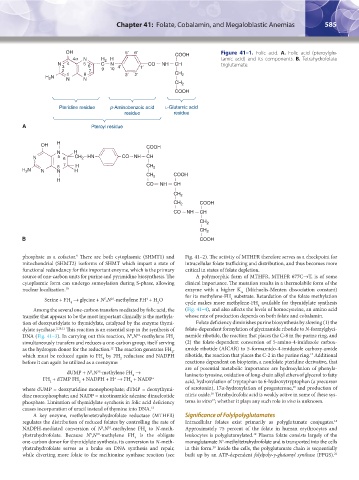
Figure 41–1. Folic acid. A. Folic acid (pteroylglu-
tamic acid) and its components. B. Tetrahydrofolate
triglutamate.
phosphate as a cofactor. There are both cytoplasmic (SHMT1) and Fig. 41–2). The activity of MTHFR therefore serves as a checkpoint for
9
mitochondrial (SHMT2) isoforms of SHMT which impart a state of intracellular folate trafficking and distribution, and thus becomes more
functional redundancy for this important enzyme, which is the primary critical in states of folate depletion.
source of one-carbon units for purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis. The A polymorphic form of MTHFR, MTHFR 677C→T, is of some
cytoplasmic form can undergo sumoylation during S-phase, allowing clinical importance. The mutation results in a thermolabile form of the
nuclear localization. 10 enzyme with a higher K (Michaelis-Menten dissociation constant)
m
for its methylene-FH substrate. Retardation of the folate methylation
Serine + FH → glycine + N ,N -methylene FH + H O 4
10
5
4
4 2 cycle makes more methylene-FH available for thymidylate synthesis
4
Among the several one-carbon transfers mediated by folic acid, the (Fig. 41–4), and also affects the levels of homocysteine, an amino acid
transfer that appears to be the most important clinically is the methyla- whose rate of production depends on both folate and cobalamin.
tion of deoxyuridylate to thymidylate, catalyzed by the enzyme thymi- Folate deficiency diminishes purine biosynthesis by slowing (1) the
dylate synthase. 2,10,11 This reaction is an essential step in the synthesis of folate-dependent formylation of glycinamide ribotide to N-formylglyci-
DNA (Fig. 41–3). In carrying out this reaction, N ,N -methylene FH namide ribotide, the reaction that places the C-8 in the purine ring, and
5
10
4
simultaneously transfers and reduces a one-carbon group, itself serving (2) the folate-dependent conversion of 5-amino-4-imidazole carbox-
as the hydrogen donor for the reduction. The reaction generates FH , amide ribotide (AICAR) to 5-formamido-4-imidazole carboxy-amide
12
2
14
which must be reduced again to FH by FH reductase and NADPH ribotide, the reaction that places the C-2 in the purine ring. Additional
2
4
before it can again be utilized as a coenzyme: reactions dependent on biopterin, a nonfolate pteridine derivative, that
are of potential metabolic importance are hydroxylation of phenyla-
dUMP + N ,N -methylene FH → lanine to tyrosine, oxidation of long-chain alkyl ethers of glycerol to fatty
5
10
4
FH + dTMP FH + NADPH + H → FH + NADP +
+
2 2 4 acid, hydroxylation of tryptophan to 6-hydroxytryptophan (a precursor
15
where dUMP = deoxyuridine monophosphate; dTMP = deoxythymi- of serotonin), 17α-hydroxylation of progesterone, and production of
16
dine monophosphate; and NADP = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide nitric oxide. Tetrahydrofolic acid is weakly active in some of these sys-
17
phosphate. Limitation of thymidylate synthesis in folic acid deficiency tems in vitro ; whether it plays any such role in vivo is unknown.
causes incorporation of uracil instead of thymine into DNA. 13
A key enzyme, methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) Significance of Folylpolyglutamates
regulates the distribution of reduced folates by controlling the rate of Intracellular folates exist primarily as polyglutamate conjugates.
18
NADPH-mediated conversion of N ,N -methylene FH to N-meth- Approximately 75 percent of the folate in human erythrocytes and
5
10
4
yltetrahydrofolate. Because N ,N -methylene FH is the obligate leukocytes is polyglutamylated. Plasma folate consists largely of the
19
10
5
4
one-carbon donor for thymidylate synthesis, its conversion to N-meth- monoglutamate N -methyltetrahydrofolate and is transported into the cells
5
yltetrahydrofolate serves as a brake on DNA synthesis and repair, in this form. Inside the cells, the polyglutamate chain is sequentially
20
while diverting more folate to the methionine synthase reaction (see built up by an ATP-dependent folylpoly-γ-glutamyl synthase (FPGS).
21
Kaushansky_chapter 41_p0583-0616.indd 585 9/17/15 6:23 PM