Page 611 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 611
586 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 41: Folate, Cobalamin, and Megaloblastic Anemias 587
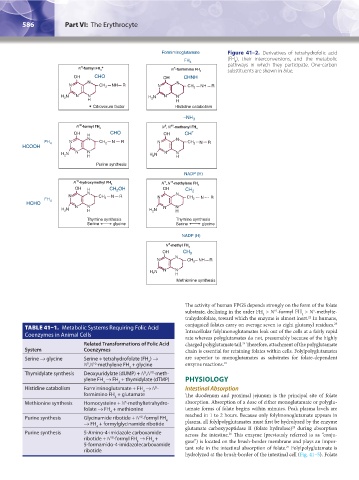
Formiminoglutamate Figure 41–2. Derivatives of tetrahydrofolic acid
FH 4 (FH ), their interconversions, and the metabolic
4
5
N -formyl FH * N -formimino FH 4 pathways in which they participate. One-carbon
5
substituents are shown in blue.
4
OH CHO OH CHNH
N N
N CH 2 NH R N CH 2 NH R
H N N N H N N N
2
H 2 H
* Citrovorum factor Histidine catabolism
–NH 3
10
5
10
N -formyl FH 4 N , N -methenyl FH 4
OH H CHO OH CH +
FH 4 N N CH 2 N R N N CH 2 N R
HCOOH
H N N N H N N N
H
2
H
2
Purine synthesis
NADP (H)
10
N -hydroxymethyl FH 4 N , N -methylene FH 4
5
10
OH H CH 2 OH OH CH 2
N N CH 2 N R N N CH N R
FH 4 2
HCHO N
H N N H H 2 N N N
H
2
Thymine synthesis Thymine synthesis
Serine glycine Serine glycine
NADP (H)
5
N -methyl FH 4
OH CH 3
N
N CH 2 NH R
N N N
H 2
H
Methionine synthesis
The activity of human FPGS depends strongly on the form of the folate
substrate, declining in the order FH > N -formyl FH > N -methylte-
10
5
4
4
trahydrofolate, toward which the enzyme is almost inert. In humans,
22
conjugated folates carry on average seven to eight glutamyl residues.
23
TABLE 41–1. Metabolic Systems Requiring Folic Acid Intracellular folylmonoglutamates leak out of the cells at a fairly rapid
Coenzymes in Animal Cells
rate whereas polyglutamates do not, presumably because of the highly
Related Transformations of Folic Acid charged polyglutamate tail. Therefore, attachment of the polyglutamate
24
System Coenzymes chain is essential for retaining folates within cells. Folylpolyglutamates
Serine → glycine Serine + tetrahydrofolate (FH ) → are superior to monoglutamates as substrates for folate-dependent
4
N ,N -methylene FH + glycine enzyme reactions. 19
5
10
4
Thymidylate synthesis Deoxyuridylate (dUMP) + N ,N -meth-
10
5
ylene FH → FH + thymidylate (dTMP) PHYSIOLOGY
4 2
Histidine catabolism Formiminoglutamate + FH → N - Intestinal Absorption
5
4
formimino FH + glutamate The duodenum and proximal jejunum is the principal site of folate
4
Methionine synthesis Homocysteine + N -methyltetrahydro- absorption. Absorption of a dose of either monoglutamate or polyglu-
5
folate → FH + methionine tamate forms of folate begins within minutes. Peak plasma levels are
4
10
Purine synthesis Glycinamide ribotide + N -formyl FH 4 reached in 1 to 2 hours. Because only folylmonoglutamate appears in
→ FH + formylglycinamide ribotide plasma, all folylpolyglutamates must first be hydrolyzed by the enzyme
4 glutamate carboxypeptidase II (folate hydrolase) during absorption
25
Purine synthesis 5-Amino-4-imidazole carboxamide across the intestine. This enzyme (previously referred to as “conju-
26
ribotide + N -formyl FH → FH + gase”) is located on the brush-border membrane and plays an impor-
10
4
4
5-formamido-4-imidazolecarboxamide 27
ribotide tant role in the intestinal absorption of folate. Folylpolyglutamate is
hydrolyzed at the brush-border of the intestinal cell (Fig. 41–5). Folate
Kaushansky_chapter 41_p0583-0616.indd 586 9/17/15 6:23 PM