Page 880 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 880
854 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 55: Alloimmune Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn 855
80
A 1.5 MOM
70 B 1.29 MOM
MCA peak velocity 50 Median
60
40
30
20
20 25 30 35
Gestational age (wk)
A B
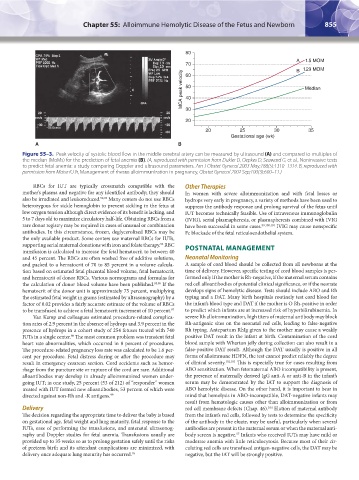
Figure 55–3. Peak velocity of systolic blood flow in the middle cerebral artery can be measured by ultrasound (A) and compared to multiples of
the median (MoMs) for the prediction of fetal anemia (B). (A, reproduced with permission from Dukler D, Oepkes D, Seaward G, et al., Noninvasive tests
to predict fetal anemia: a study comparing Doppler and ultrasound parameters. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003 May;188(5):1310–1314. B, reproduced with
permission from Moise KJ Jr, Management of rhesus alloimmunization in pregnancy, Obstet Gynecol 2002 Sep;100(3):600–11.)
RBCs for IUT are typically crossmatch compatible with the Other Therapies
mother’s plasma and negative for any identified antibody; they should In women with severe alloimmunization and with fetal losses or
also be irradiated and leukoreduced. 92,93 Many centers do not use RBCs hydrops very early in pregnancy, a variety of methods have been used to
heterozygous for sickle hemoglobin to prevent sickling in the fetus at suppress the antibody response and prolong survival of the fetus until
low oxygen tension although direct evidence of its benefit is lacking, and IUT becomes technically feasible. Use of intravenous immunoglobulin
5 to 7 days old to maximize circulatory half-life. Obtaining RBCs from a (IVIG), serial plasmapheresis, or plasmapheresis combined with IVIG
rare donor registry may be required in cases of unusual or combination have been successful in some cases. 89,100,101 IVIG may cause nonspecific
antibodies. In this circumstance, frozen, deglycerolized RBCs may be Fc blockade of the fetal reticuloendothelial system.
the only available product. Some centers use maternal RBCs for IUTs,
supporting serial maternal donations with iron and folate therapy. RBC
94
transfusion is calculated to increase the fetal hematocrit to between 40 POSTNATAL MANAGEMENT
and 45 percent. The RBCs are often washed free of additive solutions, Neonatal Monitoring
and packed to a hematocrit of 70 to 85 percent in a volume calcula- A sample of cord blood should be collected from all newborns at the
tion based on estimated fetal placental blood volume, fetal hematocrit, time of delivery. However, specific testing of cord blood samples is per-
and hematocrit of donor RBCs. Various normograms and formulas for formed only if the mother is Rh-negative, if the maternal serum contains
the calculation of donor blood volume have been published. 95,96 If the red cell alloantibodies of potential clinical significance, or if the neonate
hematocrit of the donor unit is approximately 75 percent, multiplying develops signs of hemolytic disease. Tests should include ABO and Rh
the estimated fetal weight in grams (estimated by ultrasonography) by a typing and a DAT. Many birth hospitals routinely test cord blood for
factor of 0.02 provides a fairly accurate estimate of the volume of RBCs the infant’s blood type and DAT if the mother is O Rh-positive in order
to be transfused to achieve a fetal hematocrit increment of 10 percent. 97 to predict which infants are at increased risk of hyperbilirubinemia. In
Van Kamp and colleagues estimated procedure-related complica- severe Rh alloimmunization, high titers of maternal antibody may block
tion rates of 2.9 percent in the absence of hydrops and 3.9 percent in the Rh-antigenic sites on the neonatal red cells, leading to false-negative
presence of hydrops in a cohort study of 254 fetuses treated with 740 Rh typing. Antepartum RhIg given to the mother may cause a weakly
IUTs in a single center. The most common problem was transient fetal positive DAT result in the infant at birth. Contamination of the cord
98
heart rate abnormalities, which occurred in 8 percent of procedures. blood sample with Wharton jelly during collection can also result in a
The procedure-related pregnancy loss rate was calculated to be 1.6 per- false-positive DAT result. Although the DAT usually is positive in all
cent per procedure. Fetal distress during or after the procedure may forms of alloimmune HDFN, the test cannot predict reliably the degree
result in emergency cesarean section. Cord accidents such as hemor- of clinical severity. 102,103 This is especially true for cases resulting from
rhage from the puncture site or rupture of the cord are rare. Additional ABO sensitization. When fetomaternal ABO incompatibility is present,
alloantibodies may develop in already alloimmunized women under- the presence of maternally derived IgG anti-A or anti-B in the infant’s
going IUT; in one study, 25 percent (53 of 212) of “responder” women serum may be demonstrated by the IAT to support the diagnosis of
treated with IUT formed new alloantibodies, 53 percent of which were ABO hemolytic disease. On the other hand, it is important to bear in
directed against non-Rh and -K antigens. 99 mind that hemolysis in ABO-incompatible, DAT-negative infants may
result from hematologic causes other than alloimmunization or from
Delivery red cell membrane defects (Chap. 46). Elution of maternal antibody
104
The decision regarding the appropriate time to deliver the baby is based from the infant’s red cells, followed by tests to determine the specificity
on gestational age, fetal weight and lung maturity, fetal response to the of the antibody in the eluate, may be useful, particularly when several
IUTs, ease of performing the transfusions, and antenatal ultrasonog- antibodies are present in the maternal serum or when the maternal anti-
raphy and Doppler studies for fetal anemia. Transfusions usually are body screen is negative. Infants who received IUTs may have mild or
57
provided up to 35 weeks so as to prolong gestation safely until the risks moderate anemia with little reticulocytosis. Because most of their cir-
of preterm birth and its attendant complications are minimized, with culating red cells are transfused antigen-negative cells, the DAT may be
delivery once adequate lung maturity has occurred. 76 negative, but the IAT will be strongly positive.
Kaushansky_chapter 55_p0847-0862.indd 855 9/18/15 11:52 PM